J Korean Surg Soc.
2013 Aug;85(2):89-92. 10.4174/jkss.2013.85.2.89.
Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor mimicking hepatocellular carcinoma with dense lipiodol uptake
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yongaaa5972@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Pathology, Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2212523
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2013.85.2.89
Abstract
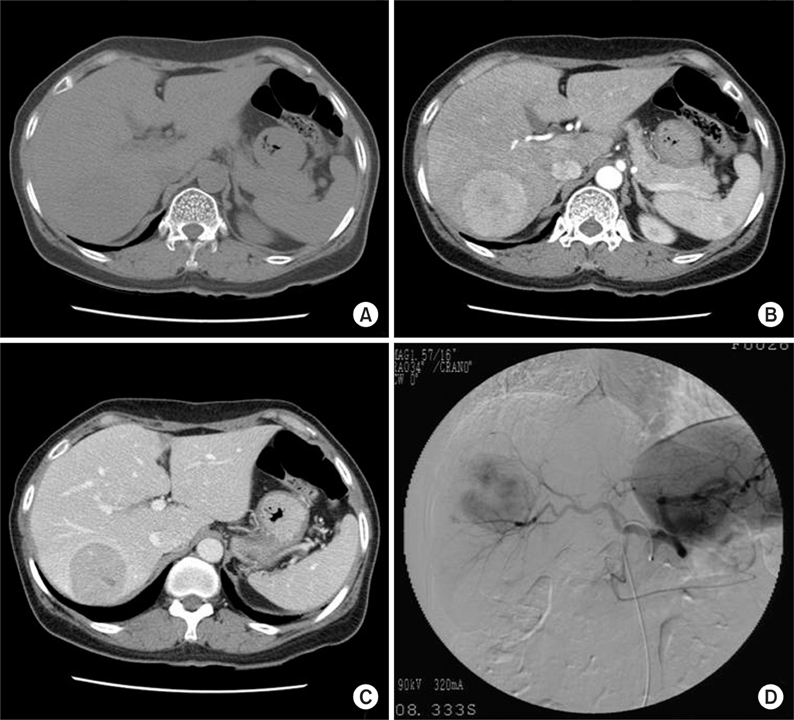
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) of the liver is a very rare lesion that has radiologic similarity with malignant liver tumor. Differential diagnosis of IMT from a malignant lesion of the liver is very important because surgical resection is not mandatory for IMT. Lipiodol computed tomography is a very sensitive and specific diagnostic tool for hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC). Herein, we describe a case of IMT that had dense lipiodol uptake in the tumor and mimicked HCC. To our knowledge, previously, only one case of IMT with dense lipiodol retention has been reported.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dehner LP. The enigmatic inflammatory pseudotumours: the current state of our understanding, or misunderstanding. J Pathol. 2000. 192:277–279.2. Yamaguchi J, Sakamoto Y, Sano T, Shimada K, Kosuge T. Spontaneous regression of inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver:report of three cases. Surg Today. 2007. 37:525–529.3. Tsou YK, Lin CJ, Liu NJ, Lin CC, Lin CH, Lin SM. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver: report of eight cases, including three unusual cases, and a literature review. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. 22:2143–2147.4. Zheng XH, Guan YS, Zhou XP, Huang J, Sun L, Li X, et al. Detection of hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison of multi-detector CT with digital subtraction angiography and Lipiodol CT. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. 11:200–203.5. Fukuya T, Honda H, Matsumata T, Kawanami T, Shimoda Y, Muranaka T, et al. Diagnosis of inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver: value of CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994. 163:1087–1091.6. Torzilli G, Inoue K, Midorikawa Y, Hui AM, Takayama T, Makuuchi M. Inflammatory pseudotumors of the liver: prevalence and clinical impact in surgical patients. Hepatogastroenterology. 2001. 48:1118–1123.7. Park KS, Jang BK, Chung WJ, Cho KB, Hwang JS, Kang YN, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumor of liver: a clinical review of 15 cases. Korean J Hepatol. 2006. 12:429–438.8. Ngan H. Lipiodol computerized tomography: how sensitive and specific is the technique in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma? Br J Radiol. 1990. 63:771–775.9. Nakakuma K, Tashiro S, Hiraoka T, Uemura K, Konno T, Miyauchi Y, et al. Studies on anticancer treatment with an oily anticancer drug injected into the ligated feeding hepatic artery for liver cancer. Cancer. 1983. 52:2193–2200.10. Choi BI, Kim HC, Han JK, Park JH, Kim YI, Kim ST, et al. Therapeutic effect of transcatheter oily chemoembolization therapy for encapsulated nodular hepatocellular carcinoma: CT and pathologic findings. Radiology. 1992. 182:709–713.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnostic Value of Immediate CT after Chemoembolization in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Comparison with 2-3 Week Delayed CT
- MRI Findings of Lipiodol Uptake in Hepatocellular Carcinomas: A Focus on Signal Intensity
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of Nasal Septum after Septoplasty: A Case Report
- Safety of Superselective Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization through Cystic Artery for Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- An A to Z of Lipiodol Beyond the Clinical Practice in the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma