J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2015 Nov;56(11):1720-1727. 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.11.1720.
Comparison of Biometric Measurements and Refractive Results between Applanation Ultrasonography and Three Different Interferometries
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Sahmyook Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, St. Paul's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. eyedoc@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2214180
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2015.56.11.1720
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare ocular biometry and refractive results measured using conventional applanation ultrasonography and 3 different optical interferometries, Lenstar LS900(R), AL-Scan(R) and OA-2000(R).
METHODS
The biometries of 31 cataractous eyes were measured using ultrasonography, Lenstar LS900(R), AL-Scan(R) or OA-2000(R). The axial length, anterior chamber depth and keratometry were measured. The SRK/T formula was used to calculate intraocular lens power. Two months after cataract surgery, the refractive outcome was determined and results from the 4 different biometry methods were compared.
RESULTS
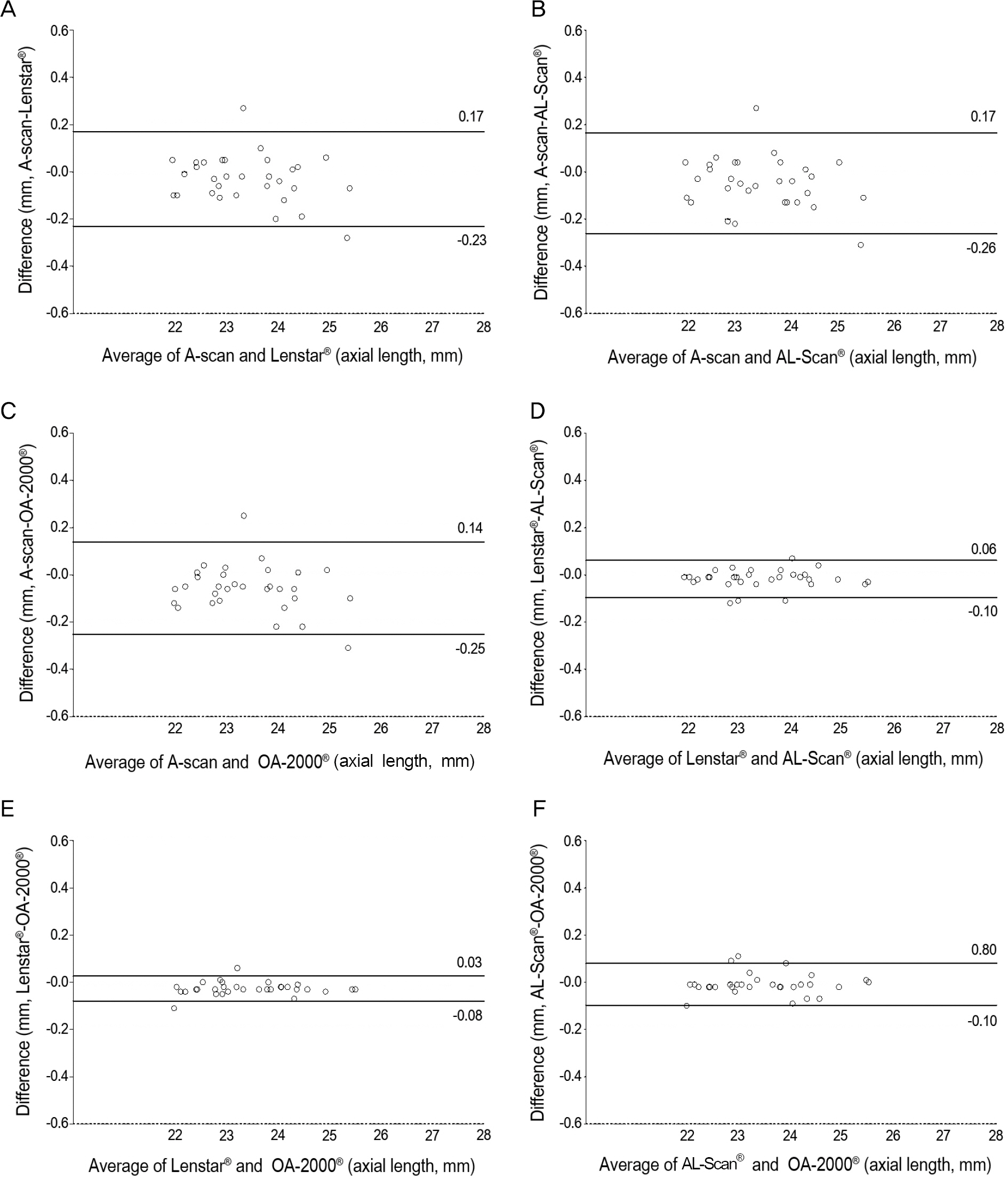
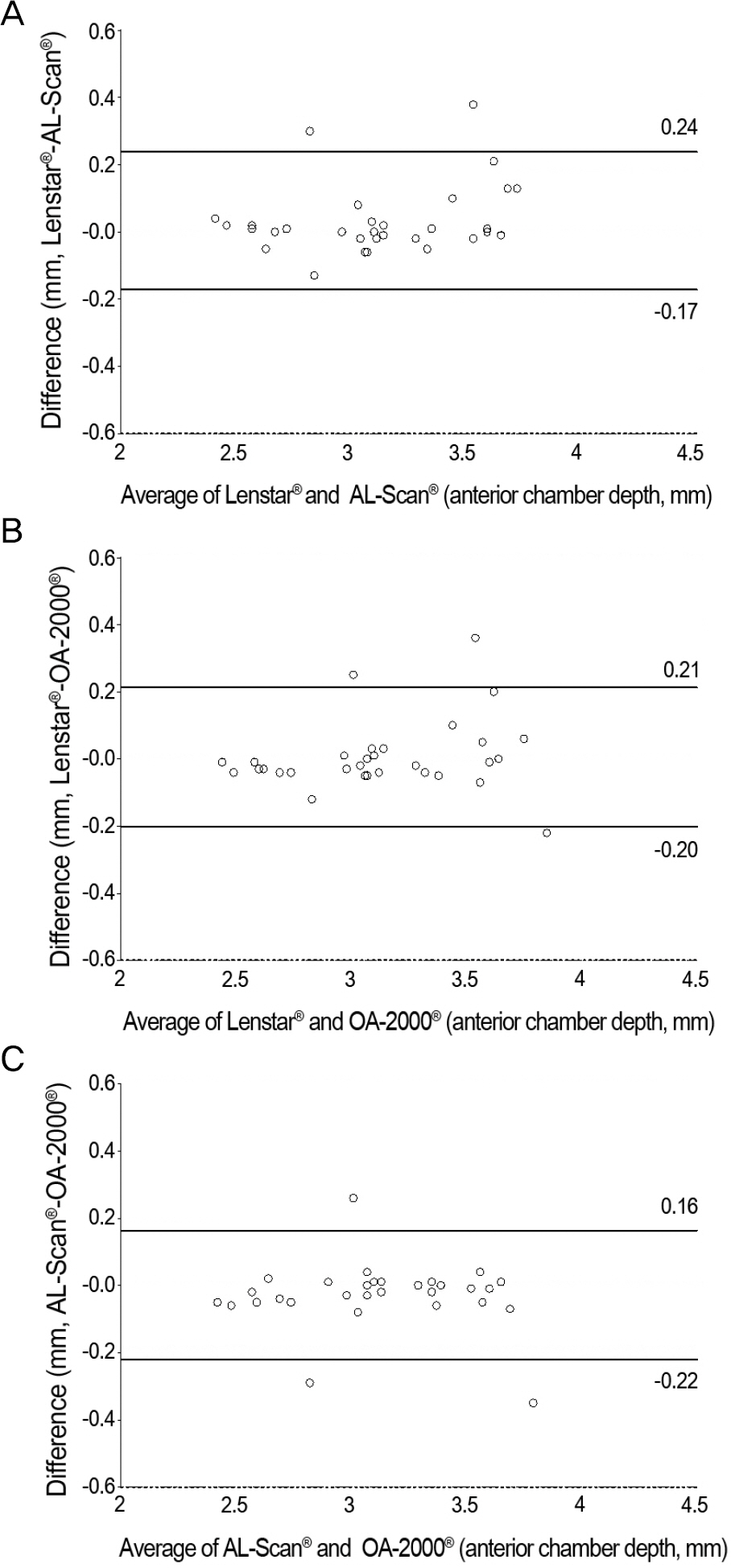
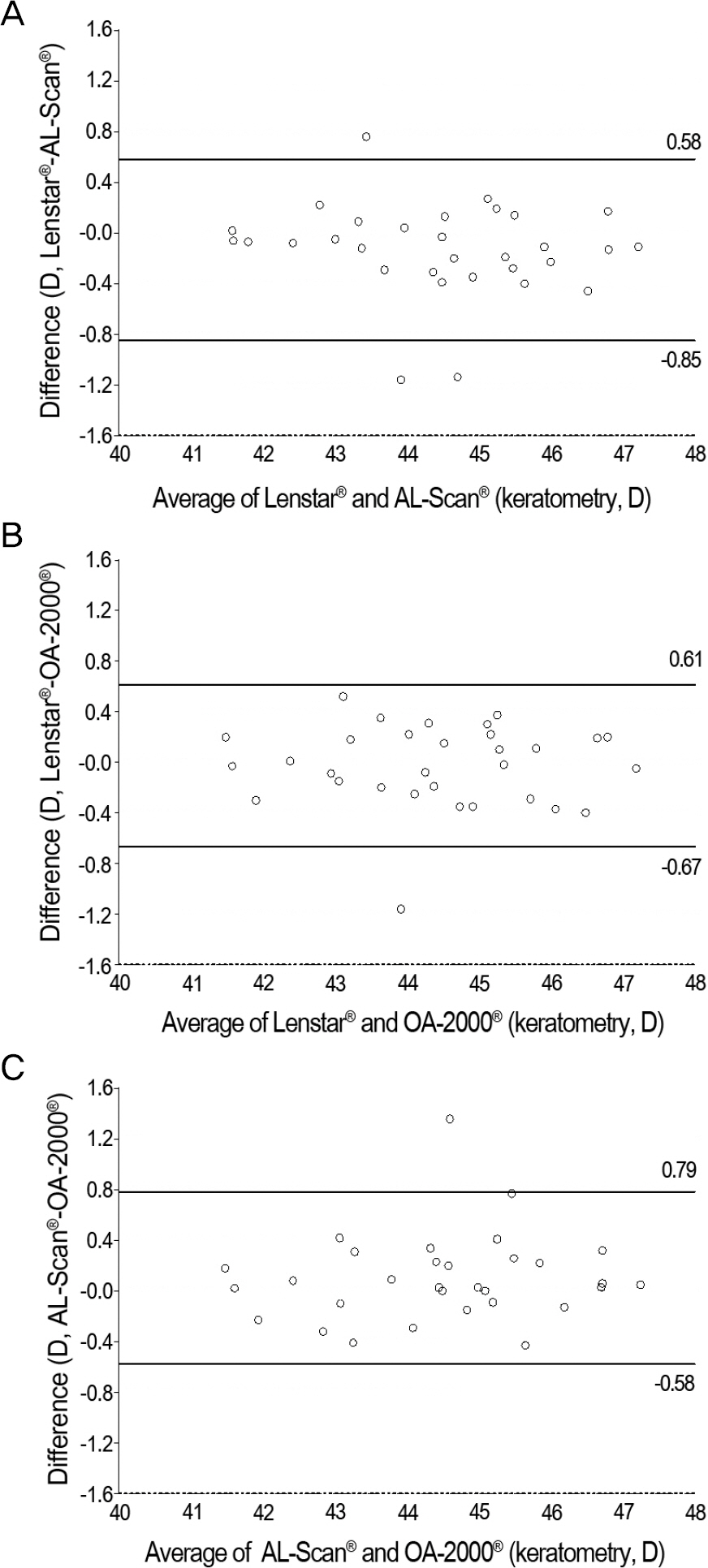
Axial lengths were 23.39 +/- 0.95 mm, 23.42 +/- 0.98 mm, 23.43 +/- 0.98 mm and 23.44 +/- 0.98 mm measured using ultrasonography, Lenstar LS900(R), AL-Scan(R) and OA-2000(R), respectively with no statistically significant differences observed (p = 0.996). The anterior chamber depth and keratometry were 3.14 +/- 0.41 mm, 3.10 +/- 0.38 mm and 3.13 +/- 0.39 mm (p = 0.936) and 44.41 +/- 1.52 D, 44.54 +/- 1.57 D and 44.44 +/- 1.52 D (p = 0.937) for Lenstar LS900(R), AL-Scan(R) and OA-2000(R) respectively. There were no statistically significant differences between the 3 optical devices. The mean absolute error of the 4 different devices were not statistically significant (p = 0.722).
CONCLUSIONS
The ocular biometric measurements and prediction of postoperative refraction using ultrasonography, Lenstar LS900(R), AL-Scan(R) or OA-2000(R) showed no significant differences.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comparison of Biometric Measurements and Refractive Results among Low-coherence Reflectometry, Partial Interferometry and Applanation Ultrasonography
Sung Hoon Lee, Hyung Keun Lee
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2017;58(1):43-49. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2017.58.1.43.
Reference
-
References
1. Giers U, Epple C. Comparison of A-scan device accuracy. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:235–42.
Article2. Tehrani M, Krummenauer F, Blom E, Dick HB. Evaluation of the practicality of optical biometry and applanation ultrasound in 253 eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:741–6.
Article3. Holzer MP, Mamusa M, Auffarth GU. Accuracy of a new partial coherence interferometry analyser for biometric measurements. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009; 93:807–10.
Article4. Cruysberg LP, Doors M, Verbakel F. . Evaluation of the Lenstar LS 900 non-contact biometer. Br J Ophthalmol. 2010; 94:106–10.
Article5. Kaswin G, Rousseau A, Mgarrech M. . Biometry and intra-ocular lens power calculation results with a new optical biometry device: comparison with the gold standard. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2014; 40:593–600.
Article6. Huang J, Savini G, Li J. . Evaluation of a new optical biometry device for measurements of ocular components and its comparison with IOLMaster. Br J Ophthalmol. 2014; 98:1277–81.
Article7. Grajciar B, Pircher M, Hitzenberger CK. . High sensitive measurement of the human axial eye length in vivo with Fourier domain low coherence interferometry. Opt Express. 2008; 16:2405–14.
Article8. Aristodemou P, Knox Cartwright NE, Sparrow JM, Johnston RL. Formula choice: Hoffer Q, Holladay 1, or SRK/T and refractive outcomes in 8108 eyes after cataract surgery with biometry by partial coherence interferometry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:63–71.
Article9. Olsen T. Sources of error in intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1992; 18:125–9.
Article10. Haigis W, Lege B, Miller N, Schneider B. Comparison of im-mersion ultrasound biometry and partial coherence interferometry for intraocular lens calculation according to Haigis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2000; 238:765–73.
Article11. Hoffer KJ, Shammas HJ, Savini G. Comparison of 2 laser instru-ments for measuring axial length. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:644–8.
Article12. Santodomingo-Rubido J, Mallen EA, Gilmartin B, Wolffsohn JS. A new non-contact optical device for ocular biometry. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86:458–62.
Article13. Lam AK, Chan R, Pang PC. The repeatability and accuracy of axial length and anterior chamber depth measurements from the IOLMaster. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2001; 21:477–83.14. Szalai E, Berta A, Hassan Z, Módis L Jr. Reliability and repeat-ability of swept-source Fourier-domain optical coherence tomog-raphy and Scheimpflug imaging in keratoconus. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:485–94.
Article15. Kim SI, Kang SJ, Oh TH. . Accuracy of ocular biometry and postoperative refraction in cataract patients with AL-Scan(R). J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:1688–93.16. Shin JW, Seong M, Kang MH. . Comparison of ocular bio-metry and postoperative refraction in cataract patients between Lenstar(R) and IOL Master(R). J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:833–8.17. Shin JA, Chung SK. Comparison of the refractive results measured by ultrasound and partial coherence interferometers. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:723–7.
Article18. Kwag JY, Choi SH. Comparison of ocular biometry measured by ultrasound and two kinds of partial coherence interferometers. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:169–74.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Ocular Biometry Measured Using Four Applanation Ultrasonographic Biometry Devices
- Comparison of Biometric Measurements and Refractive Results among Low-coherence Reflectometry, Partial Interferometry and Applanation Ultrasonography
- Comparison of the Refractive Results Measured by Ultrasound and Partial Coherence Interferometers
- The Correlation between Angle Kappa and Ocular Biometry in Koreans
- Comparison of Intraocular Pressure via Goldmann-applanation Tonometry and TonoPen in Thyroid-associated Ophthalmopathy Accompanying Restrictive Strabismus