J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2013 Jan;54(1):65-71. 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.1.65.
Refractive Eerror According to the Anterior Chamber Depth and Corneal Refractive Power in Short Eyes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mskim@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2216451
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2013.54.1.65
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the accuracy of the chosen formula in short eyes and the effect of the anterior chamber depth (ACD) and corneal refractive power on the accuracy.
METHODS
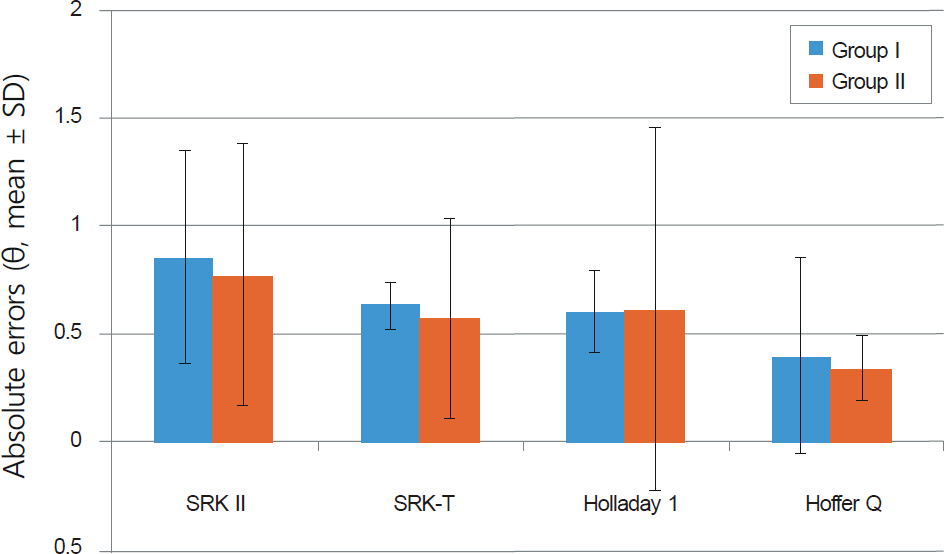
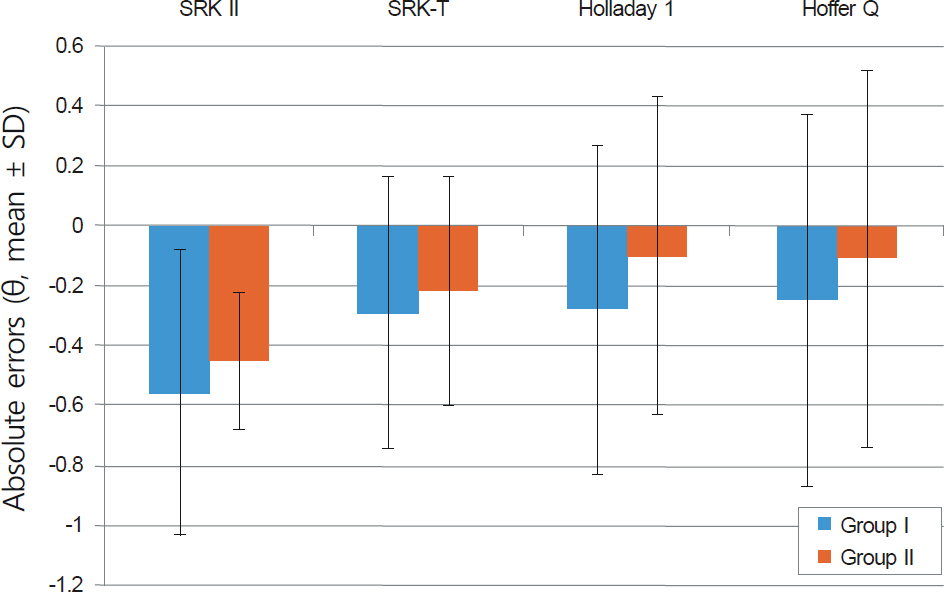
A total of 251 eyes out of 185 patients (axial length below 22.0 mm) who underwent cataract surgery in our hospital were retrospectively studied. Introcular lens (IOL) power was calculated with the Hoffer Q, SRK II, SRK-T and Holladay 1 formulas and refractive outcome was measured. Patients were divided into 2 groups based on ACD. The accuracy of the 4 formulas was compared and the errors according to the ACD were also evaluated.
RESULTS
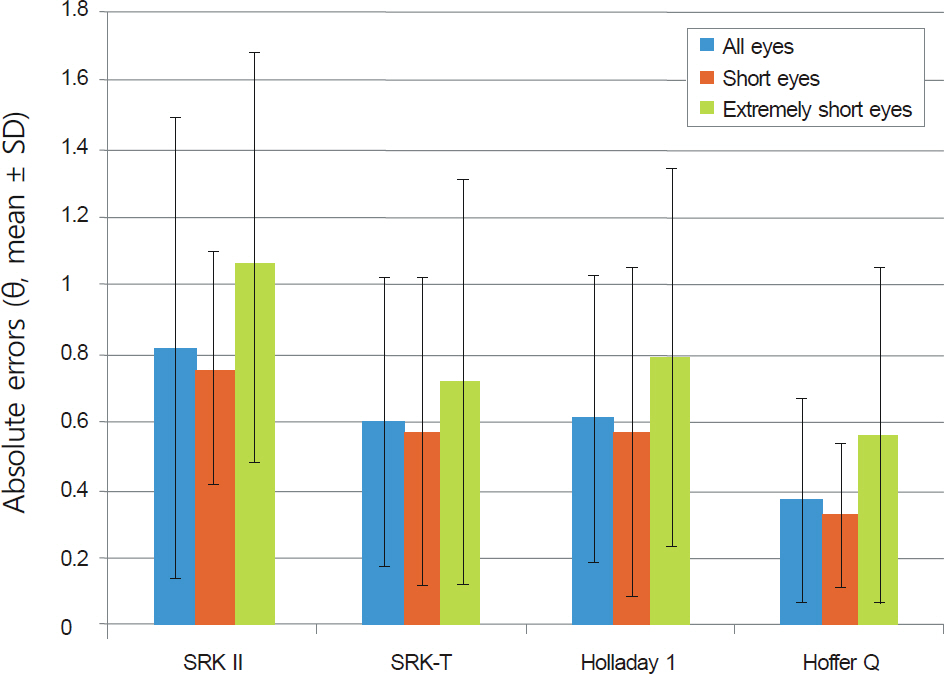
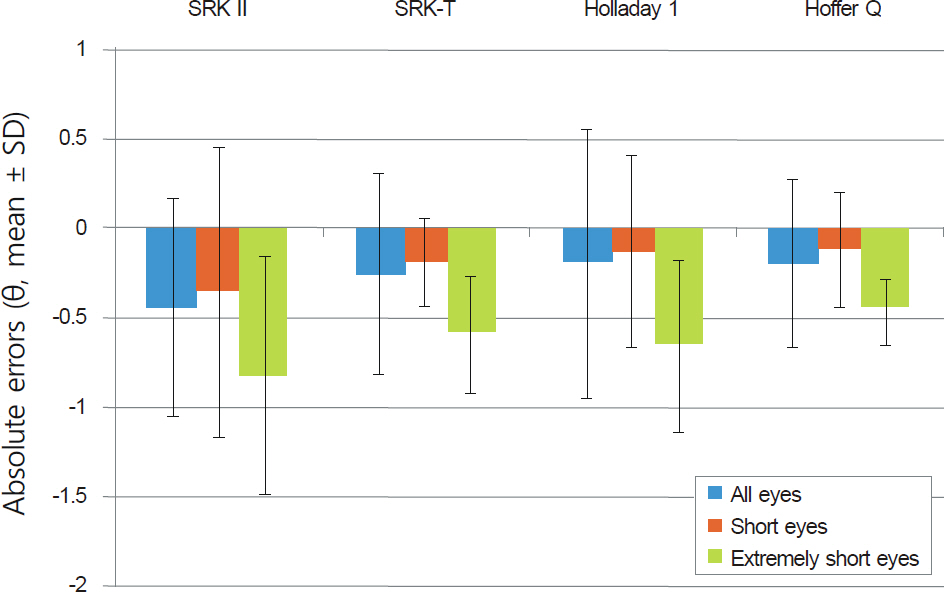
In eyes with short axial lengths, all formulas showed a tendency for hyperopic shifts. The Hoffer Q formula showed significantly high predictive accuracy. This tendency for hyperopic shifts was similar in the eyes with extremely short axial length, but a large refractive error deviation was observed. The 2 groups based on ACD showed no significant difference in the refractive error, but the group with deep ACD had a tendency for hyperopic shifts. The difference of the calculated IOL power between the 4 formulas was more pronounced in eyes with lower corneal refractive power.
CONCLUSIONS
In eyes with short axial lengths, preoperative ACD and corneal refractive power had an influence on the accuracies of predicted IOL power. Therefore, these factors should be considered in IOL power determination.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Comparison of Three Formulas for Intraocular Lens Power Formula Accuracy
Ki Woong Lee, Jinsoo Kim, Dong Hyun Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2020;61(1):27-33. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2020.61.1.27.Analysis of Factors that Influence on Accuracy of Intraocular Lens Power Calculation
Bo Hyuck Kim, Won Ryang Wee, Mee Kum Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(2):173-181. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.2.173.
Reference
-
References
1. Holladay JT, Prager TC, Ruiz RS, et al. Improving the abdominal of intraocular lens power calculations. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986; 104:539–41.2. Eleftheriadis H. IOLMaster biometry: refractive results of 100 consecutive cases. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003; 87:960–3.
Article3. Findl O, Kriechbaum K, Sacu S, et al. Influence of operator abdominal on the performance of ultrasound biometry compared to abdominal biometry before cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:1950–5.4. Lee YE, Choi KR, Jun RM. Accuracy of intraocular lens power calculations according to the formulas and anterior chamber depth in short eyes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010; 51:1338–44.
Article5. Holladay JT, Prager TC. Accurate ultrasonic biometry in pseudophakia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1989; 107:189–90.
Article6. Retzlaff JA, Sanders DR, Kraff MC. Development of the SRK/T intraocular lens implant power calculation formula. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:333–40.
Article7. Holladay JT. Standardizing constants for ultrasonic biometry, abdominal, and intraocular lens power calculations. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997; 23:1356–70.8. Hoffer KJ. The Hoffer Q formula: a comparison of theoretic and abdominal formulas. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1993; 19:700–12.9. Hoffer KJ. Clinical results using the Holladay 2 intraocular lens power formula. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000; 26:1233–7.
Article10. Donoso R, Mura JJ, López M, Papic A. [Emmetropization at abdominal surgery. Looking for the best IOL power calculation formula according to the eye length]. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2003; 78:477–80.11. MacLaren RE, Natkunarajah M, Riaz Y, et al. Biometry and abdominal accuracy with intraocular lenses used for cataract surgery in extreme hyperopia. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007; 143:920–31.12. Maeng HS, Ryu EH, Chung TY, Chung ES. Effects of anterior chamber depth and axial length on refractive error after intraocular lens implantation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010; 51:195–202.
Article13. Hennessy MP, Franzco , Chan DG. Contact versus immersion abdominal of axial length before cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:2195–8.14. Rhim JW, Kang SY, Kim HM. Comparative analysis of contact and immersion technique in ultrasonographic biometry. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1795–9.
Article15. Giers U, Epple C. Comparison of A-scan device accuracy. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:235–42.
Article16. Binkhorst RD. The accuracy of ultrasonic measurement of the abdominal length of the eye. Ophthalmic Surg. 1981; 12:363–5.17. Drexler W, Findl O, Menapace R, et al. Partial coherence abdominal: a novel approach to biometry in cataract surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 1998; 126:524–34.18. Holzer MP, Mamusa M, Auffarth GU. Accuracy of a new partial coherence interferometry analyser for biometric measurements. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009; 93:807–10.
Article19. Su PF, Lo AY, Hu CY, Chang SW. Anterior chamber depth abdominal in phakic and pseudophakic eyes. Optom Vis Sci. 2008; 85:1193–200.20. Sheng H, Bottjer CA, Bullimore MA. Ocular component abdominal using the Zeiss IOLMaster. Optom Vis Sci. 2004; 81:27–34.21. Yi CH, Choi SH, Chung ES, Chung TY. Accuracy of the Haigis abdominal based on axial length and anterior chamber depth. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:175–81.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Sudden Refractive Change with Intraocular Pressure Change Following Trauma
- Predictability of Postoperative Refractive Error after Secondary Lens Implantation
- Comparison of Corneal Measurement Values between Two Types of Topography
- Ciliary Sulcus Size according to Refractive Error using Ultrasound Biomicroscopy
- A Study of the Ocular Findings According to Subdivided Myepia