J Korean Soc Transplant.
2011 Mar;25(1):15-21. 10.4285/jkstn.2011.25.1.15.
Artificial Liver Devices and Bioartificial Liver Systems: Current Status
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sklee3464@skku.edu
- 2Department of Medical Biotechnology, Dongguk University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Biomedical Research Institute, Lifeliver Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea.
- 4Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2202344
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/jkstn.2011.25.1.15
Abstract
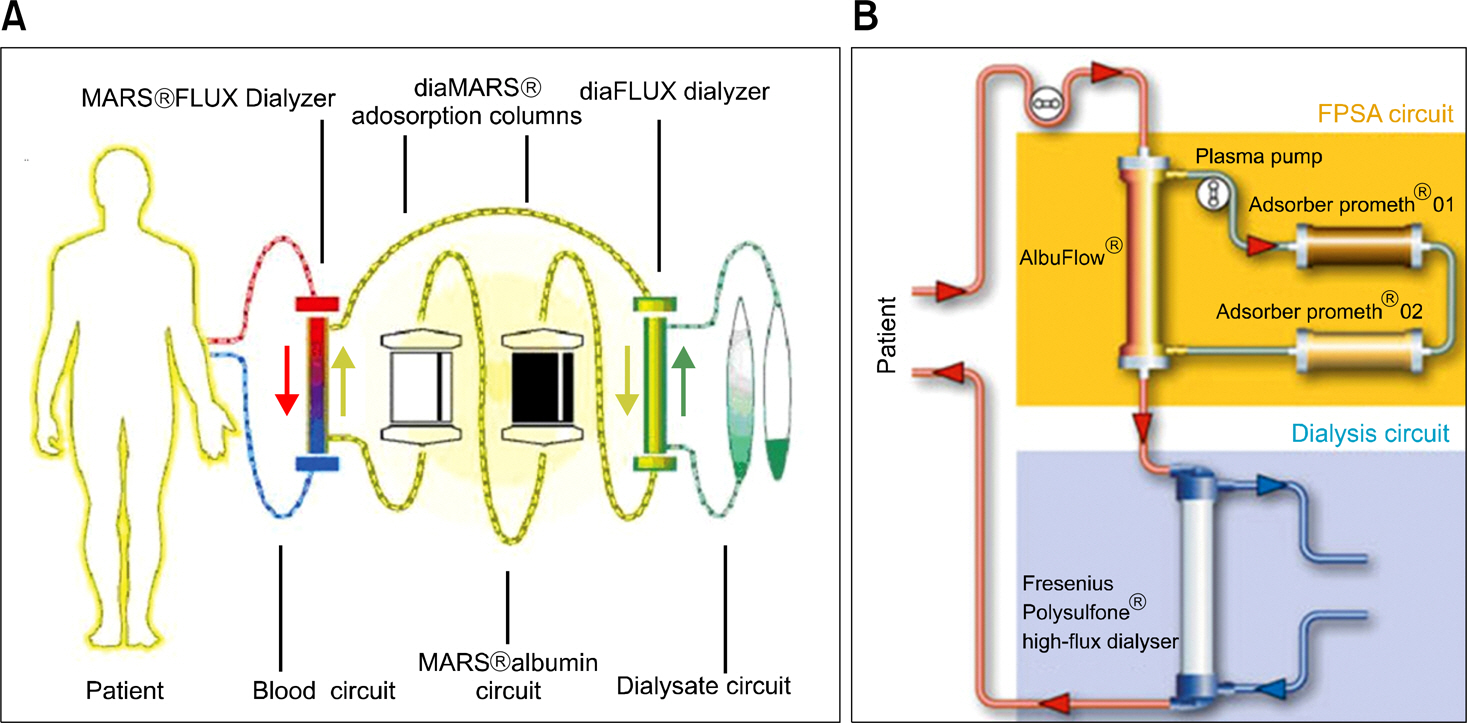
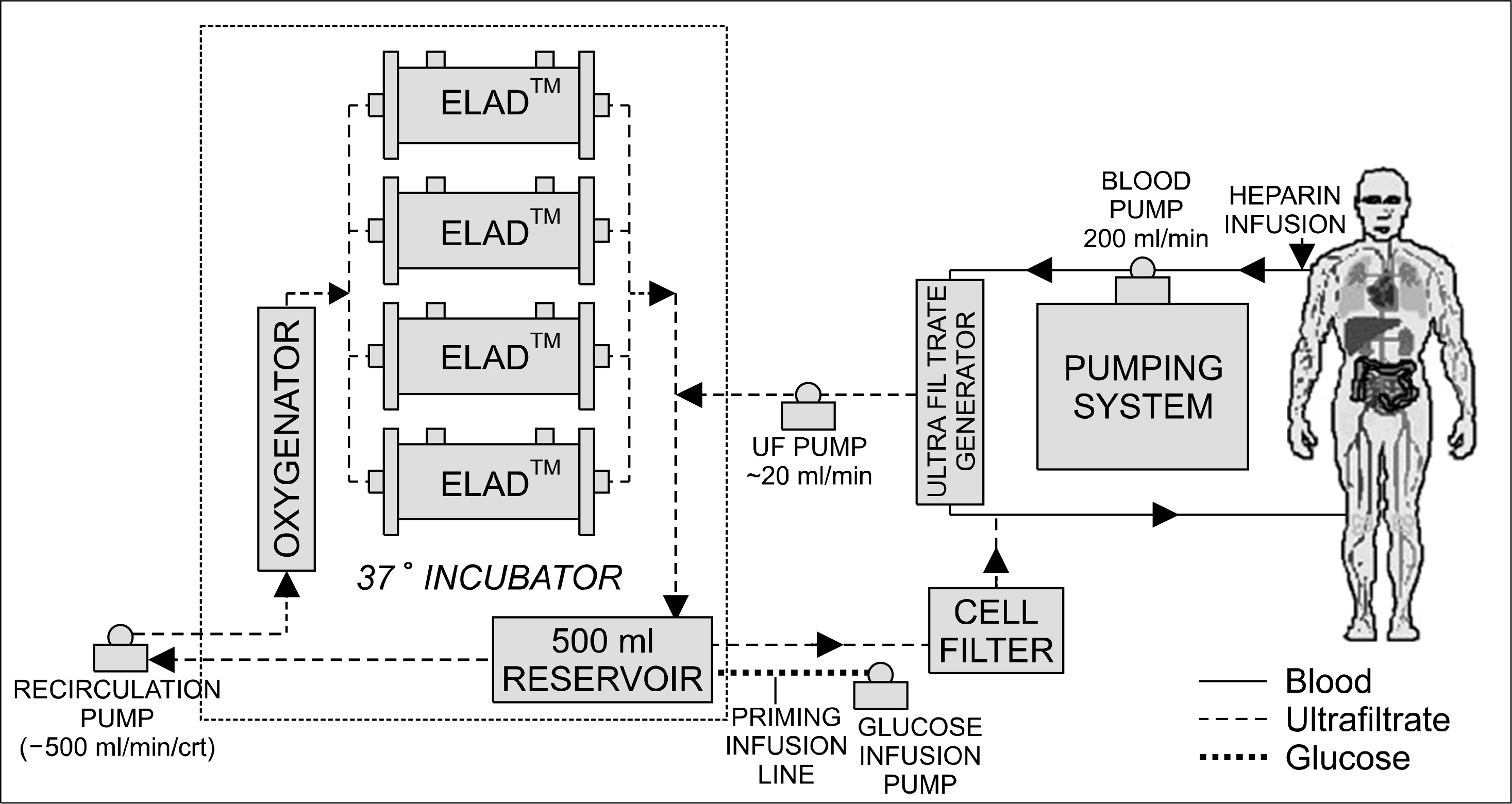
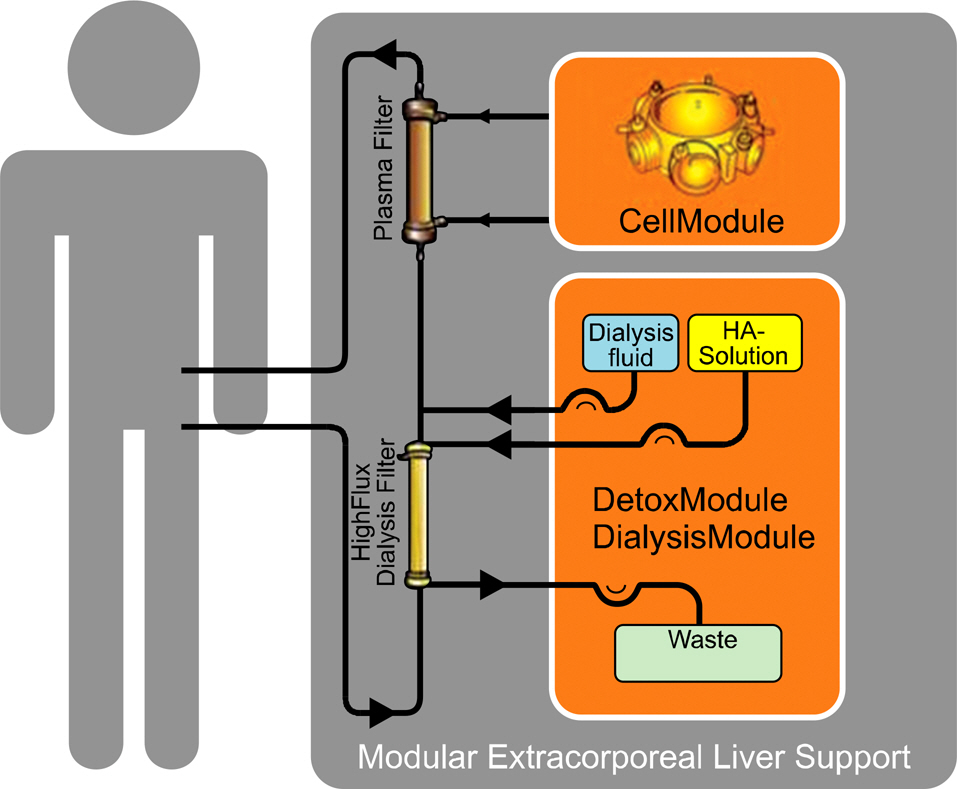
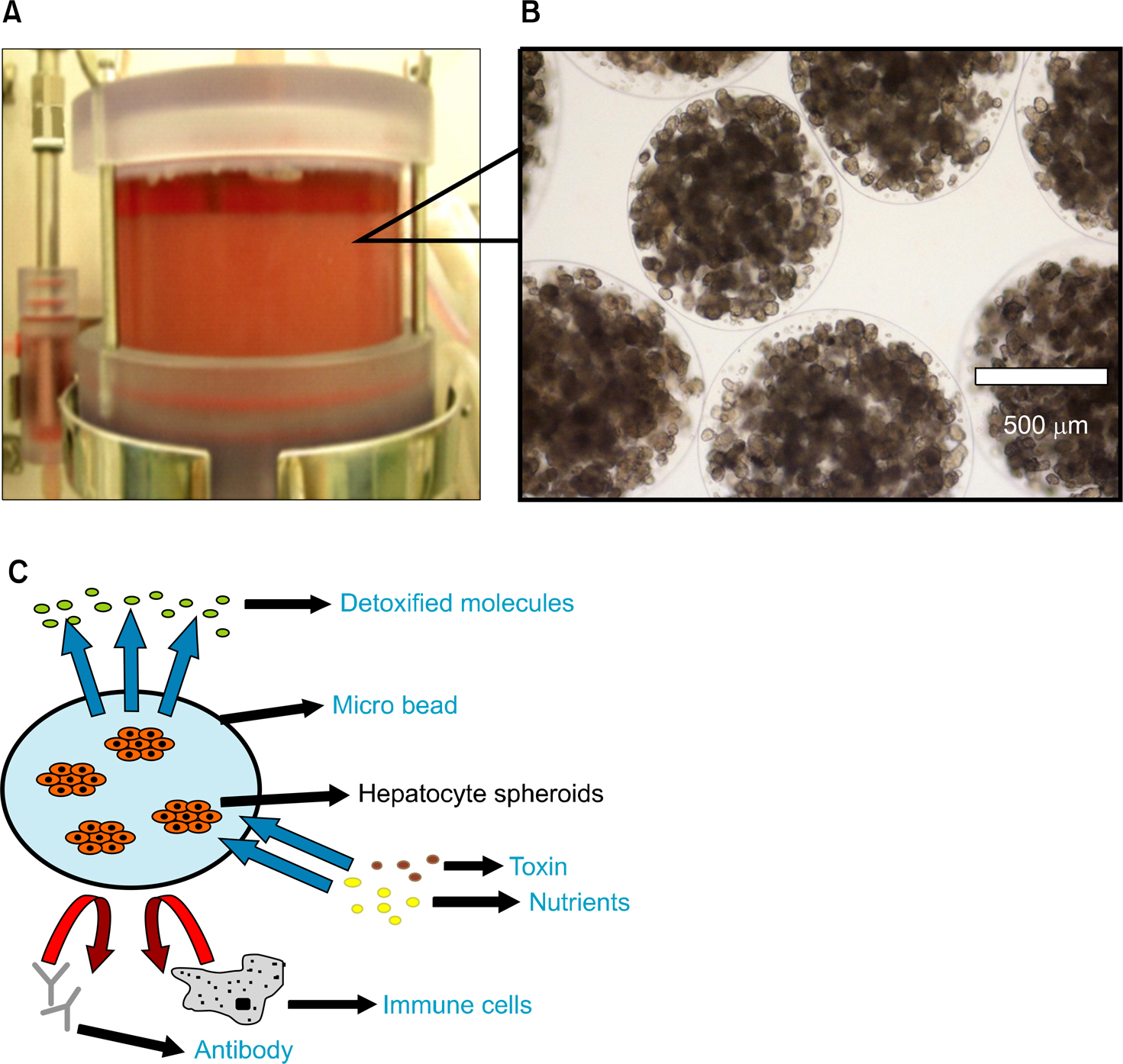
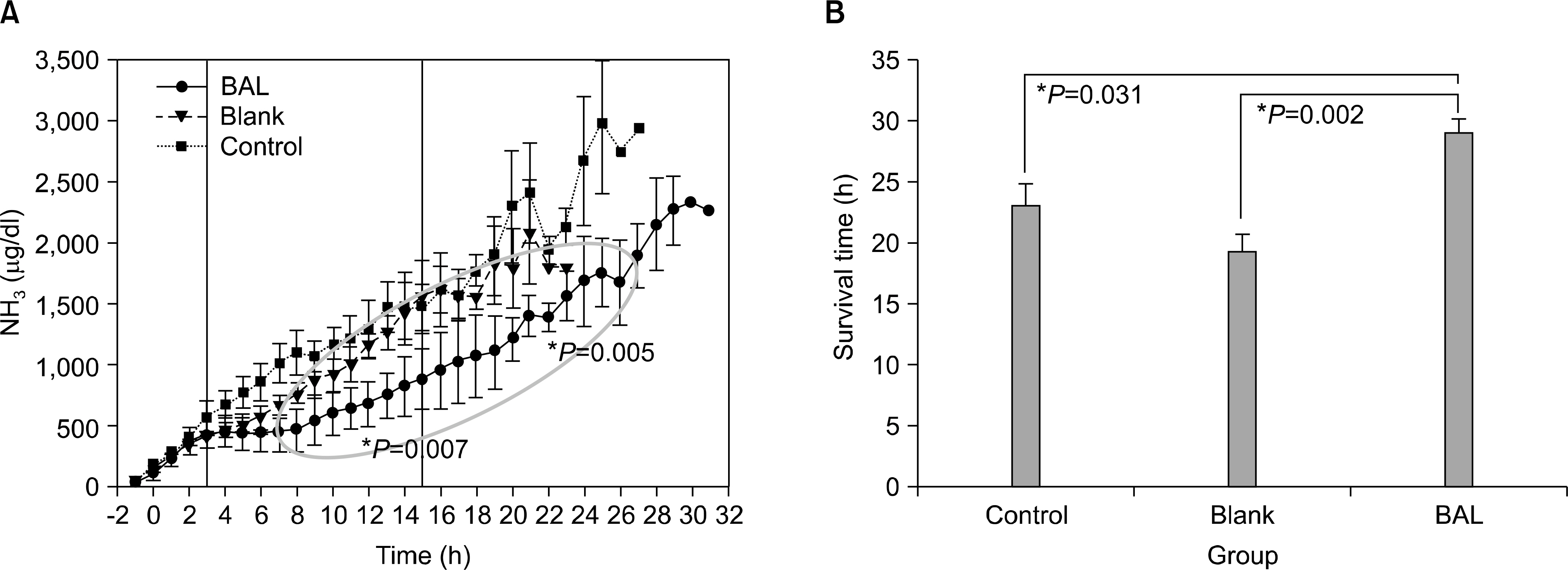
- Acute liver failure is a rapidly progressive disease of the liver associated with high morbidity and mortality without liver transplantation. Although good survival after transplantation can be achieved, due to the disparity between patients awaiting transplantation and available organs, many patients die due to progression of the disease while waiting for a liver graft. To reduce the high morbidity and mortality associated with acute liver failure, attempts have been made during the last several decades to develop a temporary liver support system, such as artificial and bioartificial livers. The artificial liver is a non-biological device mainly aimed at the removal of accumulated toxins during liver failure, and the bioartificial liver is a biological device that has bioreactors containing living hepatocytes which provide both biotransformation and synthetic liver functions. There are currently 3 artificial livers available in the market that have been actively used in the clinical field, and 11 bioartificial livers that have been developed and have undergone clinical trials. In this article, we will discuss about the 3 artificial liver devices and 5 bioartificial liver systems that are the most advanced and have been widely evaluated clinically. Also, the characteristics and the preclinical data of the first bioartificial liver system developed in Korea that is currently under clinical investigation, will be discussed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1). Ash SR, Blake DE, Carr DJ, Carter C, Howard T, Makowka L. Neurologic improvement of patients with hepatic failure and coma during sorbent suspension dialysis. ASAIO Trans. 1991; 37:M332–4.2). Ash SR, Blake DE, Carr DJ, Carter C, Howard T, Makowka L. Clinical effects of a sorbent suspension dialysis system in treatment of hepatic coma (the BioLogic-DT). Int J Artif Organs. 1992; 15:151–61.3). Mitzner SR, Stange J, Klammt S, Risler T, Erley CM, Bader BD, et al. Improvement of hepatorenal syndrome with extracorporeal albumin dialysis MARS: results of a prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Liver Transpl. 2000; 6:277–86.
Article4). Krisper P, Haditsch B, Stauber R, Jung A, Stadlbauer V, Trauner M, et al. In vivo quantification of liver dialysis: comparison of albumin dialysis and fractionated plasma separation. J Hepatol. 2005; 43:451–7.
Article5). Allen JW, Hassanein T, Bhatia SN. Advances in bioartificial liver devices. Hepatology. 2001; 34:447–55.
Article6). Ellis AJ, Hughes RD, Wendon JA, Dunne J, Langley PG, Kelly JH, et al. Pilot-controlled trial of the extracorporeal liver assist device in acute liver failure. Hepatology. 1996; 24:1446–51.
Article7). Millis JM, Cronin DC, Johnson R, Conjeevaram H, Conlin C, Trevino S, et al. Initial experience with the modified extracorporeal liver-assist device for patients with fulminant hepatic failure: system modifications and clinical impact. Transplantation. 2002; 74:1735–46.
Article8). Demetriou AA, Brown RS Jr, Busuttil RW, Fair J, McGuire BM, Rosenthal P, et al. Prospective, randomized, multicenter, controlled trial of a bioartificial liver in treating acute liver failure. Ann Surg. 2004; 239:660–7. discussion 667–70.
Article9). Mazariegos GV, Kramer DJ, Lopez RC, Shakil AO, Rosenbloom AJ, DeVera M, et al. Safety observations in phase I clinical evaluation of the Excorp Medical Bioartificial Liver Support System after the first four patients. ASAIO J. 2001; 47:471–5.
Article10). Sauer IM, Kardassis D, Zeillinger K, Pascher A, Gruenwald A, Pless G, et al. Clinical extracorporeal hybrid liver support-phase I study with primary porcine liver cells. Xenotransplantation. 2003; 10:460–9.11). Sauer IM, Zeilinger K, Pless G, Kardassis D, Theruvath T, Pascher A, et al. Extracorporeal liver support based on primary human liver cells and albumin dialysis-treatment of a patient with primary graft non-function. J Hepatol. 2003; 39:649–53.12). Poyck PP, van Wijk AC, van der Hoeven TV, de Waart DR, Chamuleau RA, van Gulik TM, et al. Evaluation of a new immortalized human fetal liver cell line (cBAL111) for application in bioartificial liver. J Hepatol. 2008; 48:266–75.
Article13). van de Kerkhove MP, Hoekstra R, Chamuleau RA, van Gulik TM. Clinical application of bioartificial liver support systems. Ann Surg. 2004; 240:216–30.
Article14). Park JK, Lee SK, et al. Bioartificial Liver. Meyer U, Meyer T, editors. Fundamentals of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. 1st ed.Berlin: Springer-Verlag;2009. p. 397–408.
Article15). Millis JM, Cronin DC, Conjeevaram HS, Faust TW, Trevino S, Conlin C, et al. Improvement of hemodya-namic parameters in fulminant hepatic failure patients with extracorporeal liver assist device (ELAD) treatment. Hepatology. 2000; 32:613a–a.16). Sgroi A, Serre-Beinier V, Morel P, Bühler L. What clinical alternatives to whole liver transplantation? Current status of artificial devices and hepatocyte transplantation. Transplantation. 2009; 87:457–66.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hybrid Bioartificial Liver
- Cell Sources, Liver Support Systems and Liver Tissue Engineering: Alternatives to Liver Transplantation
- Artificial Liver Assist Devices
- Nonsurgical Management of Fulmninant Hepatic Failure: Hepatocyte transplantation and bioartificial liver
- Rat-Hepatocyte Culture and Differentiation in Hormone-Supplemented Media