J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2011 Mar;52(3):308-314. 10.3341/jkos.2011.52.3.308.
Comparison of Measured Intraocular Pressure Change According to the Methods of Corneal Refractive Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jimoon@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Apgujung St. Mary's Eye Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2214295
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2011.52.3.308
Abstract
- PURPOSE
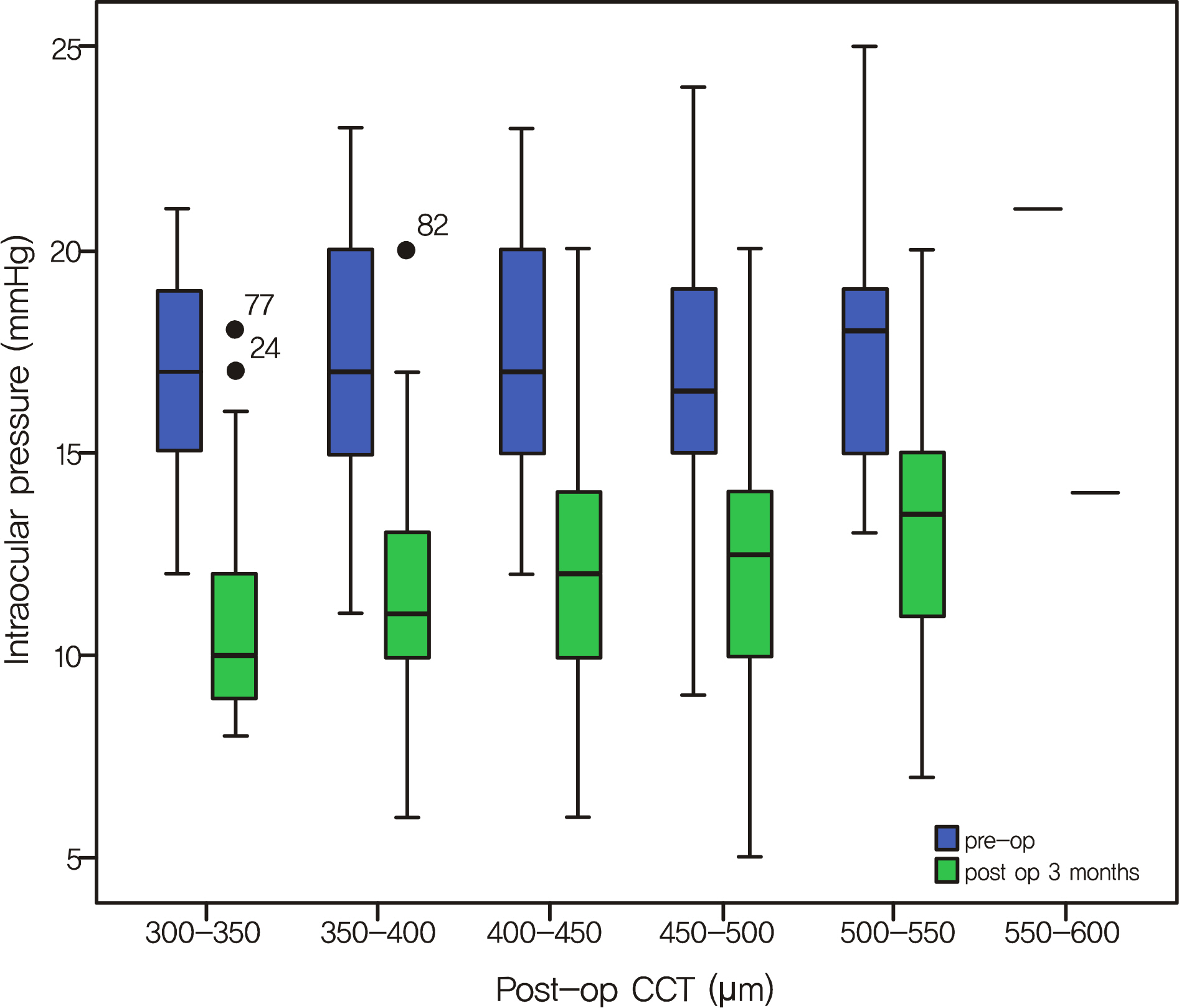
To evaluate differences in intraocular pressure change after three different methods of corneal refractive surgery.
METHODS
The medical records of 296 eyes of 150 patients who underwent corneal refractive surgery were reviewed. Spherical equivalent, central corneal thickness (CCT), and intraocular pressure before surgery, and one month, three months and six months after surgery were analyzed.
RESULTS
The patients included those having undergone laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis (LASIK; 96 eyes), IntraLASIK (98 eyes), laser assisted sub-epithelial keratomileusis (LASEK; 102 eyes). Post operative intraocular pressure in ablated corneal depth and in CCT showed a meaningful correlation. Intraocular pressure decreased significantly after refractive surgery; however, there were no differences among the three groups.
CONCLUSIONS
Post operative intraocular pressure after corneal refractive surgery is influenced by CCT. There were no differences in intraocular pressure change among the three groups.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Analysis of Postoperative Intraocular Pressure Underestimation Measured with Non Contact Tonometry after Corneal Refractive Surgery
Wook Kyum Kim, Eun Young Cho, Hee Sun Kim, Hee Kyung Lee, Jin Kuk Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(2):167-172. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.2.167.
Reference
-
References
1. Albert DM, Jokobiec FA. Principles and Practice of Ophthalmology. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co.;1994. p. 1291.2. Wolfs RC, Klaver CC, Vingerling JR, et al. Distribution of central corneal thickness and its association with intraocular pressure: The Rotterdam Study. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997; 123:767–72.
Article3. Whitacre MM, Stein RA, Hassanein K. The effect of corneal thickness on applanation tonometry. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993; 115:592–6.
Article4. Ehlers N, Bramsen T, Sperling S. Applanation tonometry and central corneal thickness. Acta Ophthalmol. 1975; 53:34–43.
Article5. Dohadwala AA, Munger R, Damji KF. Positive correlation between Tono-Pen intraocular pressure and central corneal thickness. Ophthalmology. 1998; 105:1849–54.
Article6. Mark HH. Corneal curvature in applanation tonometry. Am J Ophthalmol. 1973; 76:223–4.
Article7. Trokel SL, Srinivasan R, Braren B. Excimer laser surgery of the cornea. Am J Ophthalmol. 1983; 96:710–5.
Article8. Seiler T, Holschbach A, Derse M, et al. Complications of myopic photorefractive keratectomy with the excimer laser. Ophthalmology. 1994; 101:153–60.
Article9. Gartry DS, Kerr Muir MG, Marshall J. Excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy: 18 months followup. Ophthalmology. 1992; 99:1209–19.10. Seiler T, Wollensak J. Myopic photorefractive keratectomy with excimer laser: one-year followup. Ophthalmology. 1991; 98:1156–63.11. Shields MB, Ritch R. Glaucoma, Intraocular Pressure and Tonometry. 2nd ed.St. Louis: Mosby;1996. p. 407–28.12. Dimitrios SS, Georgios IP, Carlos M. Assessment of the Pascal dy-namic contour tonometer in monitoring intraocular pressure in un-operated eyes and eyes after LASIK. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:746–51.13. Bissen-Miyajima H, Suzuki S, Ohashi Y, Minami K. Experimental observation of intraocular pressure changes during microkeratome suctioning in laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:590–4.
Article14. Suzuki CR, Farah ME. Retinal peripheral changes after laser in situ keratomileusis in patients with high myopia. Can J Ophthalmol. 2004; 39:69–73.
Article15. Mirshahi A, Kohnen T. Effect of microkeratome suction during LASIK on ocular structures. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:645–9.
Article16. Hamilton DR, Manche EE, Rich LF, Maloney RK. Steroidinduced glaucoma after laser in situ keratomileusis associated with inter-face fluid. Ophthalmology. 2002; 109:659–65.
Article17. Shaikh NM, Shaikh S, Singh K, Manche E. Progression to end-stage glaucoma after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:356–9.
Article18. Levy Y, Hefetz L, Zadok D, et al. Refractory intraocular pressure increase after photorefractive keratectomy. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997; 23:593–4.
Article19. Samuelson TW. Refractive surgery in glaucoma. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004; 15:112–8.
Article20. Chihara E. Assessment of true intraocular pressure: the gap between theory and practical data. Surv Ophthalmol. 2008; 53:203–18.
Article21. Koh SI, Kim SD, Kim JD. The effect of the changes in central corneal thickness and curvature on measurement of intraocular pressure after LASIK. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:2464–72.22. Wittenberg S, Green MK. The effect of tears in intraocular pressure as measured with the NCT. Invest Ophthalmol. 1976; 15:139–42.23. Kwon GR, Kang SW, Kee C. The influence of central corneal thickness on intraocular pressures measured with Goldmann applanation tonometer and non-contact tonometer. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1998; 39:1494–8.24. Schipper I, Senn P, Thomas U, Suppinger M. Intraocular pressure after excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy for myopia. J Refract Corneal Surg. 1995; 11:366–70.
Article25. Zadok D, Tran DB, Twa M, et al. Pneumotonometry versus Goldmann tonometry after laser in situ keratomileusis for myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1999; 25:1344–8.26. Qazi MA, Sanderson JP, Mahmoud AM, et al. Postoperative changes in intraocular pressure and corneal biomechanical met-rics: Laser in situ keratomileusis versus laser-assisted subepithelial keratectomy. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:1774–88.27. Kirwan C, O'Keefe M. Measurement of intraocular pressure in LASIK and LASEK patients using the Reichert Ocular Response Analyzer and Goldmann applanation tonometry. J Refract Surg. 2008; 24:366–70.
Article28. Sánchez-Navés J, Furfaro L, Piro O, Balle S. Impact and perma-nence of LASIK-induced structural changes in the cornea on pneu-motonometric measurements: contributions of flap cutting and stromal ablation. J Glaucoma. 2008; 17:611–8.
Article29. Samuelson TW. Refractive surgery in glaucoma. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004; 15:112–8.
Article30. Cronemberger S, Guimarães CS, Calixto N, Calixto JM. Intraocular pressure and ocular rigidity after LASIK. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2009; 72:439–43.
Article31. Roy AS, Dupps WJ Jr. Effects of altered corneal stiffness on native and postoperative LASIK corneal biomechanical Behavior: a whole-eye Finite Element Analysis. J Refract Surg. 2009; 25:875–87.
Article32. Kohli PG, Randhawa BK, Singh KD, et al. Relation between central corneal thickness and intraocular pressure in Punjabi population. J Med Eng Technol. 2010; 34:1–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Sudden Refractive Change with Intraocular Pressure Change Following Trauma
- Influence of Central Corneal Thickness Change on Intraocular Pressure Measurement after LASIK and LASEK
- The Effect of Strabismus Surgery on Refractive Error Measured with Corneal Topography
- Surgical treatment for myopia
- Anterior Chamber Depth, Corneal Thickness and Corneal Endothelial Change following Decreased Intraocular Pressure