J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2009 Oct;47(4):435-444. 10.4047/jkap.2009.47.4.435.
The influence of magnet on tissue healing after immediate implantation in fresh extraction sites in dogs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, College of Dentistry, Dankook University, Korea. cho8511@dku.edu
- KMID: 2195592
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2009.47.4.435
Abstract
- STATEMENT OF PROBLEM: The clinical use of electric and electomagnetic fields for fracture healing applications began in the early 1970s. Since then, several technologies have been developed and shown to promote healing of fractures. Developments of these devices have been aided in recent years by basic research and several well controlled clinical trials not only in the medical field but in dentistry.
PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to compare alveolar bone reduction following immediate implantation using implants onto which magnets were attached in fresh extracted sockets.
MATERIAL AND METHODS: Four mongrel dogs were involved. Full buccal and lingual mucoperiosteal flaps were elevated and third and fourth premolars of the mandible were removed. Implants with magnets and implants without magnets were installed in the fresh extracted sockets and after 3 months of healing the animals were sacrificed. The mandibles were dissected and each implant sites were sampled and processed for histological examination.
RESULTS
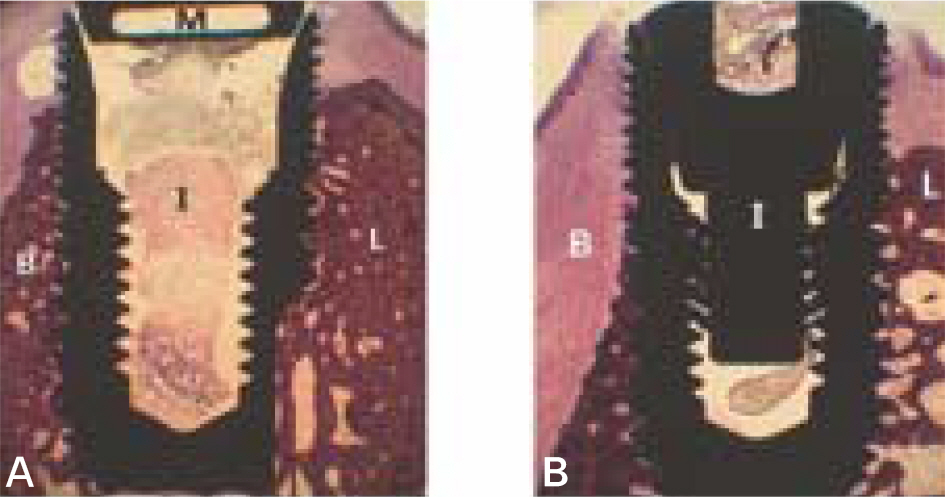
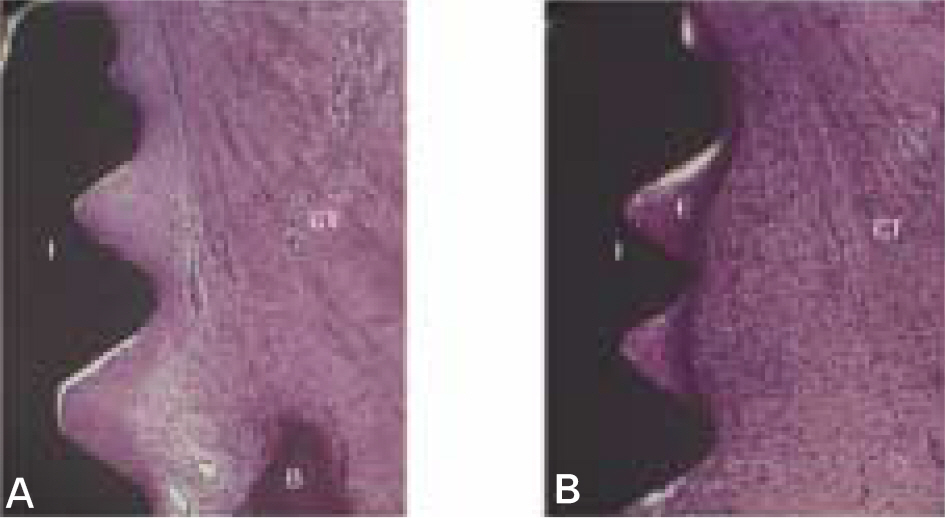
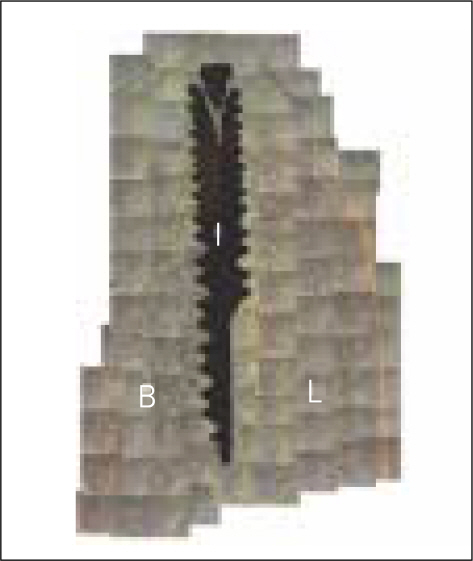
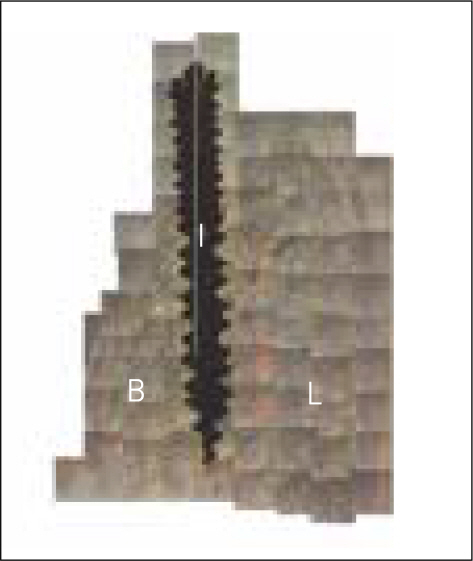
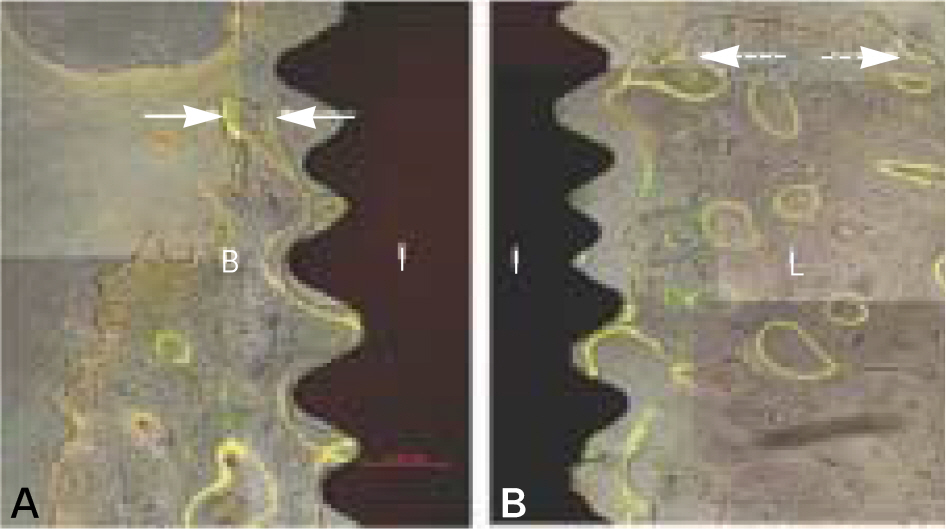
The marginal gaps that were present between the implant and walls of the sockets at the implantation stage disappeared in both groups as a result of bone fill and resorption of the bone crest. The buccal bone crests were located apical of its lingual counterparts. At the 12 week interval the mean of marginal bone resorption in the control group was significantly higher than that of the magnet group. The majority of specimens in magnet group presented early bone formation and less resorption of the buccal marginal bone compared to the control group.
CONCLUSION
Within the limitations of this study, it could be concluded that implants with magnets attached in the early stages of implantation may provide more favorable conditions for early bone formation and reduce resorption and remodeling of marginal bone.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Bassett CA., Pawluk RJ., Pilla AA. Augmentation of bone repair by inductively coupled electromagnetic fields. Science. 1974. 184:575–7.
Article2.Bassett CAL., Mitchell SN., Norton L., Pilla AA. A nonoperative salvage of surgically resistant pseudoarthoses and nonunions by pulsing electromagnetic fields: A preliminary report. Clin Orthop. 1977. 1245:128–43.3.Brighton CT., Black J., Friedenberg ZB., Esterhai JL., Day LJ., Connolly JF. A multicenter study of the treatment of non-union with constant direct current. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981. 63:2–13.
Article4.Ryaby JT. Clinical effects of electromagnetic and electric fields on fracture healing. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998. 355:S205–15.5.Yan QC., Tomita N., Ikada Y. Effects of static magnetic field on bone formation of rat femurs. Med Eng Phys. 1998. 20:397–402.
Article6.Kotani H., Kawaguchi H., Shimoaka T., Iwasaka M., Ueno S., Ozawa H., Nakamura K., Hoshi K. Strong static magnetic field stimulates bone formation to a definite orientation in vitro and in vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 2002. 17:1814–21.7.Cho YW., Lee SB., Choi BB. The effect of magnetism (neodymium magnet) on activity of osteoblast. J Korean Acad Stomato Func Occl. 2003. 19:185–94.8.Lee SM., Lee SB., Choi BB. Effect of magnetism (neodymium magnet) on growth factor receptors of osteoblast. J Korean Acad Stomato Func Occl. 2003. 19:87–96.9.Hwang YT., Lee SB., Choi DG., Choi BB. The change of bone formation according to magnetic intensity of magnet placed into titanium implant specimens. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2005. 43:232–45.10.Park MW., Lee SB., Kwon KR., Choi DG. The effect of magnetism (neodymium magnet) on bone formation around titanium implants inserted into the tibia of rabbit. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2005. 43:519–27.11.Sullivan M., Casey DM., Alberico R., Litwin A., Schaaf NG. Hyperostosis in an orbital defect with craniofacial implants and open-field magnets: a clinical report. J Prosthet Dent. 2007. 97:196–9.
Article12.Adell R., Lekholm U., Rockler B., Bra � nemark PI. A 15-year study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Int J Oral Surg. 1981. 10:387–416.
Article13.Atwood DA. Some clinical factors related to rate of resorption of residual ridges. 1962. J Prosthet Dent. 2001. 86:119–25.14.Atwood DA. Postextraction changes in the adult mandible as illustrated by microradiographs of midsagittal sections and serial cephalometric roentgenograms. J Prosthet Dent. 1963. 13:810–25.
Article15.Tallgren A. The continuing reduction of the residual alveolar ridges in complete denture wearers: a mixed-longitudinal study covering 25 years. J Prosthet Dent. 1972. 27:120–32.
Article16.Johnson K. A study of the dimensional changes occurring in the maxilla after tooth extraction-part I. Normal healing. Australian Dent J. 1963. 8:428–33.17.Johnson K. A study of the dimensional changes occuring in the maxilla following tooth extraction. Australian Dent J. 1969. 14:241–4.18.Pietrokovski J., Massler M. Alveolar ridge resorption following tooth extraction. J Prosthet Dent. 1967. 17:21–7.
Article19.Arau 、jo MG., Lindhe J. Dimensional ridge alterations following tooth extraction. An experimental study in the dog. J Clin Periodontol. 2005. 32:212–8.
Article20.Arau 、jo MG., Sukekava F., Wennstro ¨m JL., Lindhe J. Ridge alterations following implant placement in fresh extraction sockets: an experimental study in the dog. J Clin Periodontol. 2005. 32:645–52.
Article21.Botticelli D., Berglundh T., Lindhe J. Hard-tissue alterations following immediate implant placement in extraction sites. J Clin Periodontol. 2004. 31:820–8.
Article22.Arau 、jo MG., Sukekava F., Wennstro ¨m JL., Lindhe J. Tissue modeling following implant placement in fresh extraction sockets. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006. 17:615–24.
Article23.Arau 、jo MG., Wennstro ¨m JL., Lindhe J. Modeling of the buccal and lingual bone walls of fresh extraction sites following implant installation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006. 17:606–14.
Article24.Lazzara RJ. Immediate implant placement into extraction sites: surgical and restorative advantages. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1989. 9:332–43.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Histomorphometric evaluation of osteogenesis with brushite implant surfaces in dogs
- Magnet Displacement Following Cochlear Implantation
- COMPARATIVE STUDY ON THE MARGINAL BONE LOSS OF IMMEDIATE NONSUBMERGED AND SUBMERGED ENDOSSEOUS DENTAL IMPLANTS PLACED INTO EXTRACTION SOCKETS OF DOGS
- Histopathologic Study of the Effect of two Bovine Bone Powder on Healing of Extraction Socket of Dogs
- Radiologic study of the healing process of the extracted socket of beagle dogs using cone beam CT