J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med.
2014 Dec;18(4):323-331. 10.13104/jksmrm.2014.18.4.323.
Preoperative Evaluation of Lower Rectal Cancer by Pelvic MR with and without Gel Filling
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. pavane@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Radiology, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Gyeonggi-do, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2206929
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/jksmrm.2014.18.4.323
Abstract
- PURPOSE
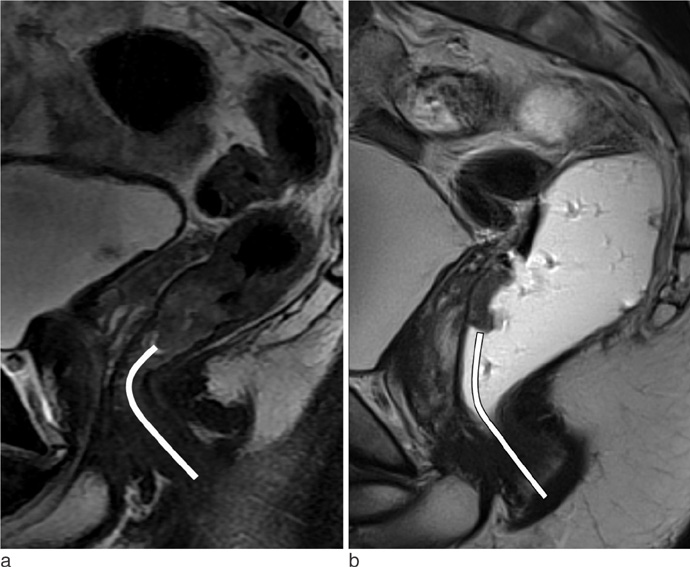
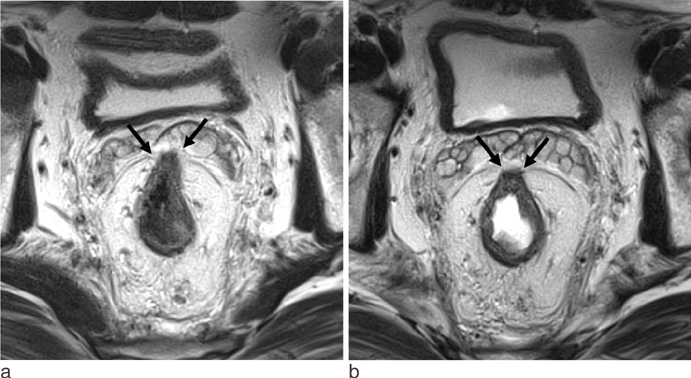
To assess the usefulness of rectal filling using ultrasonographic gel in patients with lower rectal cancer.
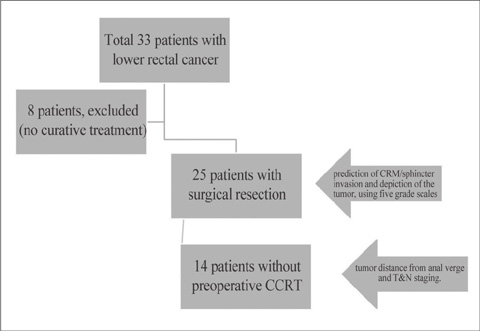
MATERIALS AND METHODS
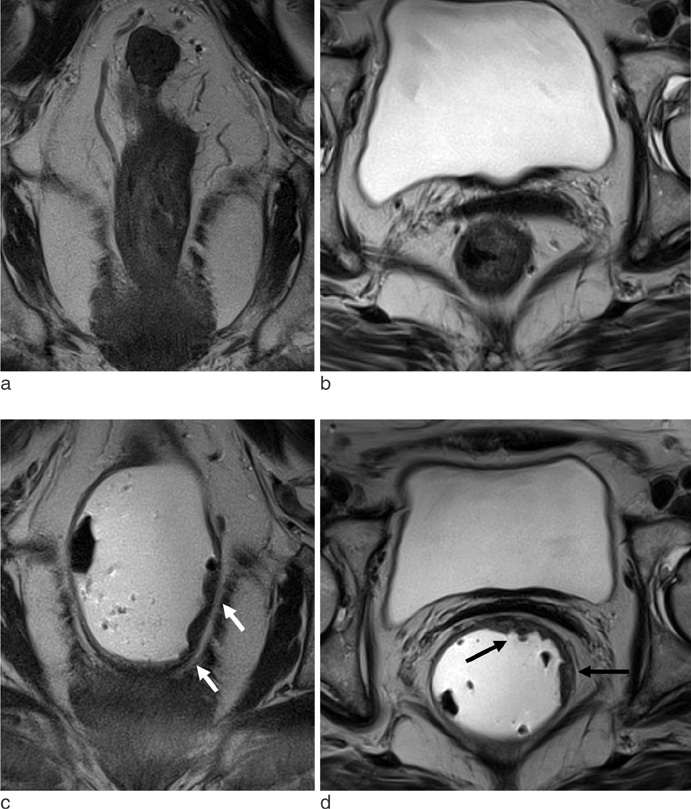
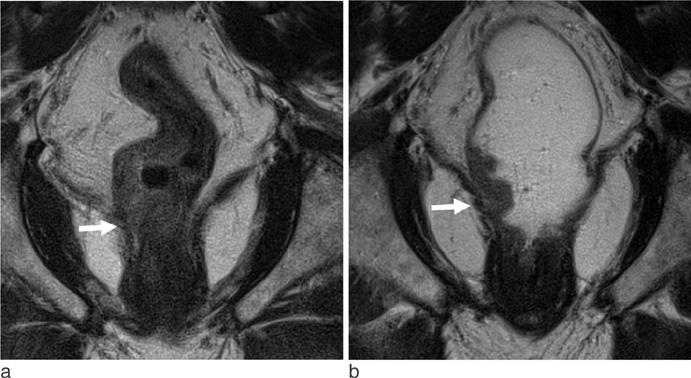
Twenty five patients with lower rectal cancer were enrolled. High resolution pelvic MR was performed twice before and after gel filling. Independently and retrospectively, two radiologists reviewed each set of MR images using five-grade scales for sphincter involvement, CRM (circumferential resection margin) involvement and depiction of the tumor. Same two radiologists retrospectively performed consensus review of each set of MR images for tumor distance from the anal verge and T&N staging.
RESULTS
Tumor depiction scores from MR with gel filling were significantly higher than those of MR without distention (p<0.001). Compared to MR without distension, MR with gel filling had no significant differences in prediction of CRM or sphincter involvement (p>0.05). Distance from the anal verge was significantly different between MR with gel filling and rigid endoscopy (6.8 +/- 1.6 cm vs. 5.8 +/- 1.6 cm, p=0.001). There were no significant differences between pathological staging and MR staging with or without gel filling.
CONCLUSION
MR with gel filling improved tumor depiction. And also MR with gel filling revealed same ability for the predictions of CRM or sphincter invasion in patients with lower rectal cancer, comparing with MR without gel filling.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Leo E, Belli F, Andreola S, et al. Sphincter-saving surgery for low rectal cancer. The experience of the National Cancer Institute, Milano. Surg Oncol. 2004; 13:103–109.2. Holzer B, Urban M, Hölbling N, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging predicts sphincter invasion of low rectal cancer and influences selection of operation. Surgery. 2003; 133:656–661.3. Iafrate F, Laghi A, Paolantonio P, et al. Preoperative staging of rectal cancer with MR imaging: correlation with surgical and histopathologic findings. Radiographics. 2006; 26:701–714.4. Goh JS, Goh JP, Wansaicheong GK. Methylcellulose as a rectal contrast agent for MR imaging of rectal carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002; 178:1145–1146.5. Kim MJ, Lim JS, Oh YT, et al. Preoperative MRI of rectal cancer with and without rectal water filling: an intraindividual comparison. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004; 182:1469–1476.6. Wallengren NO, Holtas S, Andren-Sandberg A, Jonsson E, Kristoffersson DT, McGill S. Rectal carcinoma: double-contrast MR imaging for preoperative staging. Radiology. 2000; 215:108–114.7. Panaccione JL, Ros PR, Torres GM, Burton SS. Rectal barium in pelvic MR imaging: initial results. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1991; 1:605–607.8. Urban M, Rosen HR, Hölbling N, et al. MR imaging for the preoperative planning of sphincter-saving surgery for tumors of the lower third of the rectum: use of intravenous and endorectal contrast materials. Radiology. 2000; 214:503–508.9. Chassang M, Novellas S, Bloch-Marcotte C, et al. Utility of vaginal and rectal contrast medium in MRI for the detection of deep pelvic endometriosis. Eur Radiol. 2010; 20:1003–1010.10. Kikuchi I, Takeuchi H, Kuwatsuru R, et al. Diagnosis of complete cul-de-sac obliteration (CCDSO) by the MRI jelly method. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009; 29:365–370.11. Kim SH, Lee JM, Lee MW, Kim GH, Han JK, Choi BI. Sonography transmission gel as endorectal contrast agent for tumor visualization in rectal cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 191:186–189.12. Arnoletti JP, Bland KI. Neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy for rectal cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2006; 15:147–157.13. Peschaud F, Cuenod CA, Benoist S, et al. Accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging in rectal cancer depends on location of the tumor. Dis Colon Rectum. 2005; 48:1603–1609.14. Slater A, Halligan S, Taylor SA, Marshall M. Distance between the rectal wall and mesorectal fascia measured by MRI: Effect of rectal distension and implications for preoperative prediction of a tumour-free circumferential resection margin. Clin Radiol. 2006; 61:65–70.15. Kuo LJ, Chern MC, Tsou MH, et al. Interpretation of magnetic resonance imaging for locally advanced rectal carcinoma after preoperative chemoradiation therapy. Dis Colon Rectum. 2005; 48:23–28.16. Chen CC, Lee RC, Lin JK, Wang LW, Yang SH. How accurate is magnetic resonance imaging in restaging rectal cancer in patients receiving preoperative combined chemoradiotherapy? Dis Colon Rectum. 2005; 48:722–728.17. Reerink O, Verschueren RC, Szabo BG, Hospers GA, Mulder NH. A favourable pathological stage after neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy in patients with initially irresectable rectal cancer correlates with a favourable prognosis. Eur J Cancer. 2003; 39:192–195.18. Vliegen RF, Beets GL, Lammering G, et al. Mesorectal fascia invasion after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radiation therapy for locally advanced rectal cancer: accuracy of MR imaging for prediction. Radiology. 2008; 246:454–462.19. Beets-Tan RG, Beets GL. Rectal cancer: review with emphasis on MR imaging. Radiology. 2004; 232:335–346.20. Brown G, Richards CJ, Newcombe RG, et al. Rectal carcinoma: thin-section MR imaging for staging in 28 patients. Radiology. 1999; 211:215–222.21. Gagliardi G, Bayar S, Smith R, Salem RR. Preoperative staging of rectal cancer using magnetic resonance imaging with external phase-arrayed coils. Arch Surg. 2002; 137:447–451.22. Blomqvist L, Machado M, Rubio C, et al. Rectal tumor staging: MR imaging using pelvic phasedarray and endorectal coils vs endoscopic ultrasonography. Eur Radiol. 2000; 10:653–660.23. Kim JH, Beets GL, Kim MJ, Kessels AG, Beets-Tan RG. High resolution MR imaging for nodal staging in rectal cancer: are there any criteria in addition to the size? Eur J Radiol. 2004; 52:78–83.24. Brown G, Richards CJ, Bourne MW, et al. Morphologic predictors of lymph node status in rectal cancer with use of highspatial-resolution MR imaging with histopathologic comparison. Radiology. 2003; 227:371–377.25. Piscatelli N, Hyman N, Osler T. Localizing colorectal cancer by colonoscopy. Arch Surg. 2005; 140:932–935.26. Baatrup G, Bolstad M, Mortensen JH. Rigid sigmoidoscopy and MRI are not interchangeable in determining the position of rectal cancers. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2009; 35:1169–1173.27. Choi JY, Kim MJ, Chung YE, et al. Abdominal applications of 3.0-T MR imaging: comparative review versus a 1.5-T system. Radiographics. 2008; 28:e30.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pelvic MRI: Is Endovaginal or Rectal Filling Needed?
- Transrectal ultrasonography of anorectal diseases: advantages and disadvantages
- Clinical Significance of Preoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Staging of Rectal Cancer
- Clinical Implication of Lateral Pelvic Lymph Node Metastasis in Rectal Cancer Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy
- Recent Progress in Diagnosis and Treatment of Rectal Cancer