J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2009 Apr;47(2):148-155. 10.4047/jkap.2009.47.2.148.
A comparison of the fidelity of various zirconia-based all-ceramic crowns fabricated with CAD/CAM systems
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Korea. kblee@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2195610
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2009.47.2.148
Abstract
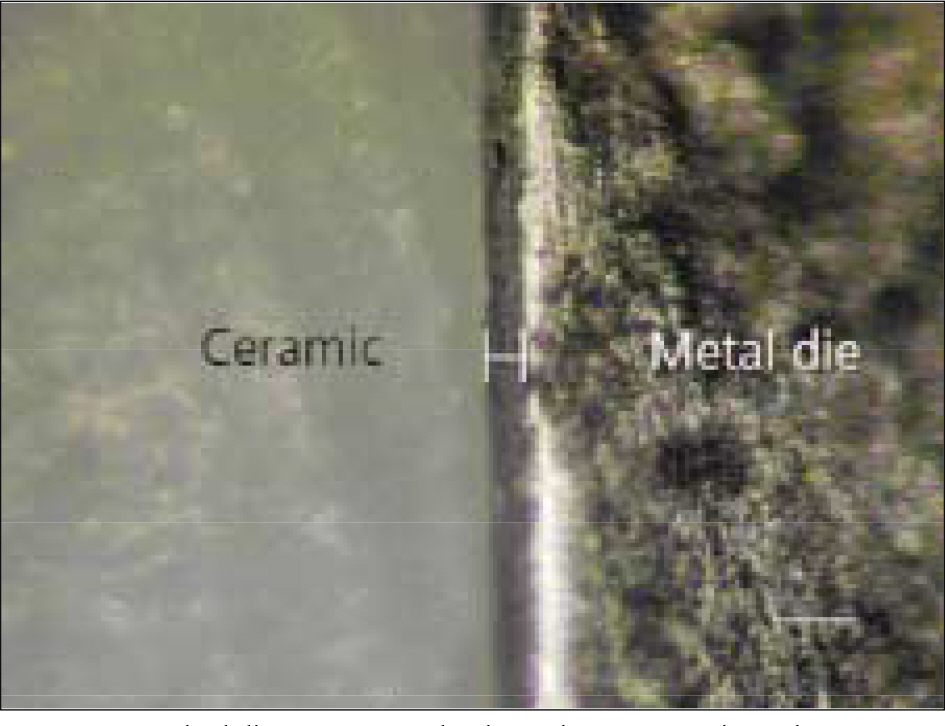
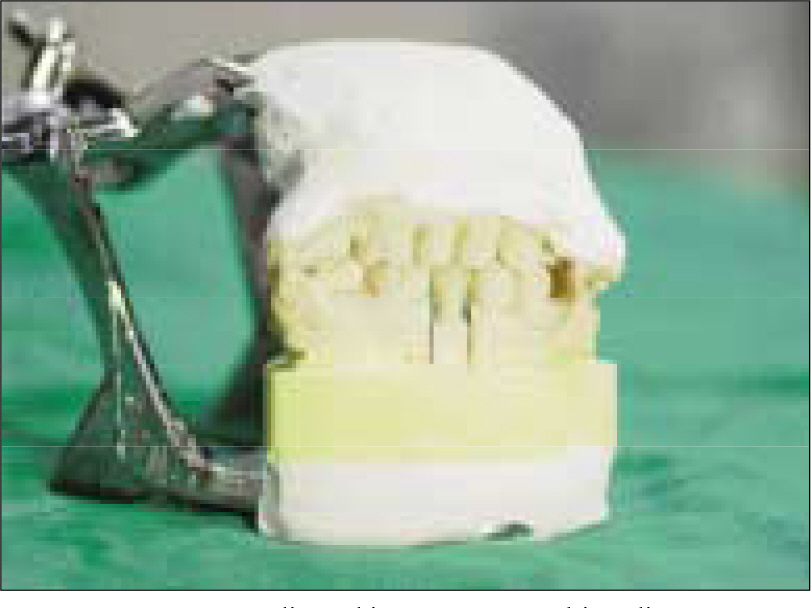
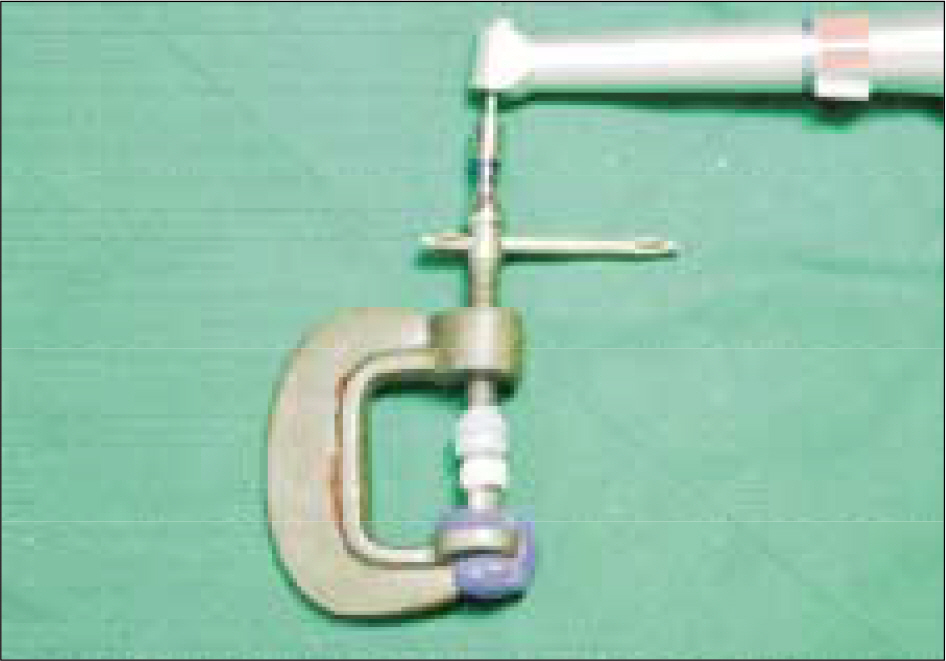
- STATEMENT OF PROBLEM: The interest in all-ceramic restorations has increased as more techniques have become available. With the introduction of machinable dental ceramics and CAD/CAM systems there is a need to evaluate the quality levels of these new fabrication techniques. PURPOSE: This study is to evaluate the crown fidelity (absolute marginal discrepancy and internal gap) of various zirconia-based all-ceramic crowns fabricated with different CAD/CAM (computer-assisted design/computer-assisted manufacturing) systems and conventional cast metal-ceramic crowns. MATERIAL AND METHODS: A resin tooth of lower right second premolar was prepared. After an impression was taken, one metal master die was made. Then 40 impressions of metal master dies were taken for working dies. 10 crowns per each system were fabricated using 40 working dies. Metal-ceramic crowns were cast by using the conventional method, and Procera, Lava, and Cerec inLab crowns were fabricated with their own CAD/CAM manufactruing procedures. The vertical marginal discrepancies and internal gaps of each crown groups were measured on a metal master die without a luting agent. The results were statistically analyzed using the one-way ANOVA and Tukey's HSD test. RESULTS: 1. Vertical marginal discrepancies were 50.6 +/- 13.9 micrometer for metal-ceramic crowns, 62.3 +/- 15.7 micrometer for Procera crowns, 45.3 +/- 7.9 micrometer for Lava crowns, and 71.2 +/- 2.0 micrometer for Cerec inLab crowns. 2. The Internal gaps were 52.6 +/- 10.1 micrometer for metal-ceramic crowns, 161.7 +/- 18.5 micrometer for Procera crowns, 63.0 +/- 10.2 micrometer for Lava crowns, and 73.7 +/- 10.7 micrometer for Cerec inLab crowns. CONCLUSION: 1. The vertical marginal discrepancies of, 4 crown groups were all within the clinically acceptable range (120 micrometer). 2. The internal gaps of LAVA, Cerec inlab, and metal-ceramic crowns were within clinically acceptable range except Procera crown (140 micrometer).
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
In vitro evaluation of the wear resistance of provisional resin materials fabricated by different methods
Jong-Ju Ahn, Jung-Bo Huh, Jae-Won Choi
J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2019;57(2):110-117. doi: 10.4047/jkap.2019.57.2.110.
Reference
-
1.Kim HS., Ju TH., Oh SC., Dong JK. A Study of the Fracture Strength of the IPS-Empress Ceramic Crown according to margin Type. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 1997. 35:296–307.2.Koo JY., Lim JH., Cho IH. Marginal Fidelities according to the Margin Types of All Ceramic Crowns. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 1997. 35:445–57.3.Seghi RR., Sorensen JA. Relative flexural strength of six new ceramic materials. Int J Prosthodont. 1995. 8:239–46.4.Tinschert J., Natt G., Mautsch W., Spickermann H., Anusavice KJ. Marginal fit of alumina-and zirconia-based fixed partial dentures produced by a CAD/CAM system. Oper Dent. 2001. 26:367–74.5.Duret F., Blouin JL., Duret B. CAD-CAM in dentistry. J Am Dent Assoc. 1988. 117:715–20.
Article6.Sturdevant JR., Bayne SC., Heymann HO. Margin gap size of ceramic inlays using second-generation CAD/CAM equipment. J Esthet Dent. 1999. 11:206–14.
Article7.Besimo C., Jeger C., Guggenheim R. Marginal adaptation of titanium frameworks produced by CAD/CAM technique. Int J Prosthodont. 1997. 10:541–6.8.Rekow ED. High-technology innovations and limitations for restorative dentistry. Dent Clin North Am. 1993. 37:513–24.9.Mormann WH., Schug J. Grinding precision and accuracy of fit of Cerec2 CAD-CAM inlays. JADA. 1997. 128:47–53.10.Andersson M., Razzoog ME., Oden A., Hegenbarth EA., Lang BR. Procera: a new way to achieve an all-ceramic crown. Quintessence Int. 1998. 29:285–96.11.Person M., Andersson M., Bergman B. The accuracy of a high-precision digitizer for CAD/CAM of crown. J Prosthet Dent. 1995. 74:223–9.12.Hung SH., Hung KS., Eick JD., Chappel RP. Marginal fit of porcelain-fused-to-metal and two types of ceramic crown. J Prosthet Dent. 1990. 63:26–31.
Article13.May KB., Russel MM., Razzoog ME., Lang BR. Precision of fit: the Procera Allceram crown. J Prosthet Dent. 1998. 80:394–404.
Article14.Kim DK., Cho IH., Lim JH., Lim HS. On the marginal fidelity of all-ceramic core using CAD/CAM system. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2003. 41:20–34.15.Nakamura T., Dei N., Kojima T., Wakabayashi K. Marginal and internal fit of Cerec 3 CAD/CAM all-ceramic crown. Int J Prosthodont. 2003. 16:244–8.16.Holmes JR., Bayne SC., Holland GA., Sulik WD. Conside-rations in measurement of marginal fit. J Prosthet Dent. 1989. 62:405–8.
Article17.Assif D., Rimer Y., Aviv I. The flow of zinc phosphate cement under a full-coverage restoration and its effect on marginal adaptation according to the location of cement application. Quitessence Int. 1987. 18:765–74.18.Christensen GJ. Marginal fit of gold inlay casting. J Prosthet Dent. 1966. 16:297–305.19.Sorensen SE., Larsen IB., Ju ¨rgensen KD. Gingival and alveolar bone reaction to marginal fit of subgingival crown margins. Scand J Dent Res. 1986. 94:109–14.
Article20.McLean JW., Von Fraunhofer JA. The estimation of cement film thickness by an in vivo technique. Br Dent J. 1971. 131:107–11.21.McLean JW. Polycarboxylate cements. Five years' experience in general practice. Br Dent J. 1972. 132:9–15.
Article22.Belser UC., Mecentee MI., Richter WA. Fit of three porcelain-fused-to-metal marginal designs in vivo: a scanning electron microscope study. J Prothet Dent. 1985. 53:24–9.23.Suttor D., Bunke K., Hoescheler S., Hauptmann H., Hertlein G. Lava® - The system for all-ceramic ZrO2 crown and Brige frameworks. Int J Compt Dent 4. 2001. 3:195–206.24.Bindl A., Mormann WH. Marginal and internal fit of all-ceramic CAD/CAM crown-copings on chamfer preparations. J Oral Rehabil. 2005. 32:441–7.
Article25.Persson A., Andersson M., Oden A., Sandborgh-Englund G. A three-dimensional evaluation of a laser scanner and a touch-probe scanner. J Prosthet Dent. 2006. 95:194–200.
Article26.Kim IS., Kim BO., Yoo KH., Kang DW. Design and fabrication of inner konus crown usingthree dimensional computer graphics. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2000. 38:544–51.27.Grey NJ., Piddock V., Wilson MA. In vitro comparison of conventional crowns and a new all-ceramic system. J Dent. 1993. 21:47–51.28.Tuntiprawon M. Wilson PR. The effect ofcement thickness on the fracture strength of all-ceramic crowns. Aust Dent J. 1995. 40:17–21.29.Jorgensen KD., Esbensen AL. The relationship between the film thickness of zinc phosphate cement and the retention of veneer crowns. Acta Odontol Scand. 1968. 26:169–75.30.Passon C., Lambert RH., Lambert RL., Newman S. The effect of multiple layers of die-spacer on crown retention. Oper Dent. 1992. 17:42–9.31.Coli P., Karlsson S. Fit of a new pressure-sintered zirconium dioxide coping. Int J Prosthodont. 2004. 17:59–64.32.Lee KB., Park CW., Kim KH., Kwon TY. Marginal and internal fit of all-ceramic crowns fabricated with two different CAD/CAM systems. Dental Materials Journal. 2008. 27:422–6.
Article33.Park SH., Lee KB. A comparison of the crown fidelity between various cores fabricated with CAD/CAM and conventional cast metal coping. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2008. 46:269–79.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Marginal fit of the digident CAD/CAM zirconia ceramic crowns
- Comparative fracture strength analysis of Lava and Digident CAD/CAM zirconia ceramic crowns
- A comparison of the fidelity between various cores fabricated with CAD/CAM systems
- Comparison of occusal aspects in monolithic zirconia crown before and after occlusal adjustment during intraoral try-in: a case report
- Evaluation of marginal fit of 2 CAD-CAM anatomic contour zirconia crown systems and lithium disilicate glass-ceramic crown