Prog Med Phys.
2015 Dec;26(4):286-293. 10.14316/pmp.2015.26.4.286.
Evaluation of Set-up Accuracy for Frame-based and Frameless Lung Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cho.byungchul@gmail.com
- KMID: 2151764
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2015.26.4.286
Abstract
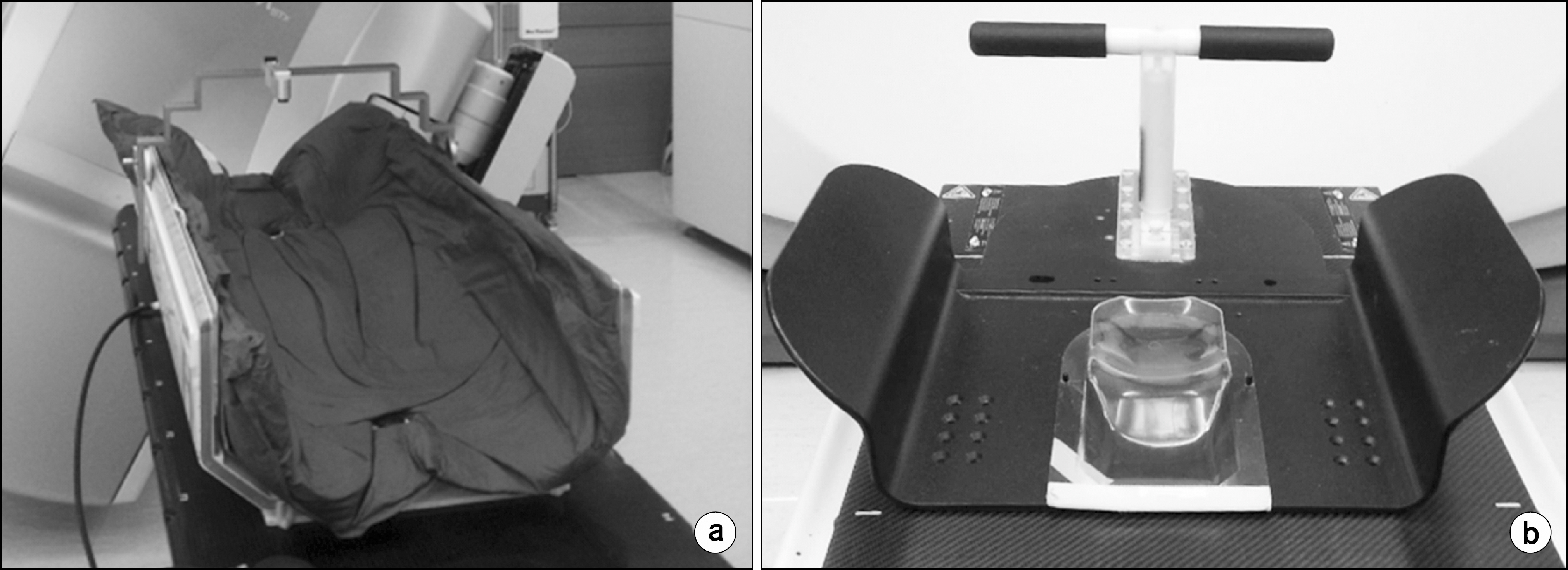
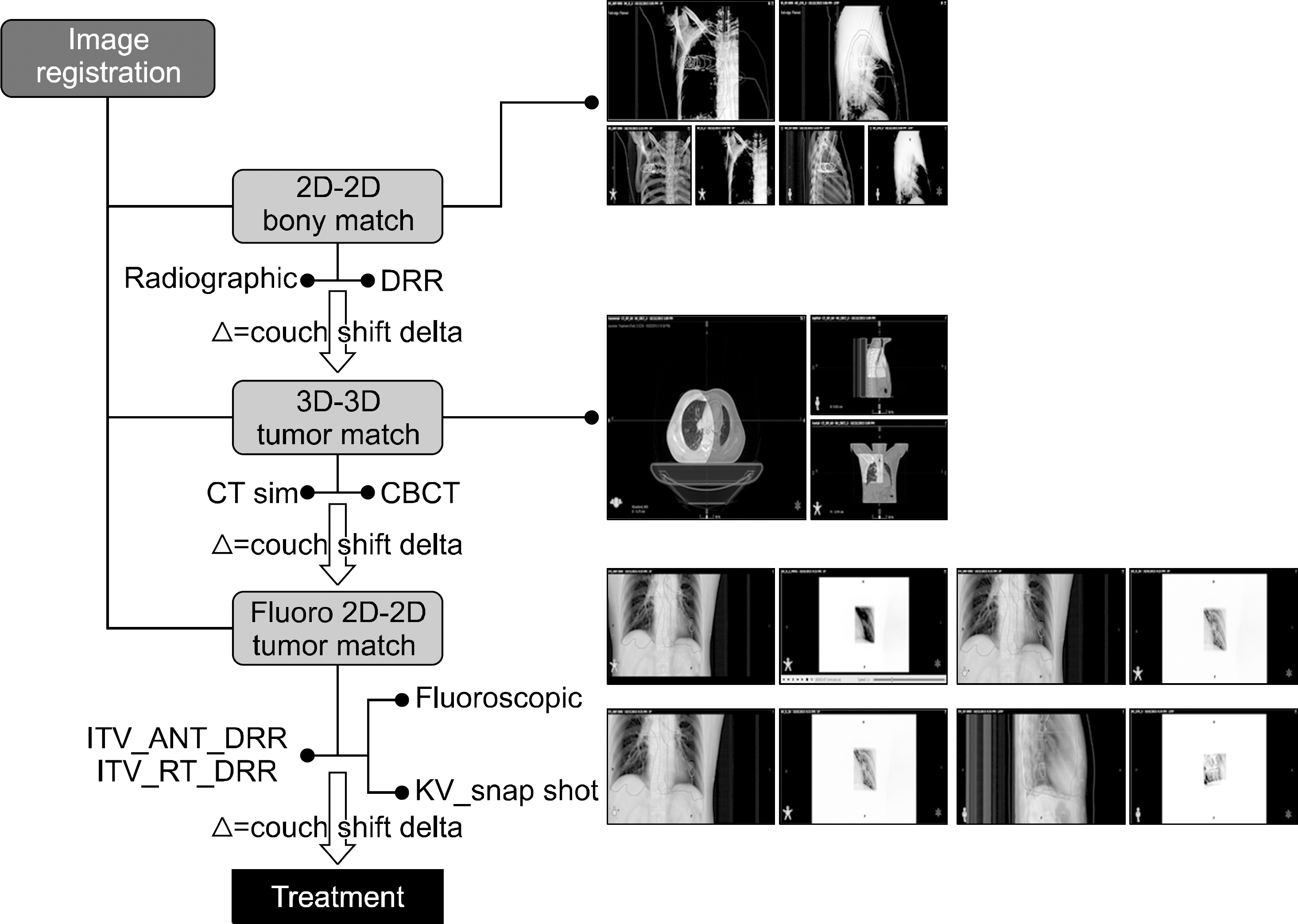
- The purpose of this study was to evaluate the set up accuracy using stereotactic body frame and frameless immobilizer for lung stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). For total 40 lung cancer patients treated by SBRT, 20 patients using stereotactic body frame and other 20 patients using frameless immobilizer were separately enrolled in each group. The setup errors of each group depending on the immobilization methods were compared and analyzed. All patients received the dose of 48~60 Gy for 4 or 5 fractions. Before each treatment, a patient was first localized to the treatment isocenter using room lasers, and further aligned with a series of image guidance procedures; orthogonal kV radiographs, cone-beam CT, orthogonal fluoroscopy. The couch shifts during these procedures were recorded and analyzed for systematic and random errors of each group. Student t-test was performed to evaluate significant difference depending on the immobilization methods. The setup reproducibility was further analyzed using F-test with the random errors excluding the systematic setup errors. In addition, the ITV-PTV margin for each group was calculated. The setup errors for SBF were 0.05+/-0.25 cm in vertical direction, 0.20+/-0.38 cm in longitudinal direction, and 0.02+/-0.30 cm in lateral direction, respectively. However the setup errors for frameless immobilizer showed a significant increase of -0.24+/-0.25 cm in vertical direction while similar results of 0.06+/-0.34 cm, -0.02+/-0.25 cm in longitudinal and lateral directions. ITV-PTV margins for SBF were 0.67 cm (vertical), 0.99 cm (longitudinal), and 0.83 cm (lateral), respectively. On the other hand, ITV-PTV margins for Frameless immobilizer were 0.75 cm (vertical), 0.96 cm (longitudinal), and 0.72 cm (lateral), indicating less than 1 mm difference for all directions. In conclusion, stereotactic body frame improves reproducibility of patient setup, resulted in 0.1~0.2 cm in both vertical and longitudinal directions. However the improvements are not substantial in clinic considering the effort and time consumption required for SBF setup.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Verification of Secondary Electron Generated by Head Screw in Gamma Knife Using Monte Carlo N-Particle Simulation
Heesoo Kim, Jeong-Woo Lee
Prog Med Phys. 2020;31(2):29-34. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2020.31.2.29.
Reference
-
References
1. Timmerman R, Paulus R, Galvin J, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA. 303:1070–6. 2010.
Article2. Iyengar P, Timmerman RD. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer: rationale and outcomes. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 10:1514–20. 2012.
Article3. F Zimmermann, Wulf J., Lax I., et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for early non-small cell lung cancer. Front Radiat Ther Oncol. 42:94–114. 2010.4. Barney BM, Lee RJ, Handrahan D, et al. Image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) for prostate cancer comparing kV imaging of fiducial markers with cone beam computed tomography (CBCT). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 80:301–5. 2011.
Article5. Moseley DJ, White EA, Wiltshire KL, et al. Comparison of localization performance with implanted fiducial markers and cone-beam computed tomography for online imageguided radiotherapy of the prostate. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 67:942–53. 2007.
Article6. Li W, Purdie TG, Taremi M, et al. Effect of immobilization and performance status on intrafraction motion for stereotactic lung radiotherapy: analysis of 133 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 81:1568–75. 2011.
Article7. Foster R, Meyer J, Iyengar P, et al. Localization accuracy and immobilization effectiveness of a stereotactic body frame for a variety of treatment sites. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2087:911–6. 2013.
Article8. Han Z, Bondeson JC, Lewis JH, et al. Evaluation of initial setup accuracy and intrafraction motion for spine stereotactic body radiation therapy using stereotactic body frames. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2015. 15:S1879–8500. 2015.9. Peguret N, Dahele M, Cuijpers JP, et al. Frameless high dose rate stereotactic lung radiotherapy: intrafraction tumor po sition and delivery time. Radiother Oncol. 107:419–22. 2013.10. Josipovic M1. Persson GF, Logadottir A, et al. Translational and rotational intra-and interfractional errors in patient and target position during a short course of frameless stereotactic body radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. 51:610–7. 2012.11. Murray B, Forster K, Timmerman R. Frame-based immobilization and targeting for stereotactic body radiation therapy. Med Dosim. 32:86–91. 2007.
Article12. Sonke JJ, Rossi M, Wolthaus J, et al. Frameless stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung cancer using four-dimensional cone beam CT guidance. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 74:567–74. 2009.
Article13. Wulf J, Hädinger U, Oppitz U, et al. Stereotactic radiotherapy of extracranial targets: CT-simulation and accuracy of treatment in the stereotactic body frame. Radiother Oncol. 2000 Nov. 57(2):225–36.14. Han K, Cheung P, Basran PS, et al. A comparison of two immobilization systems for stereotactic body radiation therapy of lung tumors. Radiother Oncol. 95:103–8. 2010.
Article15. Hansen AT, Petersen JB, H⊘yer M. Internal movement, setup accuracy and margins for stereotactic body radiotherapy using a stereotactic body frame. Acta Oncol. 45:948–52. 2006.
Article16. Shah C, Grills IS, Kestin LL, et al. Intrafraction variation of mean tumor position during imageguided hypofractionated stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 82:1636–41. 2012.
Article17. Guckenberger M, Meyer J, Wilbert J, et al. Intra-fractional uncertainties in cone-beam CT based imageguided radiotherapy (IGRT) of pulmonary tumors. Radiother Oncol. 83:57–64. 2007.
Article18. van Herk M. Errors and margins in radiotherapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 14:52–64. 2004.19. van Herk M, Remeijer P, Rasch C, et al. The probability of correct target dosage: dose-population histograms for deriving treatment margins in radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 47:1121–35. 2000.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Frameless stereotactic brain biopsy: technical considerations and clinical results regarding safety and efficacy
- How to use neuronavigation for the brain
- Fractionated Stereotactic Radiation Therapy Using Linear Accolerator in Brain Tumor and Arteriovenous Malformation
- Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Early Stage Lung Cancer
- An Analysis of Intra-Fractional Movement during Image-Guided Frameless Radiosurgery for Brain Tumor Using CyberKnife