J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2003 Sep;10(3):209-216. 10.4184/jkss.2003.10.3.209.
Molecular Biological and Pathological Aspects of Intercostal Muscles and Intervertebral Discs in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. haksunkim@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Bundang-cha Medical Center.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital.
- 4Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inchun Christian Hospital.
- KMID: 2209688
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2003.10.3.209
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: A molecular biological study of intercostal muscles and intervertebral disc cells of Korean scoliosis patients.
OBJECTIVES
To study the pathological results of intercostal muscles and molecular biological activity of intervertebral disc cells of the scoliotic major curve in Korean patients. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW : The cause of idiopathic scoliosis has been investigated in terms of many parameters. Although, molecular biological studies of intercostal muscles and intervertebral disc cells have been performed in foreign countries, few studies have been conducted in Korea.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
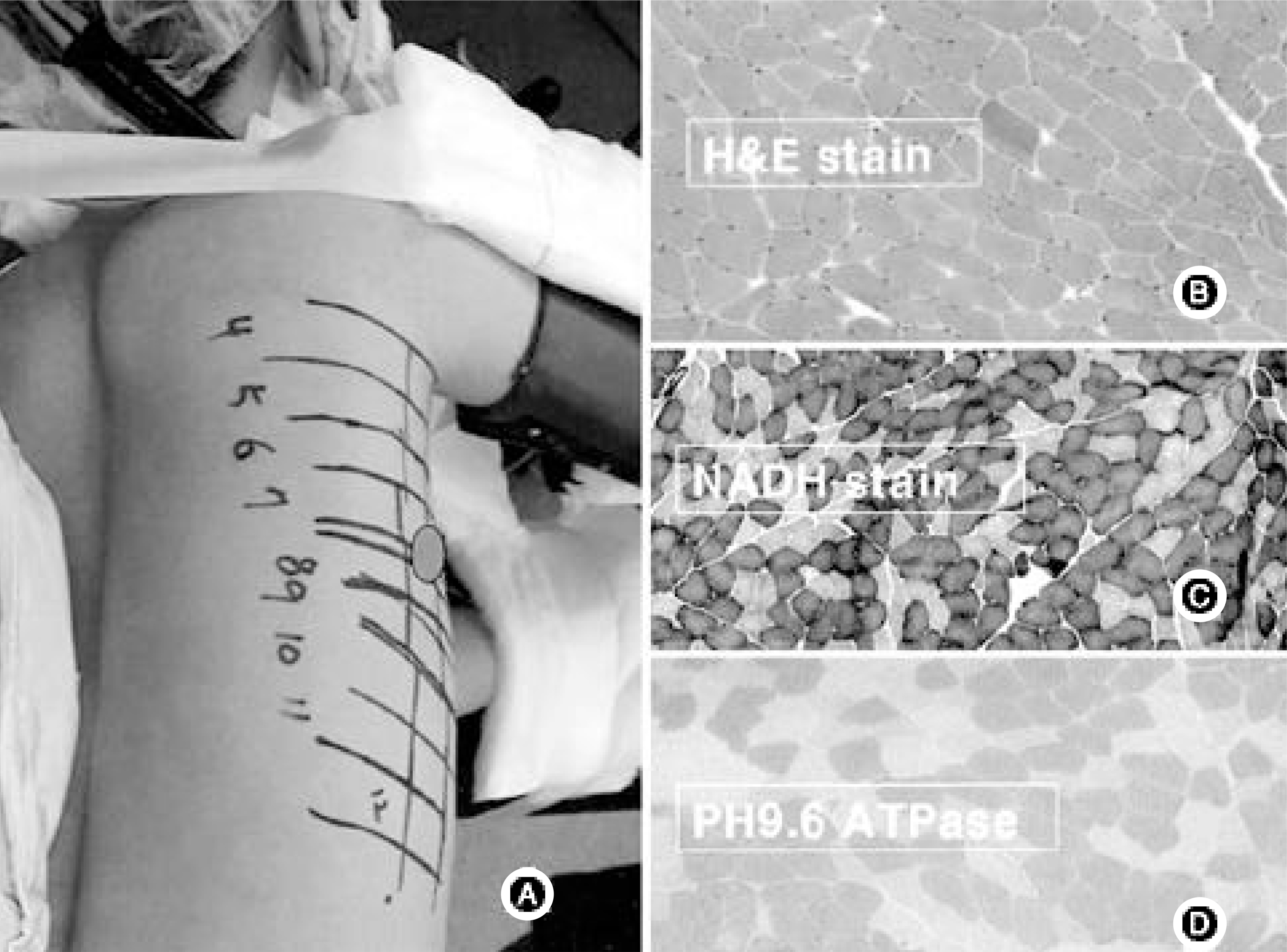
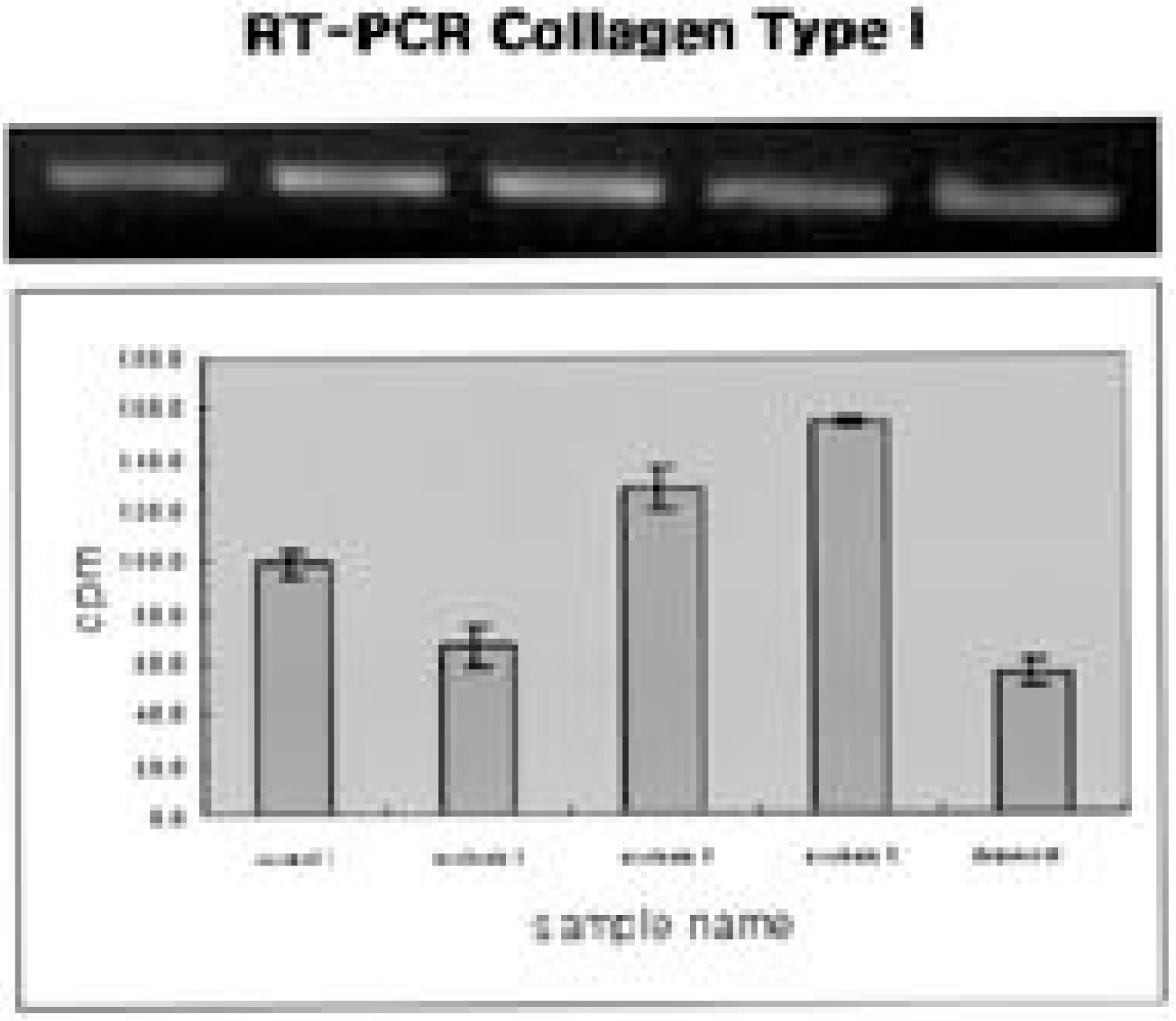
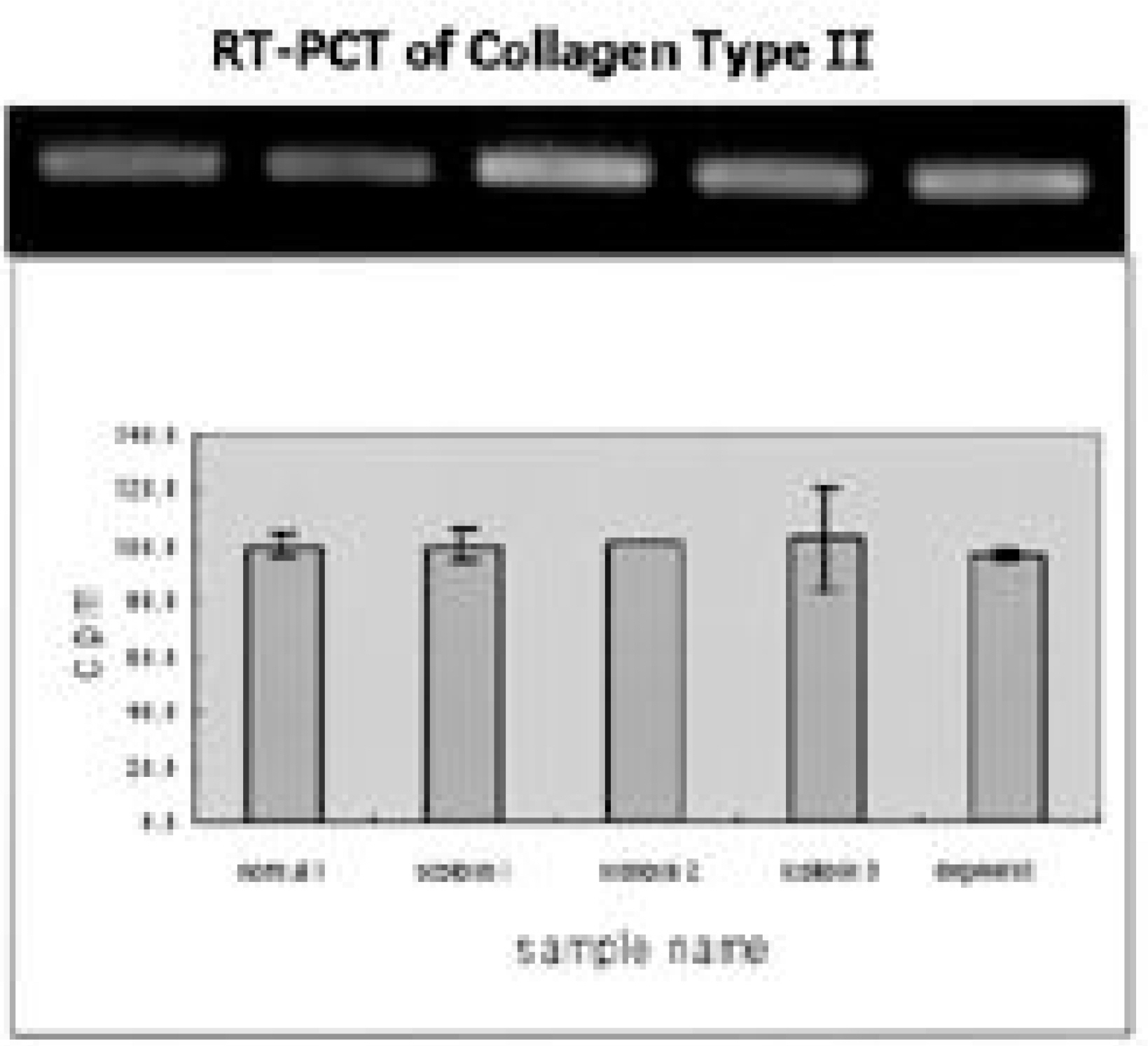
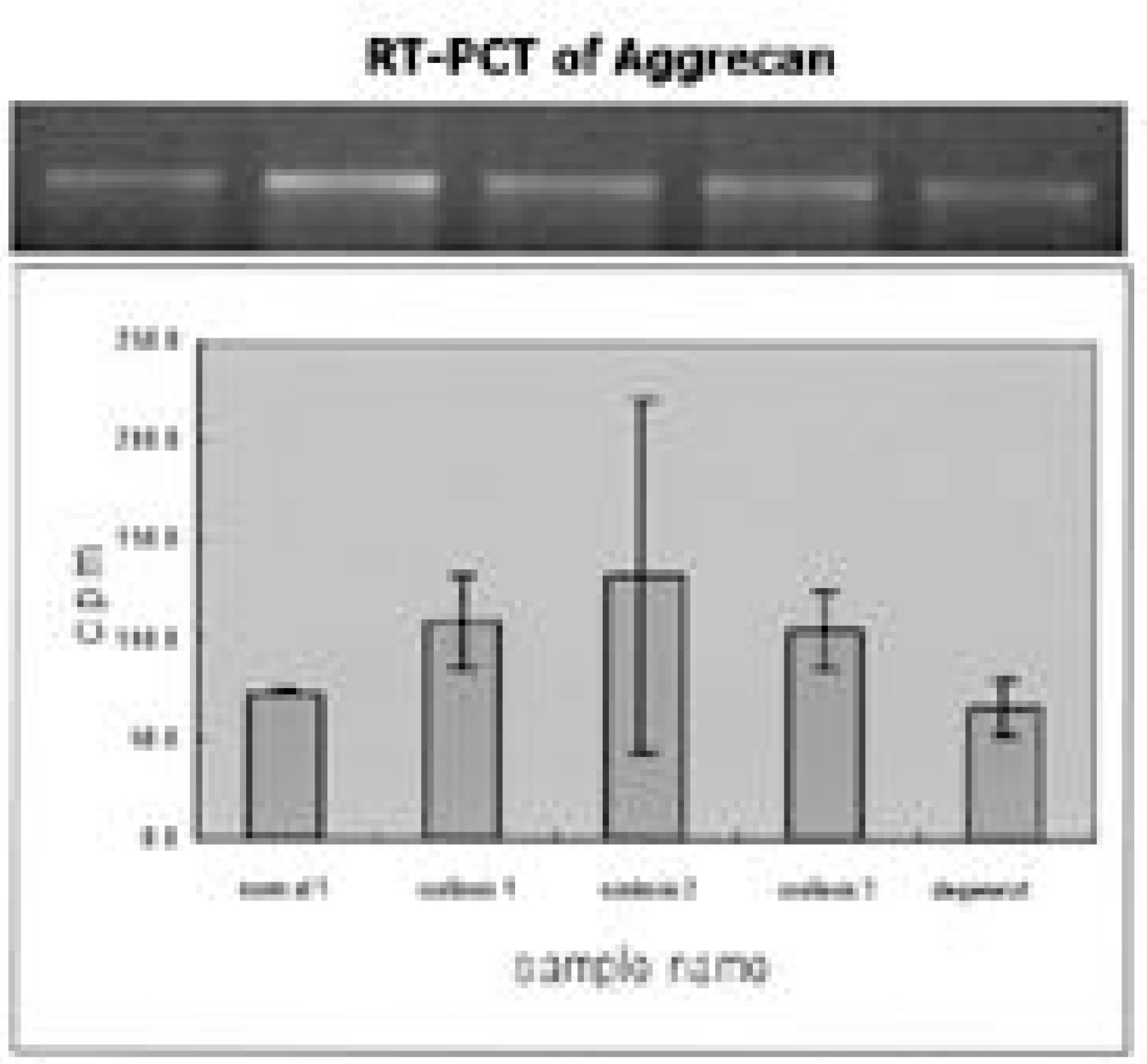
Ten patients, one male and nine female, who underwent thoracoscopic surgery were reviewed. The age range was 13 to 23 years old. Intercostal muscles were taken from the portal site of the major curve (1x1 cm sized). Ten tissues were stained with H/E and ATPase immunohistochemical staining. An appropriate amount of intervertebral disc was taken from the major curve of three scoliotic patients and each concentration of collagen type I, II, GAG gene and proteoglycan synthesis activity was measured. The results were compared with those of grade 0 and grade II degenerative change on each MRI.
RESULTS
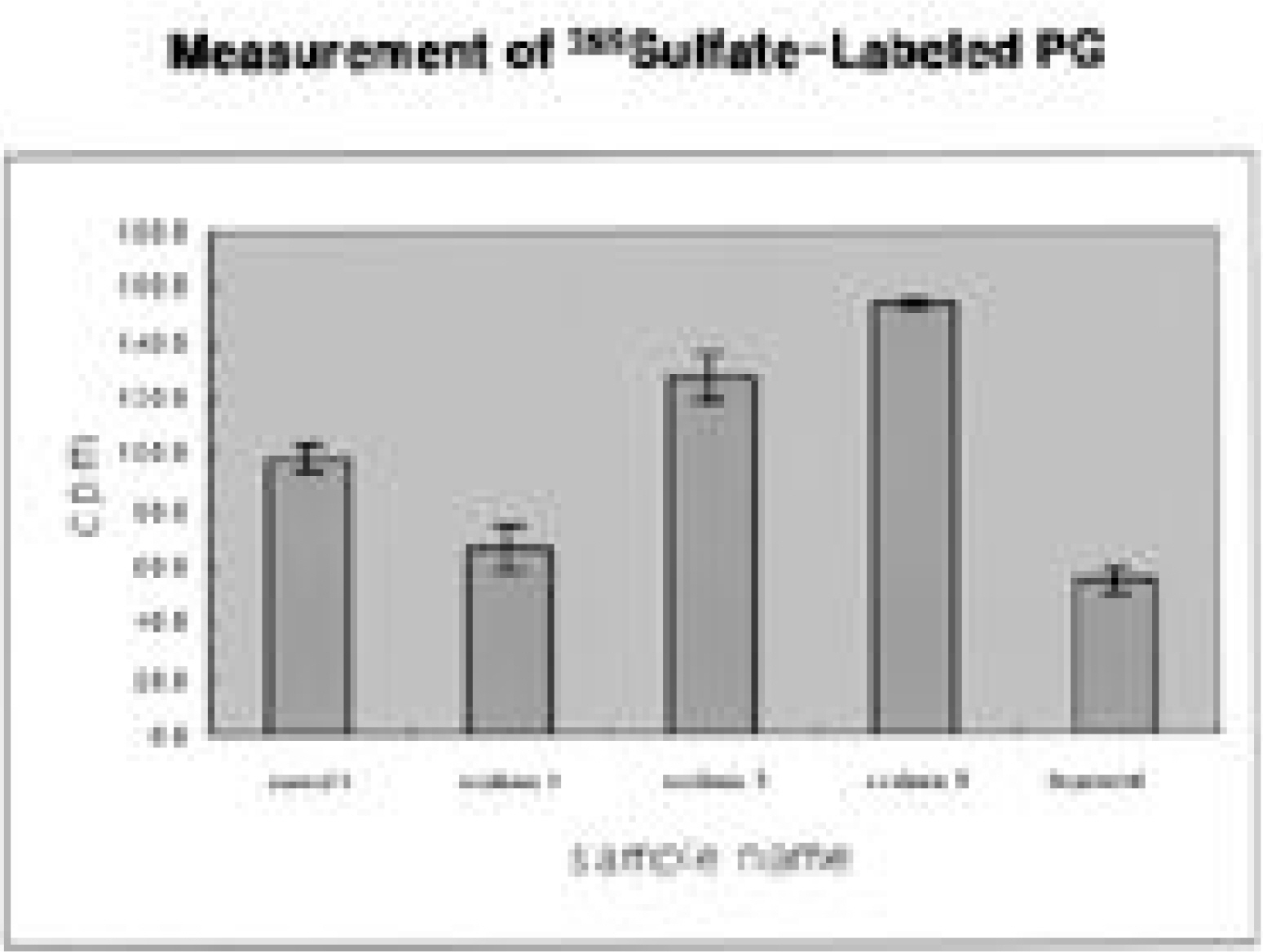
The intercostal muscle of scoliotic patients showed 60.4+/-8.4% in type I muscle fiber and 39.6+/-8.8% in type II-A. These results were not different from those of previous studies. The size of muscle fiber was 48-65 microns, which was slightly smaller than the absolute value, but the difference was not statistically significant. The amount of produced proteoglycans was slightly higher in the intervertebral disc cells of scoliotic patients, the total amount of collagen was significantly lower and there was a difference in the production of type II collagen.
CONCLUSIONS
The intercostal muscles were not affected by the muscle of scoliotic patients and there was no molecular biological significant difference between control and scoliotic patients. We can assume that scoliosis was not caused by problems of intervertebral disc or intercostal muscles.
MeSH Terms
-
Adenosine Triphosphatases
Adolescent*
Collagen
Collagen Type I
Collagen Type II
Female
Genes, gag
Humans
Intercostal Muscles*
Intervertebral Disc*
Korea*
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Male
Molecular Biology
Proteoglycans
Scoliosis*
Thoracoscopy
Young Adult
Adenosine Triphosphatases
Collagen
Collagen Type I
Collagen Type II
Proteoglycans
Figure
Reference
-
1). Bauer L and Goff CW. Orthopaedic extraordinary. Clin orthop. 1950; 8:3–6.2). Nathan PW. The etiology of lateral curvature. Am J Orthop Surg. 1909; 6:379–390.3). Whiteman A. Observation on the corrective and operative treatment of structual scoliosis. Arch Surg. 1922; 5:578–630.4). Cowell HR, Hall JN and MacEwen GD. Genetic aspects of idiopathic scoliosis. Clin Orthop. 1974; 86:121–131.
Article5). Wise CA, Herring JA, Weirich K, Edward L, Lovett M and Bowcock AM. Identification and analysis of candi -date genes for familial idiopathic scoliosis. 37th Scoliosis Research Society. 2002.6). Fidler MW and Jowett RL. Muscle imbalance in the etiology of scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg. 1976; 58-B:200–201.7). Kaplan PE, Sahgal B and Hughes R. Neuropathy in idiopathic scoliosis. Acta Orthop Scand. 1980; 51:263–266.8). Bylund P, Jansson E and Dahlberg E. Muscle fiber types in thoracic erector spine muscles. Fiber types in idiopathic and other forms of scoliosis. Clin Orthop. 1987; 214:222–228.9). Chiu JC. Morphologic studies on the erector spinae muscle in sixty consecutive scoliotic patients. Nippon Sei Ga Zas. 1988; 62:1163–1175.10). Dickson RA. The etiology of spinal deformities. Lancet. 1988; 21:1151–1155.11). Suk SI, Kim YH and Lee CK. Study on contractile pro -teins of muscles and platelets in idiopathic scoliosis patients. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1994; 29:1087–98.12). Pedrini MA, Pedrini VA, Tudisco C, Ponseti IV, Weinstein SL and Maynard JA. Proteoglycans of human scoliotic intervertbral disc. J Bone Joint Surg. 1983; 65-A:815–23.13). Zaleske DJ, Ehrlich MG and Hall JE. Association of glycosaminoglycan depletion and degradative enzyme activity in scoliosis. Clin Orthop. 1980; 148:177–181.
Article14). Bushell GR, Ghosh P, Taylor TK and Sutherland JM. The collagen of the intervertebral disc in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg. 1979; 61-B:501–508.
Article15). Antoniou JA, Arlet V, Goswami T, Aebi M and Alini M. Elevated synthetic activity in the convex side of scoliotic intervertevral discs and endplates compared with normal tissues. Spine. 2001; 26:E198–206.16). Guth L and Samaha FJ. Procedure for the histochemical demonstration of actomysin ATPase. Exp Neurol. 1970; 28:365–367.17). Moon SH, Park MS, Park JO, et al. Matrix synthesis of human intervertebral disc cells according to grade of degeneration: under the basal state and TGF-β1 stimulation. J Korean Spine Society. 2001; 8:107–112.18). Maldonado BA and Oegema TR. Initial charaterization of the metabolism of intervertebral disc cells encapsulated in microsphere. J orthop Res. 1992; 10:677–90.19). Meier MP, Klein MP, Krebs D, Grob D and Muntener M. Fiber transformations in multifidus muscle of young patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 1997; 22:2357–64.
Article20). Johnson MA, Weightman PD and Appleton D. Data on the distribution of fibre types in thirty-six human muscles an tutopsy study. J Neurol Sci. 1973; 18:111–129.21). Duggan DJ, Bittner M, Chen Y, Meltzer P and Trent JM. Expression profiling using cDNA microarrays. Nat Genet(S). 1999; 21:10–14.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study on Contractile Proteins of Muscles and Platelets in Idiopathic Scoliosis Patients
- Etiology of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Literature Review
- Spontaneous Rib Fracture during Boston Brace Treatment for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
- The Classification of Idiopathic Scoliosis
- Medical genomic approach to early-onset scoliosis