J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2012 Nov;53(11):1584-1590.
Comparison of Corneal Measurement Values between Two Types of Topography
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Institute of Vision Research, Department of Ophthalmology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. taeimkim@gmail.com
Abstract
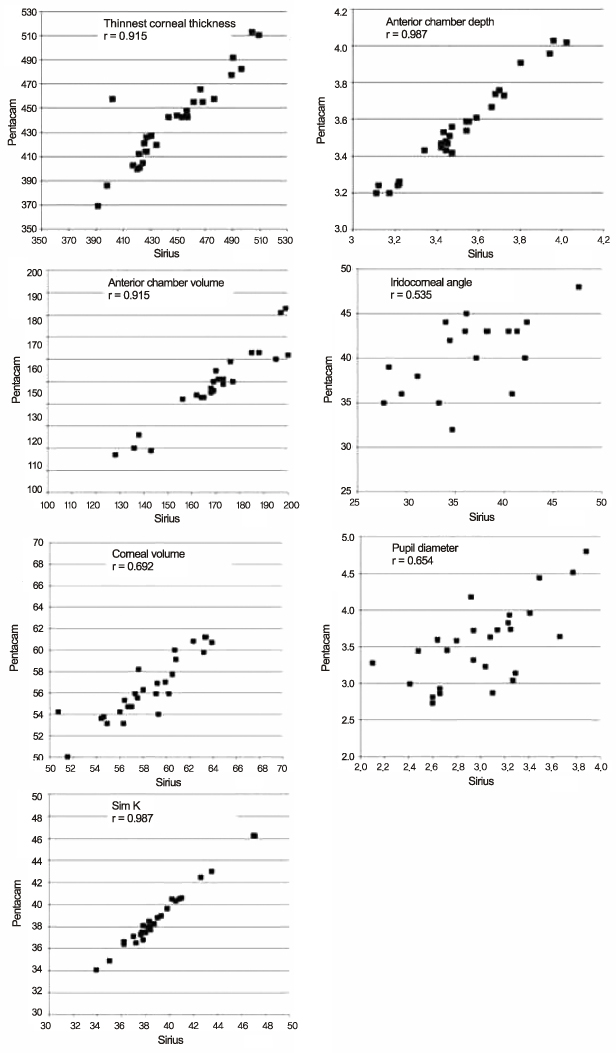
- PURPOSE
To compare the corneal measurements of Sirius and Pentacam in normal cornea and post-corneal refractive surgery patients.
METHODS
Subjects were tested by Pentacam (OCULUS, Wetzlar, Germany), and Sirius (CSO, Firenze, Italy). Measurements included central corneal thickness, thinnest corneal thickness, anterior chamber depth, anterior chamber volume, iridocorneal angle, corneal volume, pupil size, and curvature of cornea.
RESULTS
A total of 88 eyes from 44 patients were included in the present study. When comparing Sirius and Pentacam in the normal cornea, corneal thickness (p = 0.693), thinnest corneal thickness (p = 0.386), anterior chamber depth (p = 0.155), anterior chamber volume (p = 0.650), and pupil diameter (p = 0.124) did not differ significantly. Corneal curvature (p < 0.001), corneal volume (p = 0.023), and iridocorneal angle (p < 0.001) were statistically different. When comparing Sirius and Pentacam in post-corneal refractive surgery patients, corneal thickness (p = 0.056) did not differ significantly. There was a statistical difference in corneal curvature (p < 0.001), thinnest corneal thickness (p = 0.019), anterior chamber depth (p < 0.001), anterior chamber volume (p < 0.001), iridocorneal angle (p < 0.001), corneal volume (p < 0.001), and pupil diameter (p < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Anterior segment measurements with Pentacam and Sirius showed differences in post-corneal refractive surgery patients.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cairns G, McGhee CN. Orbscan computerized topography: attributes, applications, and limitations. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005. 31:205–220.2. Belin MW, Khachikian SS. An introduction to understanding elevation-based topography: how elevation data are displayed - a review. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2009. 37:14–29.3. Wegener A, Laser-Junga H. Photography of the anterior eye segment according to Scheimpflug's principle: options and limitations - a review. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2009. 37:144–154.4. American Academy of Ophthalmology. Corneal topography. Ophthalmology. 1999. 106:1628–1638.5. Shankar H, Taranath D, Santhirathelagan CT, Pesudovs K. Anterior segment biometry with the Pentacam: comprehensive assessment of repeatability of automated measurements. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008. 34:103–113.6. Kawamorita T, Nakayama N, Uozato H. Repeatability and reproducibility of corneal curvature measurements using the Pentacam and Keratron topography systems. J Refract Surg. 2009. 25:539–544.7. Menassa N, Kaufmann C, Goggin M, et al. Comparison and reproducibility of corneal thickness and curvature readings obtained by the Galilei and the Orbscan II analysis systems. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008. 34:1742–1747.8. Li H, Leung CK, Wong L, et al. Comparative study of central corneal thickness measurement with slit-lamp optical coherence tomography and visante optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2008. 115:796–801.e2.9. Savini G, Carbonelli M, Barboni P, Hoffer KJ. Repeatability of automatic measurements performed by a dual Scheimpflug analyzer in unoperated and post-refractive surgery eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011. 37:302–309.10. Savini G, Barboni P, Carbonelli M, Hoffer KJ. Repeatability of automatic measurements by a new Scheimpflug camera combined with Placido topography. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011. 37:1809–1816.11. Hashemi H, Mehravaran S. Corneal changes after laser refractive surgery for myopia: comparison of Orbscan II and Pentacam findings. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007. 33:841–847.12. Savini G, Barboni P, Carbonelli M, Hoffer KJ. Accuracy of Scheimpflug corneal power measurements for intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009. 35:1193–1197.13. Shin YJ, Kim NH, Kim DH. Comparison of Pentacam with Orbscan. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007. 48:637–641.14. Klyce SD. Corneal topography and the new wave. Cornea. 2000. 19:723–729.15. Kawamorita T, Uozato H, Kamiya K, et al. Repeatability, reproducibility, and agreement characteristics of rotating Scheimpflug photography and scanning-slit corneal topography for corneal power measurement. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009. 35:127–133.16. Jain R, Dilraj G, Grewal SP. Repeatability of corneal parameters with Pentacam after laser in situ keratomileusis. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2007. 55:341–347.17. Buehl W, Stojanac D, Sacu S, et al. Comparison of three methods of measuring corneal thickness and anterior chamber depth. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006. 141:7–12.18. Bedei A, Appolloni I, Madesani A, et al. Repeatability and agreement of 2 Scheimpflug analyzers in measuring the central corneal thickness and anterior chamber angle, volume, and depth. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2012. 22:Suppl 7. S29–S32.19. Nilforoushan MR, Speaker M, Marmor M, et al. Comparative evaluation of refractive surgery candidates with Placido topography, Orbscan II, Pentacam, and wavefront analysis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008. 34:623–631.20. González Pérez J, Cerviño A, Giraldez MJ, et al. Accuracy and precision of EyeSys and Orbscan systems on calibrated spherical test surfaces. Eye Contact Lens. 2004. 30:74–78.21. Savini G, Carbonelli M, Sbreglia A, et al. Comparison of anterior segment measurements by 3 Scheimpflug tomographers and 1 Placido corneal topographer. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011. 37:1679–1685.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Corneal Thickness Measurements Between Orbscan Topography System and Ultrasonic Pachymetry before and after LASIK
- Measurement of Angle Kappa Using Ultrasound Biomicroscopy and Corneal Topography
- The Corneal Thickness Changes in Different Gazes in Orbscan Topography
- The Effect of Trabeculeetomy on Corneal Topography
- The Change of Corneal Refractive Power Measured by Corneal Topography before and after Pterygium Surgery