J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2013 Nov;54(11):1783-1787. 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.11.1783.
Confocal Microscopic Findings in Posterior Polymorphous Corneal Dystrophy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University & Medical Research Institute School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. jongsool@pusan.ac.kr
- KMID: 2217928
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2013.54.11.1783
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To analyze the features of corneal tissue in patients with posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy (PPMD) using in vivo confocal microscopy (IVCM).
CASE SUMMARY
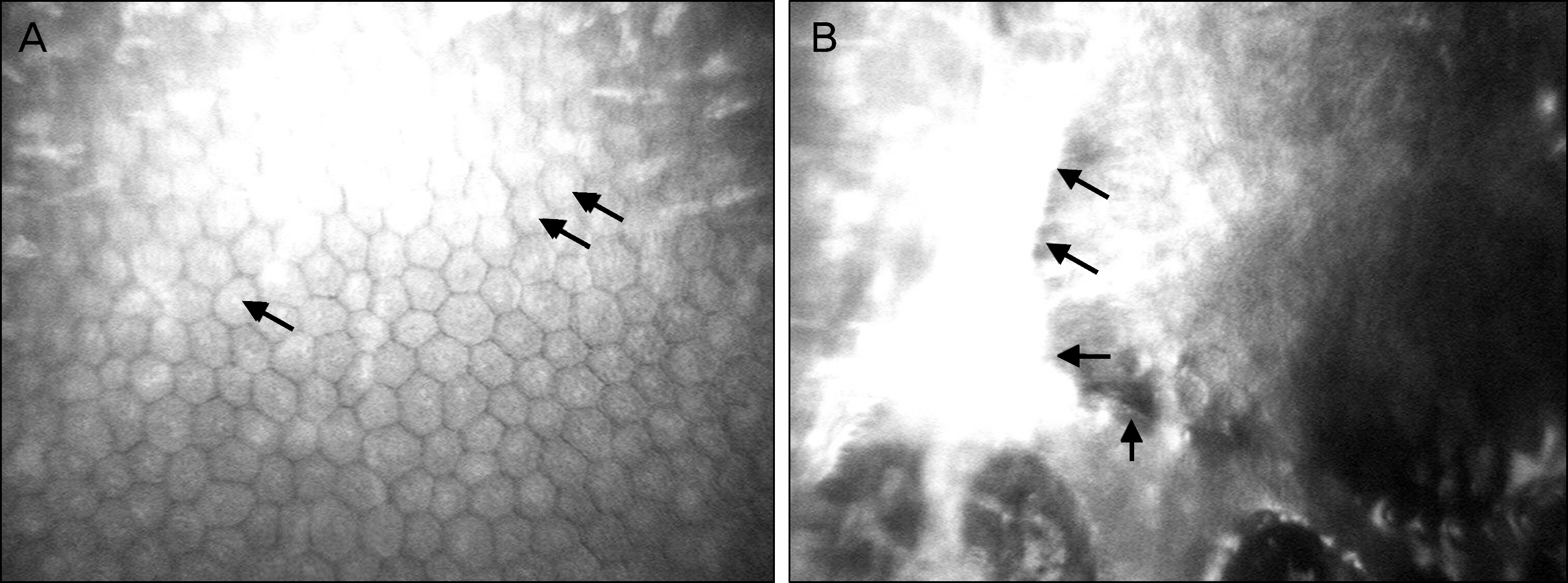
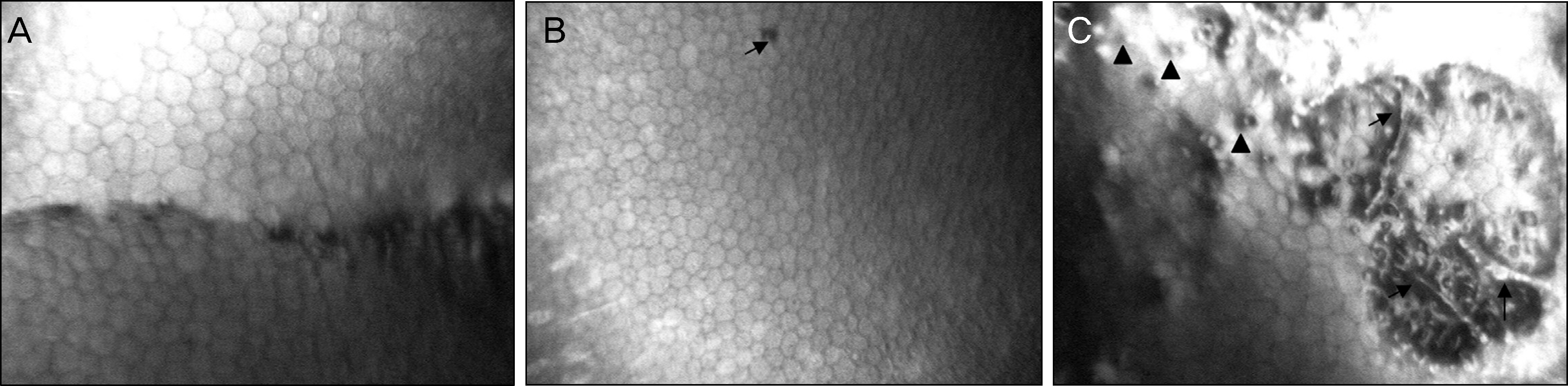
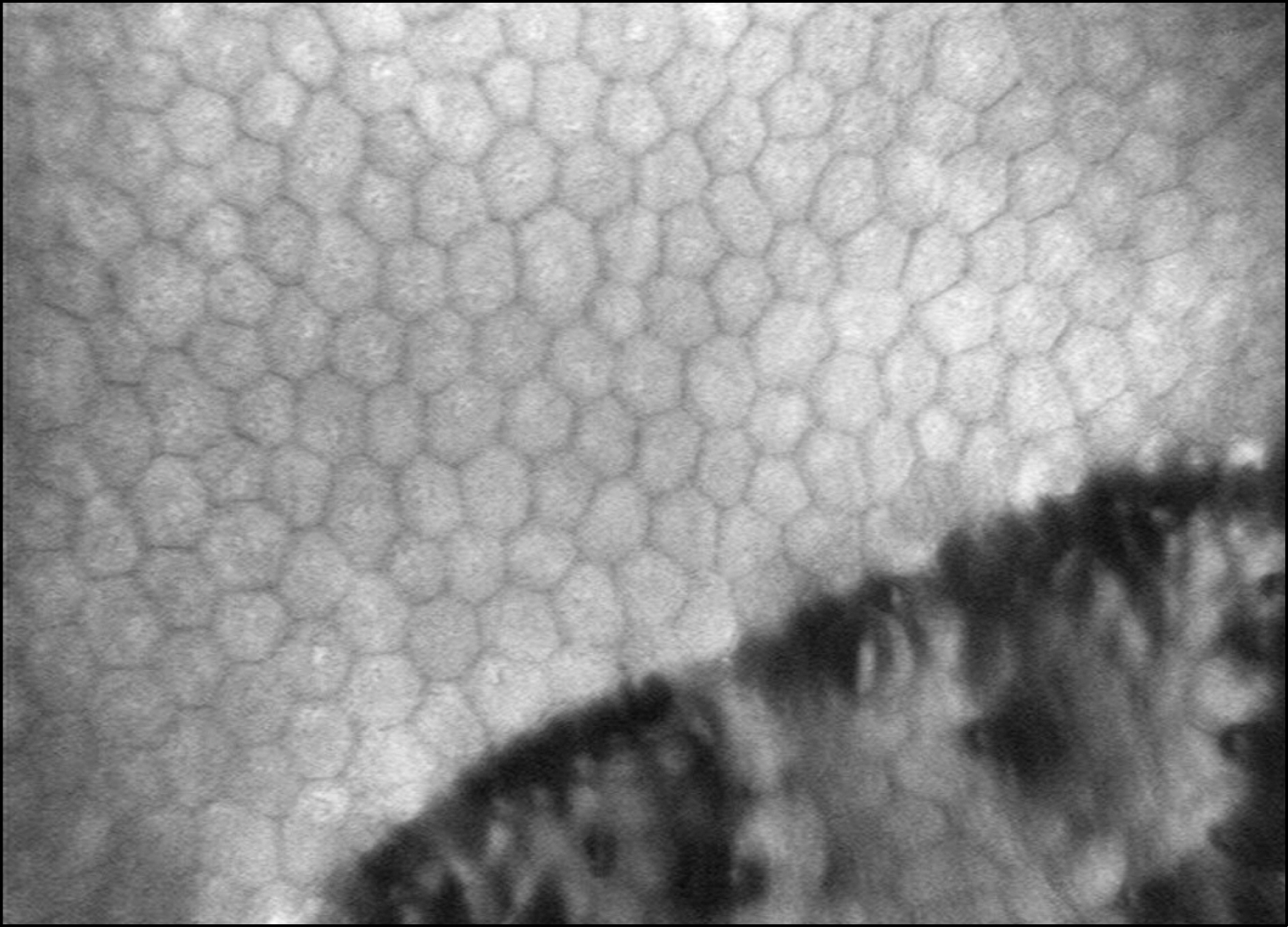
Three patients with clinically diagnosed PPMD were examined using IVCM. Cross-sectioned corneal images of the corneal epithelium, Bowman's layer, stromal layer, Descemet's membrane, and endothelium were evaluated. IVCM demonstrated a depressed crater-like lesion, hyper-dense streak-like lesion, and surface irregularity of the corneal endothelium. Endothelial hypo-reflective vesicular and band-like lesions were also found. Pleomorphism and polymegathism were present with guttae and hyper-reflective endothelial nuclei.
CONCLUSIONS
IVCM is a non-invasive and effective tool to diagnose PPMD.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Vanathi M Tand, on R, Sharma N, et al. In vivo slit scanning con- focal microscopy of normal corneas in Indian eyes. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2003; 51:225–30.2. Cibis GW, Krachmer JA, Phelps CD, Weingeist TA. The clinical spectrum of posterior polymorphous dystrophy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1977; 95:1529–37.
Article3. Krachmer JH. Posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy: a dis- ease characterized by epithelial-like endothelial cells which influ- ence management and prognosis. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1985; 83:413–75.4. Park IC, Chung SK, Myong YW, Rhee SW. A case of posterior pol- ymorphous dystrophy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1991; 32:1020–3.5. Héon E, Greenberg A, Kopp KK, et al. VSX1 : a gene for posterior polymorphous dystrophy and keratoconus. Hum Mol Genet. 2002; 11:1029–36.6. Biswas S, Munier FL, Yardley J, et al. Missense mutations in COL8A2, the gene encoding the alpha2 chain of type VIII colla- gen, cause two forms of corneal endothelial dystrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 2001; 10:2415–23.7. Waring GO 3rd, Rodrigues MM, Laibson PR. Corneal dystrophies. II. Endothelial dystrophies. Surv Ophthalmol. 1978; 23:147–68.
Article8. Laganowski HC, Sherrard ES, Muir MG. The posterior corneal surface in posterior polymorphous dystrophy: a specular micro- scopical study. Cornea. 1991; 10:224–32.9. Sekundo W, Lee WR, Kirkness CM, et al. An ultrastructural inves- tigation of an early manifestation of the posterior polymorphous dystrophy of the cornea. Ophthalmology. 1994; 101:1422–31.10. Feil SH, Barraquer J, Howell DN, Green WR. Extrusion of abnor- mal endothelium into the posterior corneal stroma in a patient with posterior polymorphous dystrophy. Cornea. 1997; 16:439–46.11. Henriquez AS, Kenyon KR, Dohlman CH, et al. Morphologic characteristics of posterior polymorphous dystrophy. A study of nine corneas and review of the literature. Surv Ophthalmol. 1984; 29:139–47.
Article12. Patel DV, Grupcheva CN, McGhee CN. In vivo confocal micro- scopy of posterior polymorphous dystrophy. Cornea. 2005; 24:550–4.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Posterior Polymorphous Dystrophy
- Iridocorneal Endothelial Syndrome with Features of Posterior Polymorphous Corneal Dystrophy
- Confocal Microscopic Findings of Corneal Tissue in Fuchs' Corneal Endothelial Dystrophy
- Confocal Microscopic Findings of Avellino Corneal Dystrophy According to Disease Severity
- Cases of Macular Corneal Dystrophy with a Family History