J Lung Cancer.
2006 Dec;5(2):89-91. 10.6058/jlc.2006.5.2.89.
On-line Setup for Lung Cancer Patient in Stereotactic Radiation Surgery using CBCT
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Asan Medical Center, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Seoul, Korea. sdahn@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2200167
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6058/jlc.2006.5.2.89
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: On-line setup procedure was performed before treatment for lung cancer patient for stereotactic radiation surgery (SRS) using recently introduced Cone Beam CT.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
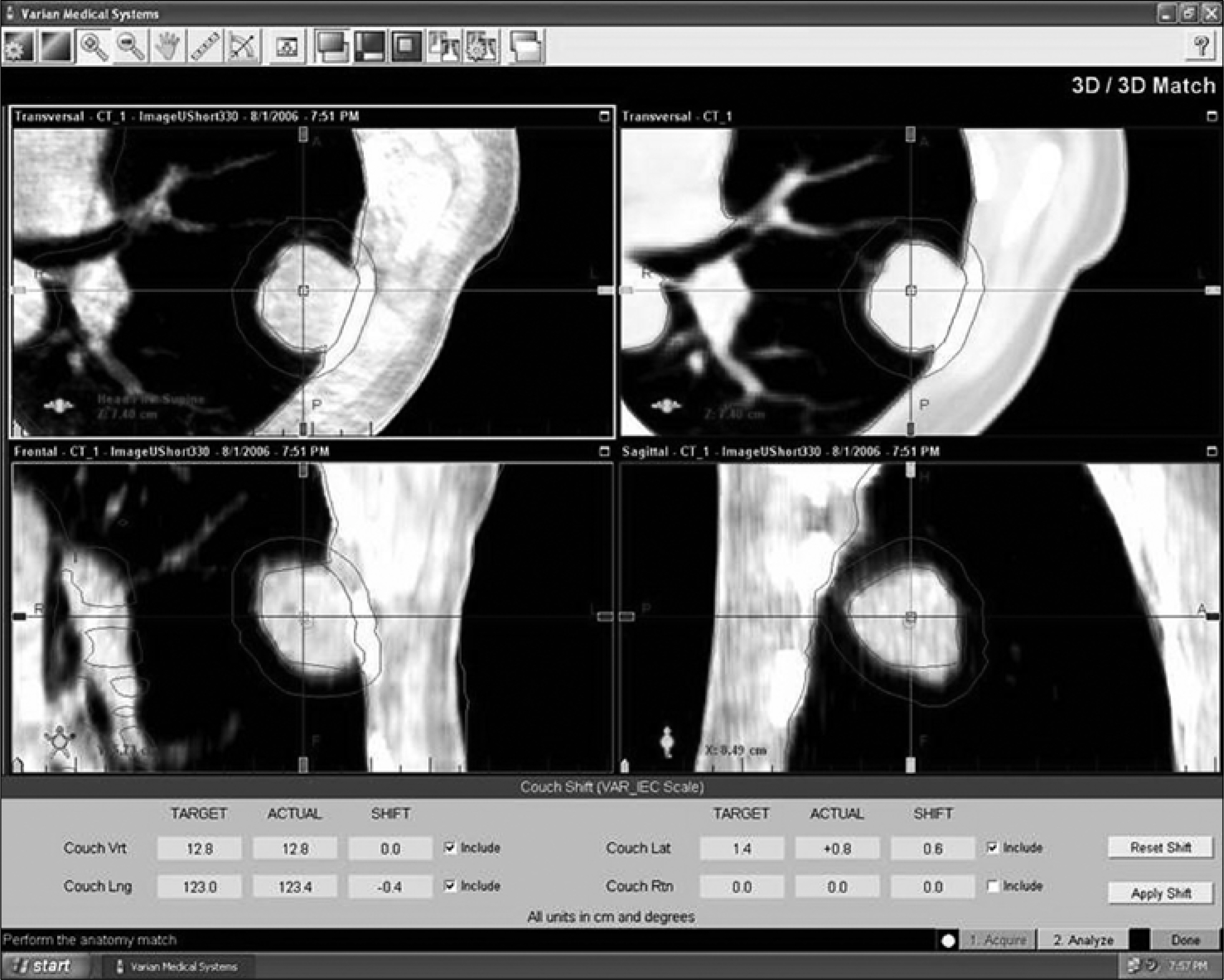
Cone Beam CT was performed for 10 patients who did SRS during 18 July and 1 September, 2006 using On Board Imager (OPB) system made by Varian, USA. The treatment position of patient was corrected comparing Images obtaining from CBCT and used in treatment planning.
RESULTS
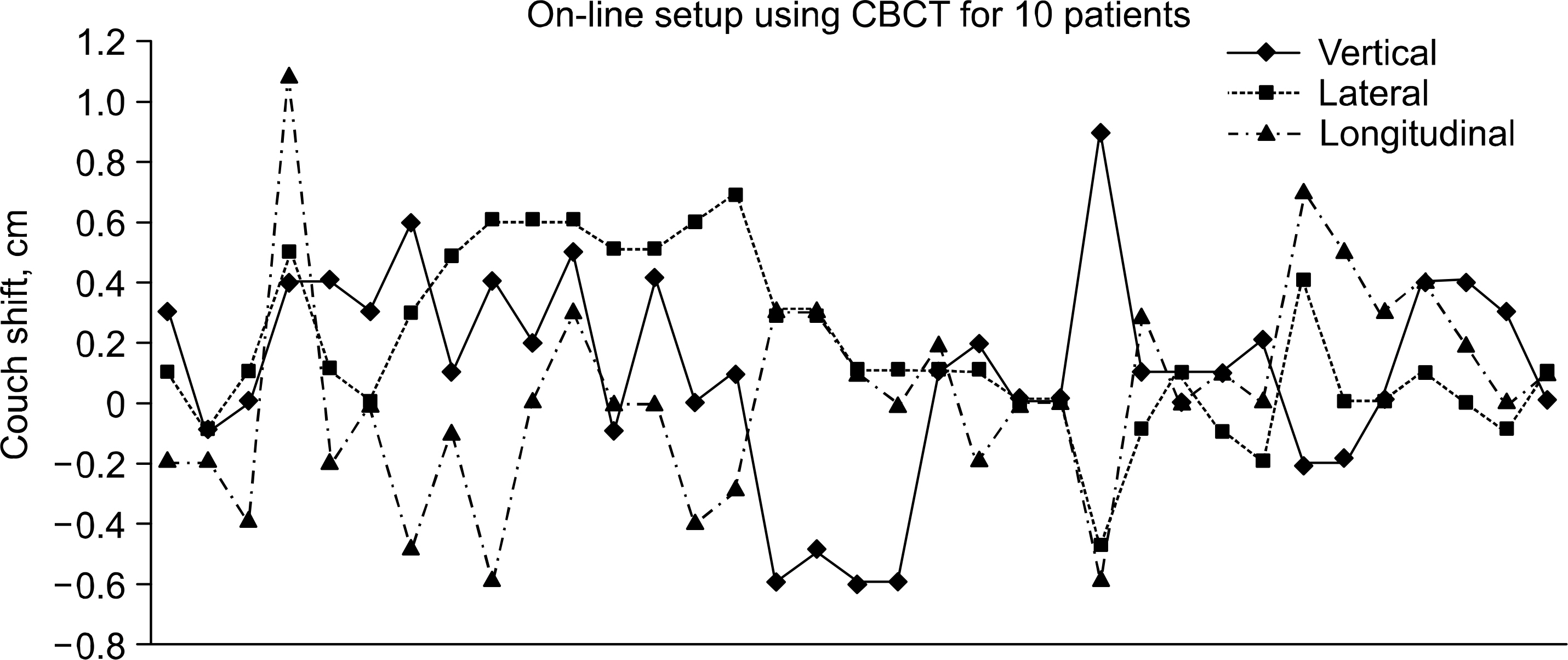
Comparing the CBCT images and CT images used in treatment planning, the movement of the couch is 2.3+/-2.3 mm, 1.8+/-2.8 mm, 0.3+/-3.5 mm for vertical, lateral, and longitudinal direction. It took about 1 hr for conventional treatment procedure in image acquisition of CT before treatment and image registration. But it took about 4~7 minute in on-line setup using CBCT (1~2 min for image acquisition using CBCT, 2~3 min for CT reconstruction of 2.5 mm slice thickness, 1~2 min for on-line setup using image registration). CONCLUTION: The accurate treatment could be performed after tumor localization for SRS using CBCT images. And the consumed time for tumor localization was reduced significantly.
Figure
Reference
-
1.Nyman J., Johansson KA., Hulten U. Stereotactic hypofractionated radiotherapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer-mature results for medically inoperable patients. Lung Cancer. 2006. 51:97–103.
Article2.Lee SW., Choi EK: Park HJ, et al. Stereotactic body frame based fractionated radiosurgery on consecutive days for primary or metastatic tumors in the lung. Lung Cancer. 2003. 40:309–315. ,.
Article3.Choi WS: Song SY., Kim JH, et al. Clinical results of stereotactic body frame based radiation therapy for primary or metastatic tumors in the lung. The 24th Annual Meeting of the Korean Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology 2006,.4.Song SY., Park SH., Shin SS, et al. Image-guided radiation therapy for stereotactic radiosurgery in lung tumor. The 24th Annual Meeting of the Korean Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology. 2006.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Early Stage Lung Cancer
- A Study on the Availability of the On-Board Imager (OBI) and Cone-Beam CT (CBCT) in the Verification of Patient Set-up
- Quantitative Evaluation of Patient Positioning Error Using CBCT 3D Gamma Density Analysis in Radiotherapy
- Evaluation of Set-up Accuracy for Frame-based and Frameless Lung Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
- Role of Radiation Therapy for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Focused on Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy in Stage I