J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2011 May;52(5):524-530. 10.3341/jkos.2011.52.5.524.
Comparison of Flap Thickness Measured with Ultrasound Subtraction Method, Direct Method, and Optical Coherence Tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hwtchah@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2214570
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2011.52.5.524
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the flap thicknesses measured with the ultrasound (US) subtraction method, the direct method, and optical coherence tomography (OCT) in femtosecond laser-assisted LASIK eyes.
METHODS
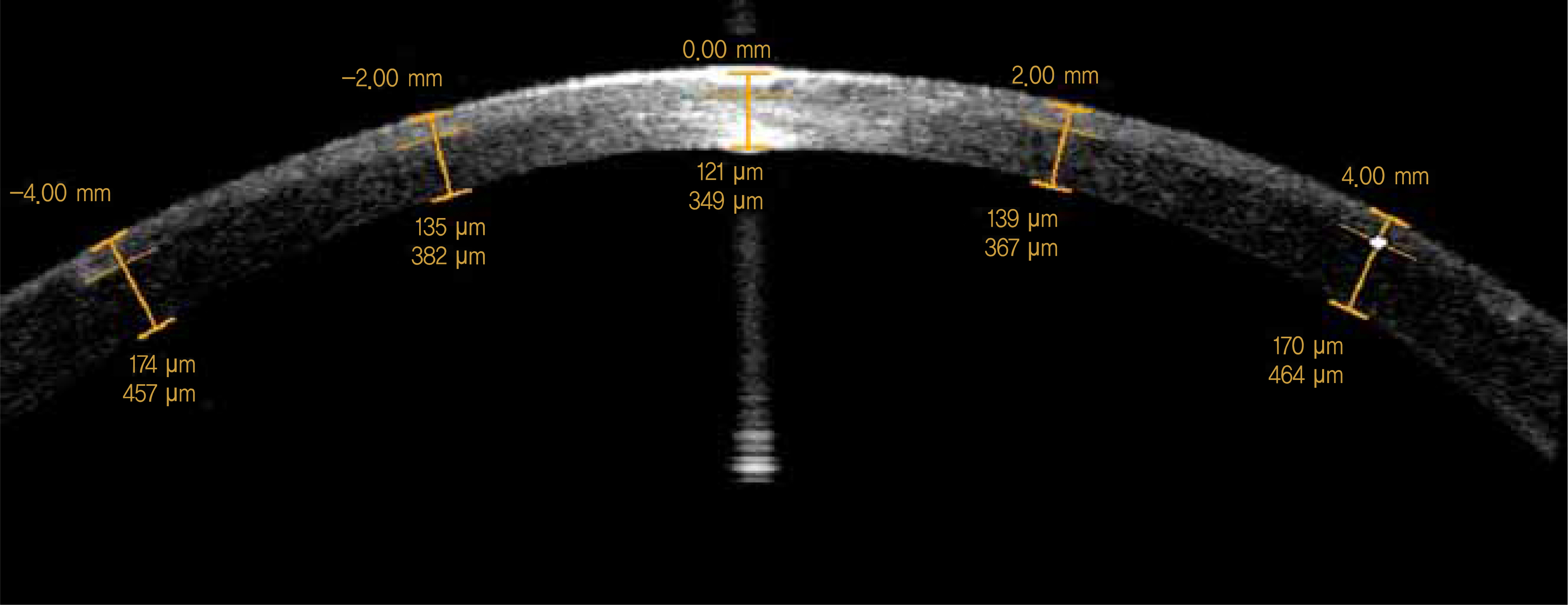
The present study included 65 eyes of 37 patients who underwent femtosecond laser-assisted LASIK surgery. Flap thickness was measured intraoperatively using the direct and subtraction methods with US pachymetry and postoperatively using anterior segment OCT. Flap thickness measurements were compared among the three methods.
RESULTS
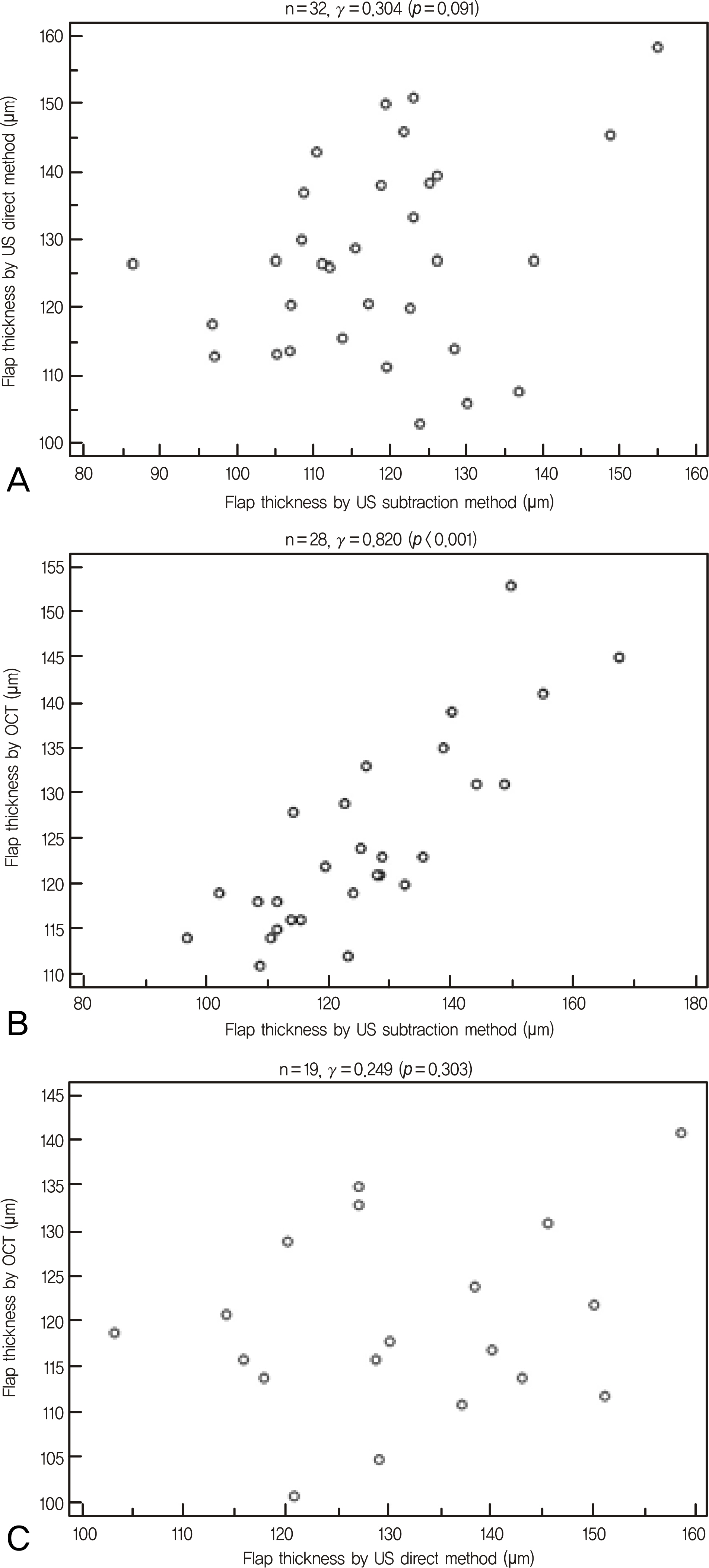
There was no significant difference between the flap thickness measured using the US subtraction method and OCT (p = 0.511). The flap thickness values obtained by these two different methods also correlated well with each other (gamma = 0.820, p < 0.001). However, flap thickness measured using the US direct method was significantly different (p < 0.001) with a low agreement value compared to the other two methods. Furthermore, the US direct method showed a lower measurement success rate compared to the US subtraction method (54% vs. 95%).
CONCLUSIONS
Flap thickness measured using the US subtraction method and OCT showed different values compared to that measured using the US direct method. Because of the lower measurement success rate and agreement value, the US direct method is not capable of being used in substitute for the US subtraction method.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Knorz M. Flap and interface complications in LASIK. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2002; 13:242–5.
Article2. Seiler T, Koufala K, Richter G. Iatrogenic keratectasia after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Refract Surg. 1998; 14:312–7.
Article3. Stulting R, Carr J, Thompson K, Waring G. Complications of laser in situ keratomileusis for the correction of myopia. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:13–20.
Article4. Solomon K, Donnenfeld E, Sandoval H, et al. Flap thickness accuracy comparison of 6 microkeratome models. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:964–77.5. Talamo J, Meltzer J, Gardner J. Reproducibility of flap thickness with IntraLase FS and Moria LSK-1 and M2 microkeratomes. J Refract Surg. 2006; 22:556–61.
Article6. Schumer DJ, Bains HS. The Nidek MK-2000 microkeratome system. J Refract Surg. 2001; 17:S250–1.
Article7. Sutton G, Hodge C. Accuracy and precision of LASIK flap thickness using the IntraLase femtosecond laser in 1000 consecutive cases. J Refract Surg. 2008; 24:802–6.
Article8. Giledi O, Mulhern M, Espinosa M, et al. Reproducibility of LASIK flap thickness using the Hansatome microkeratome. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:1031–7.
Article9. Flanagan GW, Binder PS. Precision of flap measurements for laser in situ keratomileusis in 4428 eyes. J Refract Surg. 2003; 19:113–23.
Article10. Flanagan G, Binder PS. Estimating residual stromal thickness before and after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:1674–83.
Article11. Muallem MS, Yoo SH, Romano AC, et al. Flap and stromal bed thickness in laser in situ keratomileusis enhancement. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:2295–302.
Article12. Eisner R, Binder P. Technique for measuring laser in situ keratomileusis flap thickness using the IntraLase laser. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:556–8.
Article13. Stahl JE, Durrie DS, Schwendeman FJ, Boghossian AJ. Anterior segment OCT analysis of thin IntraLase femtosecond flaps. J Refract Surg. 2007; 23:555–8.
Article14. Chen HJ, Xia YJ, Zhong YY, et al. Anterior segment optical coherence tomography measurement of flap thickness after myopic LASIK using the Moria one use-plus microkeratome. J Refract Surg. 2010; 26:403–10.
Article15. Kim HJ, Oh SH, Lee DH, et al. Reproducibility of IntraLASIK flap thickness measured with optical coherence tomography. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:1630–5.
Article16. Friedlaender M. LASIK surgery using the IntraLase femtosecond laser. Int Ophthamol Clin. 2006; 46:145–53.
Article17. Cheng AC, Ho T, Lau S, et al. Measurement of LASIK flap thickness with anterior segment optical coherence tomography. J Refract Surg. 2008; 24:879–84.
Article18. Li EY, Mohamed S, Leung CK, et al. Agreement among 3 methods to measure corneal thickness: ultrasound pachymetry, Orbscan II, and Visante anterior segment optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114:1842–7.
Article19. Zhao PS, Wong TY, Wong WL, et al. Comparison of central corneal thickness measurements by visante anterior segment optical coherence tomography with ultrasound pachymetry. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007; 143:1047–9.
Article20. Wildner K, Muller M, Dawczynski J, Strobel J. Comparison of the corneal thickness as measured by Visante anterior segment OCT versus ultrasound technique. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2007; 224:832–6.21. Li Y, Netto MV, Shekhar R, et al. A longitudinal study of LASIK flap and stromal thickness with high-speed optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114:1124–32.
Article22. Nagy ZZ, Resch M, Suveges I. Ultrasound evaluation of flap thickness, ablation depth, and corneal edema after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Refract Surg. 2004; 20:279–81.
Article23. Thomas J, Wang J, Rollins AM, Sturm J. Comparison of corneal thickness measured with optical coherence tomography, ultrasonic pachymetry, and a scanning slit method. J Refract Surg. 2006; 22:671–8.
Article24. Dawson DG, Holley GP, Geroski DH, et al. Ex vivo confocal microscopy of human LASIK corneas with histologic and ultra-structural correlation. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:634–44.
Article25. Wylegał a E, Teper S, Nowiή ska AK, et al. Anterior segment imaging: Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography versus time-domain optical coherence tomography. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:1410–4.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reproducibility of IntraLASIK Flap Thickness Measured with Optical Coherence Tomography
- Utility of the Swept Source Optical Coherence Tomography for Measurements of Central Corneal Thickness
- Comparison of Laser In Situ Keratomileusis Flap Morphology and Predictability by WaveLight FS200 Femtosecond Laser and Moria Microkeratome: An Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography Study
- Comparison of Macular Retinal Thickness among Four Optical Coherence Tomography Devices in Healthy Young Subjects
- Choroidal Thickness at the Outside of Fovea in Diabetic Retinopathy Using Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography