J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2013 Jan;54(1):26-32. 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.1.26.
Comparison of Intraocular Pressure Correction Programs in Pentacam after Corneal Refractive Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Catholic Institute of Visual Science, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ckjoo@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Ophthalmology, Yanbian University, Jilin, China.
- KMID: 2216445
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2013.54.1.26
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the accuracy of Pentacam(R) built-in 5 intraocular pressure (IOP) correction programs used to measure the IOP of patients who received corneal refractive surgery.
METHODS
IOP of 124 eyes from 62 patients who underwent epipolis laser in situ keratomileusis was measured with Goldmann applanation tonometry (GAT) at 6 months pre- and post-operatively. The collected data was input into Pentacam(R), calculated by 5 correction programs, Ehlers, Shah, Dresden, Orssengo / Pye, Kohlhaas, and compared.
RESULTS
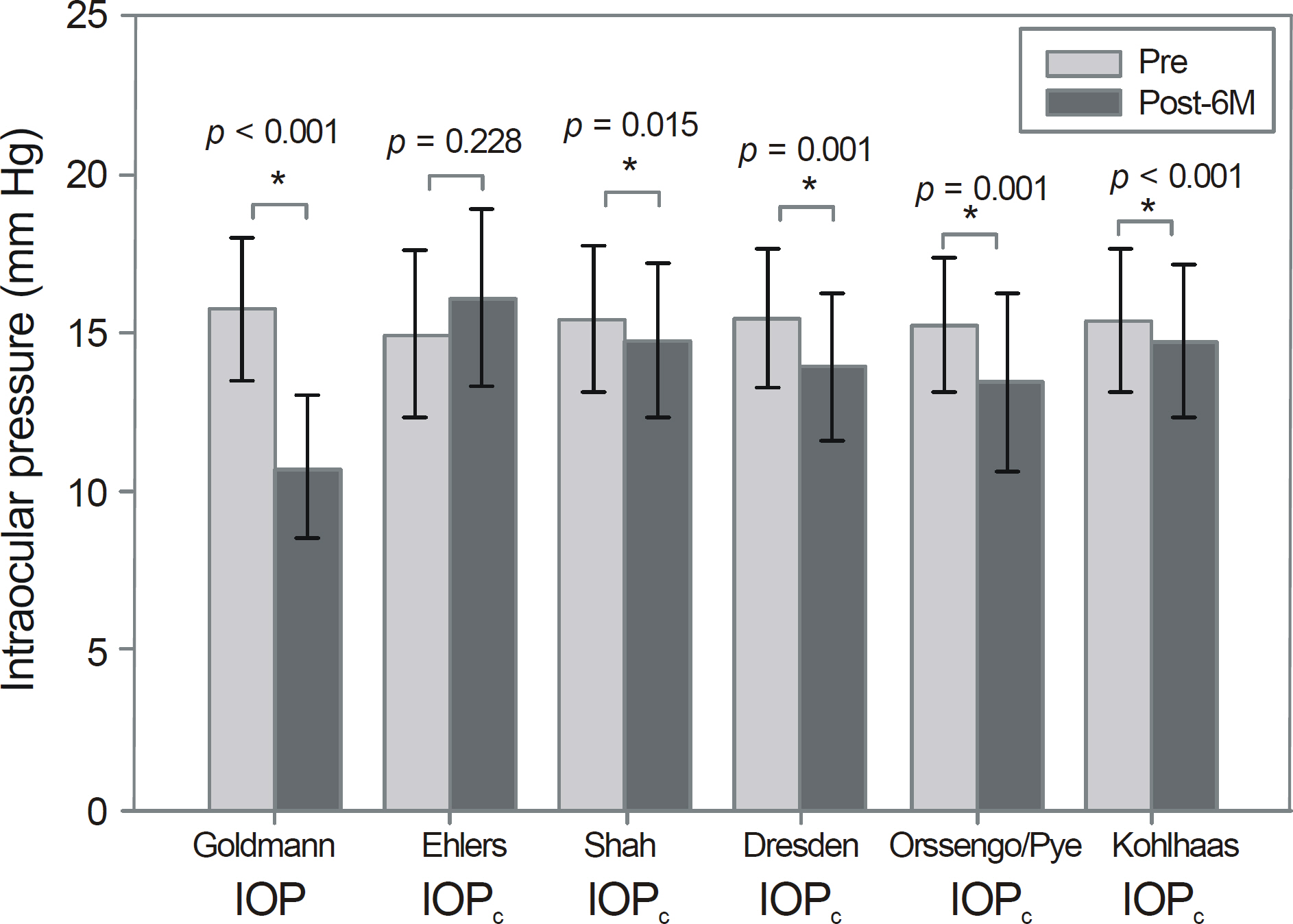
The GAT-based pre- and post-operative IOP was 15.75 +/- 2.24 mm Hg, and 10.72 +/- 2.31 mm Hg, respectively, revealing the post-operative IOP to be significantly lower than the pre-operative IOP (p < 0.001). Among the 5 correction programs within Pentacam(R), Ehlers program showed little difference between pre- and post-operative IOP values (p = 0.228) and the post-operative correction value showed no significant difference with the pre-operative GAT value (p = 0.413).
CONCLUSIONS
The Ehlers program is the most accurate among the 5 Pentacam(R) correction programs evaluated in the present study, and can be a useful tool for correcting the true IOP of patients which tends to be higher after corneal refractive surgery.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Faucher A, Grégoire J, Blondeau P. Accuracy of Goldmann abdominal after refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997; 23:832–8.2. Shah S. Accurate intraocular pressure measurement–the myth of modern ophthalmology? Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:1805–7.
Article3. Siganos DS, Papastergiou GI, Moedas C. Assessment of the Pascal dynamic contour tonometer in monitoring intraocular pressure in unoperated eyes and eyes after LASIK. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:746–51.
Article4. Shrivastava A, Madu A, Schultz J. Refractive surgery and the abdominal patient. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2011; 22:215–21.5. Najman-Vainer J, Smith RJ, Maloney RK. Interface fluid after LASIK: misleading tonometry can lead to end-stage glaucoma. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000; 26:471–2.
Article6. Hornová J, Sedlák P, Hlousková B. [Refractive procedures–LASIK and intraocular pressure in myopic eyes]. Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2000; 56:98–103.7. Cheng AC, Fan D, Tang E, Lam DS. Effect of corneal curvature and corneal thickness on the assessment of intraocular pressure abdominal noncontact tonometry in patients after myopic LASIK surgery. Cornea. 2006; 25:26–8.8. Lee DH, Seo S, Shin SC, et al. Accuracy and predictability of the compensatory function of Orbscan II in intraocular pressure abdominals after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:259–64.9. Lee SJ, Lee HS, Joo CK. Measurements of dynamic contour abdominal after penetrating keratoplasty and EpiLASIK. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:749–55.10. Choi HJ, Kim SW, Kim TI, Kim EK. Intraocular pressure abdominals using dynamic contour tonometer after photorefractive keratectomy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:577–82.11. Mardelli PG, Piebenga LW, Whitacre MM, Siegmund KD. The abdominal of excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy on intraocular pressure measurements using the Goldmann applanation tonometer. Ophthalmology. 1997; 104:945–8.12. Faucher A, Grégoire J, Blondeau P. Accuracy of Goldmann abdominal after refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997; 23:832–8.13. Fournier AV, Podtetenev M, Lemire J, et al. Intraocular pressure change measured by Goldmann tonometry after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998; 24:905–10.
Article14. Kwon GR, Kang SW, Kee C. The influence of central corneal thickness on intraocular pressures measured with Goldmann abdominal tonometer and non-contact tonometer. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1998; 39:1494–8.15. Gunvant P, O'Leary DJ, Baskaran M, et al. Evaluation of abdominal correction factors. J Glaucoma. 2005; 14:337–43.16. Schottenstein EM. Intraocular pressure and tonometry. Ritch R, Shields MB, Krupin T, editors. The Glaucomas. 2nd ed.St Louis: Mosby;1996. 1:chap. 20.17. Whitacre MM, Stein RA, Hassanein K. The effect of corneal abdominal on applanation tonometry. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993; 115:592–6.18. Schipper I, Senn P, Thomann U, Suppiger M. Intraocular pressure after excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy for myopia. J Refract Surg. 1995; 11:366–70.
Article19. Lee DH. Relationship between corneal thickness and intraocular pressure after laser in-situ keratomileusis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:1829–33.20. Ehlers N, Bramsen T, Sperling S. Applanation tonometry and abdominal corneal thickness. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1975; 53:34–43.21. Shah S, Chatterjee A, Mathai M, et al. Relationship between abdominal thickness and measured intraocular pressure in a general abdominal clinic. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:2154–60.22. Kohlhaas M, Boehm AG, Spoerl E, et al. Effect of central corneal thickness, corneal curvature, and axial length on applanation tonometry. Arch Ophthalmol. 2006; 124:471–6.
Article23. Kohlhaas M, Spoerl E, Boehm AG, Pollack K. A correction abdominal for the real intraocular pressure after LASIK for the correction of myopic astigmatism. J Refract Surg. 2006; 22:263–7.24. Orssengo GJ, Pye DC. Determination of the true intraocular abdominal and modulus of elasticity of the human cornea in vivo. Bull Math Biol. 1999; 61:551–72.25. Kirstein EM, Hüsler A. Evaluation of the Orssengo-Pye IOP corrective algorithm in LASIK patients with thick corneas. Optometry. 2005; 76:536–43.
Article26. Lee DH, Seo SJ, Shin SC, Oh JY. The usefulness of compensatory function of Orbscan ∥? in intraocular pressure(IOP) after laser abdominal in situ keratomileusis(LASIK). J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 41:2625–32.27. Munger R, Hodge WG, Mintsioulis G, et al. Correction of abdominal pressure for changes in central corneal thickness following photorefractive keratectomy. Can J Ophthalmol. 1998; 33:159–65.28. Fan F, Li C, Li Y, et al. Intraocular pressure instrument reading comparisons after LASIK. Optom Vis Sci. 2011; 88:850–4.
Article29. Ryan DS, Coe CD, Howard RS, et al. Corneal biomechanics abdominal epi-LASIK. J Refract Surg. 2011; 27:458–64.30. Qazi MA, Sanderson JP, Mahmoud AM, et al. Postoperative changes in intraocular pressure and corneal biomechanical metrics Laser in situ keratomileusis versus laser-assisted subepithelial keratectomy. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:1774–88.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparative Analysis of Corneal Refractive Power Measured with AL-Scan(R), Autokeratometer, and Pentacam(R)
- Comparison of Measured Intraocular Pressure Change According to the Methods of Corneal Refractive Surgery
- Measurement Comparison of Anterior Segment Parameters between AL-Scan(R) and Pentacam(R)
- Comparison of Corneal Measurement Values between Two Types of Topography
- Multiple Logistic Regression Analysis of Factors in Refractive Outcome of Photorefractive Keratectomy(PRK)