J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2010 Oct;48(4):266-272. 10.4047/jkap.2010.48.4.266.
The effect of implant system with reverse beveled platform design on marginal bone stress distribution
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. khjo@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2195543
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2010.48.4.266
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of the surface morphology of the implant neck on marginal bone stress measured by using finite element analysis in six implant models.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
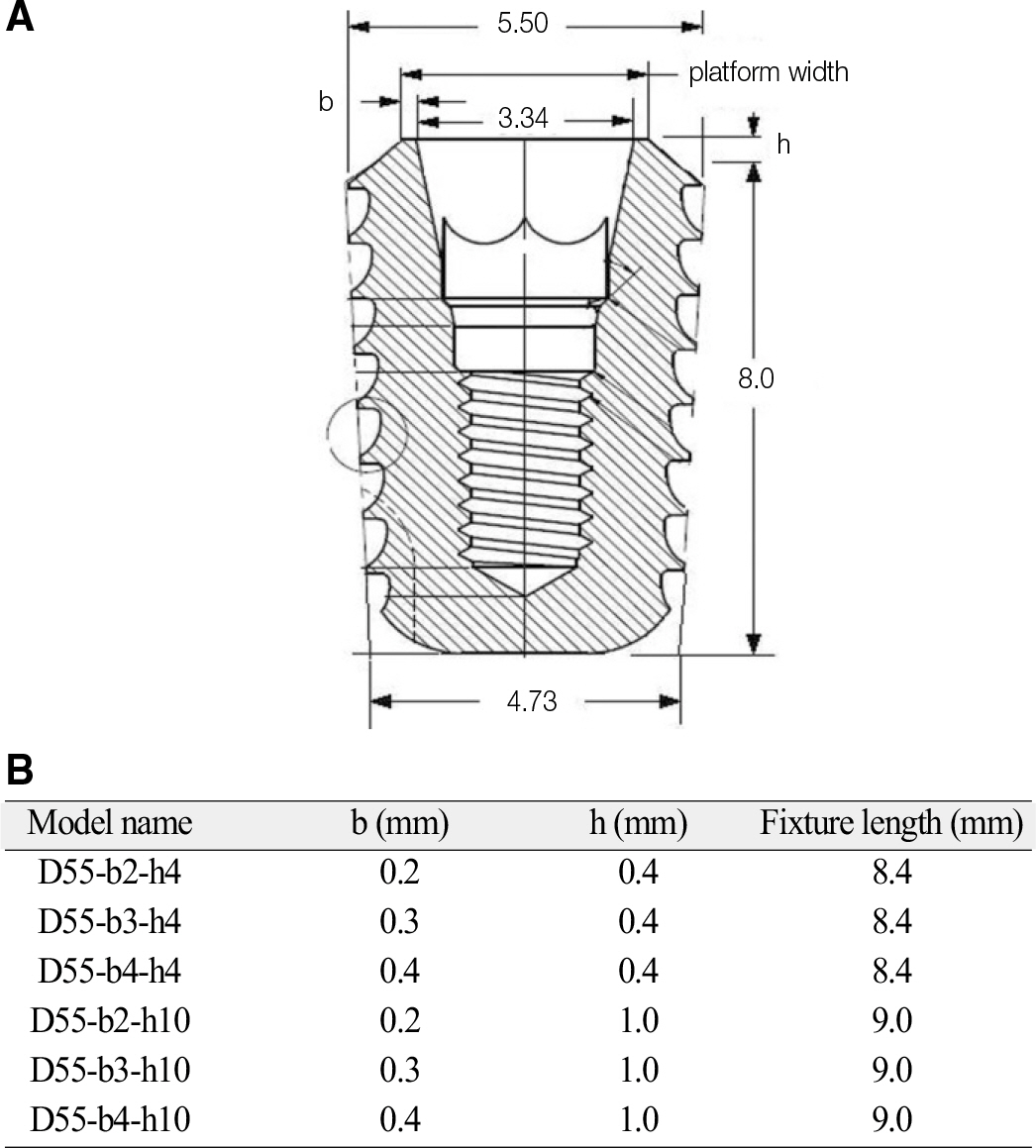
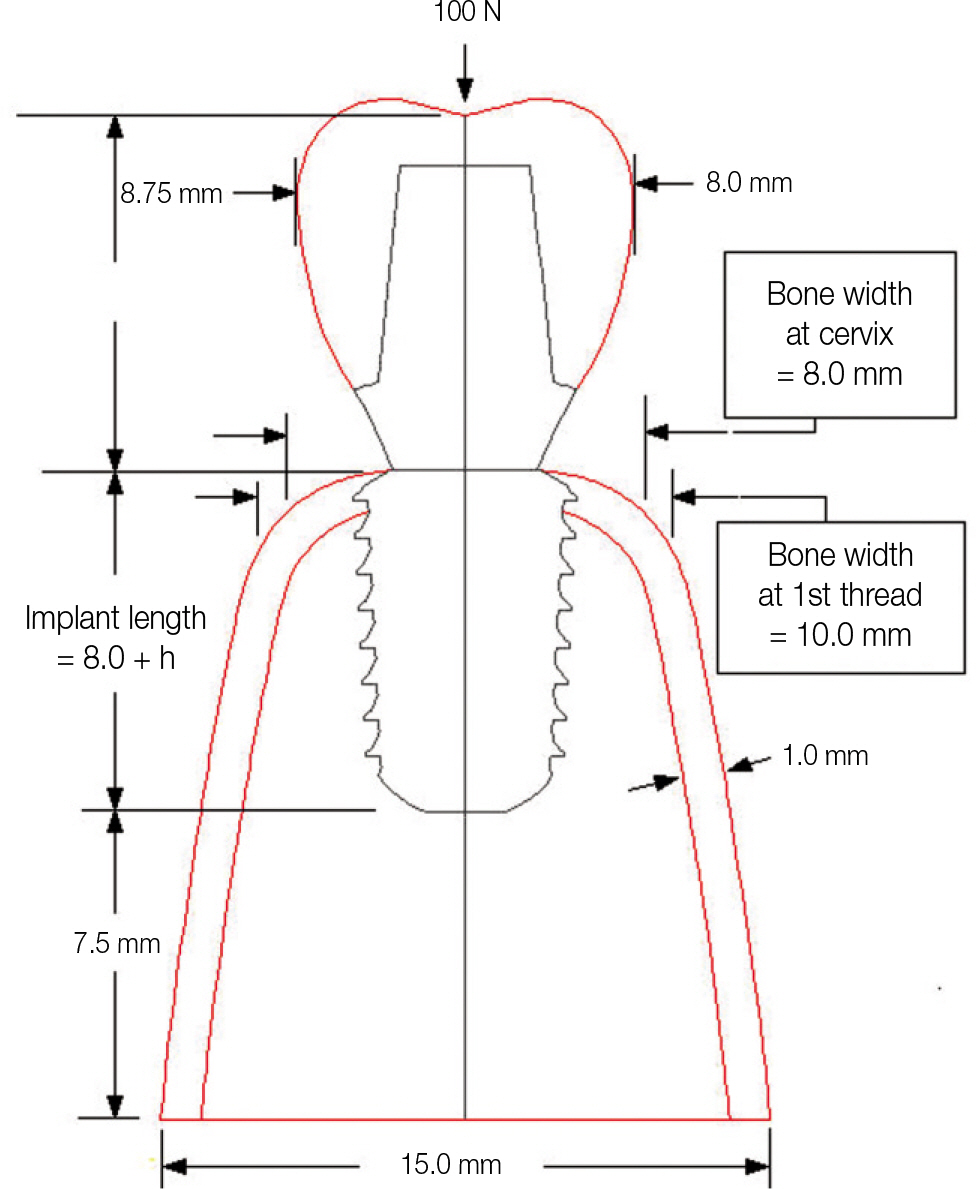
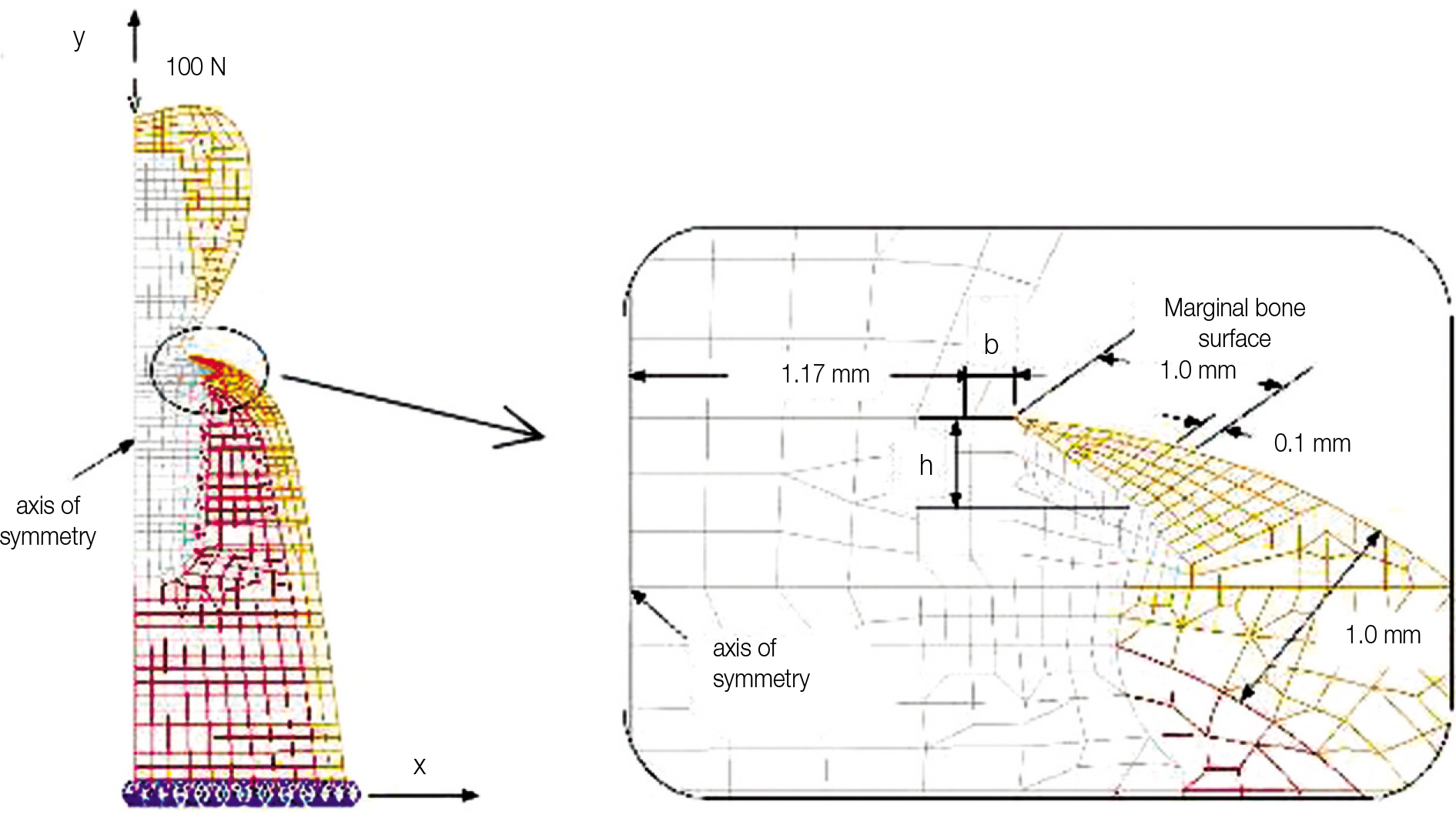
The submerged type rescue implant system (Dentis co., Daegu, Korea) was selected as an experimental model. The implants were divided into six groups whose implant necks were differently designed in terms of height (h, 0.4 and 1.0 mm) and width (platform width, w = 3.34 + 2b [b, 0.2, 0.3 and 0.4 mm]). Finite element models of implant/bone complex were created using an axisymmetric scheme. A load of 100 N was applied to the central node on the top of crown in parallel with the implant axis. The maximum compression stress was calculated and compared.
RESULTS
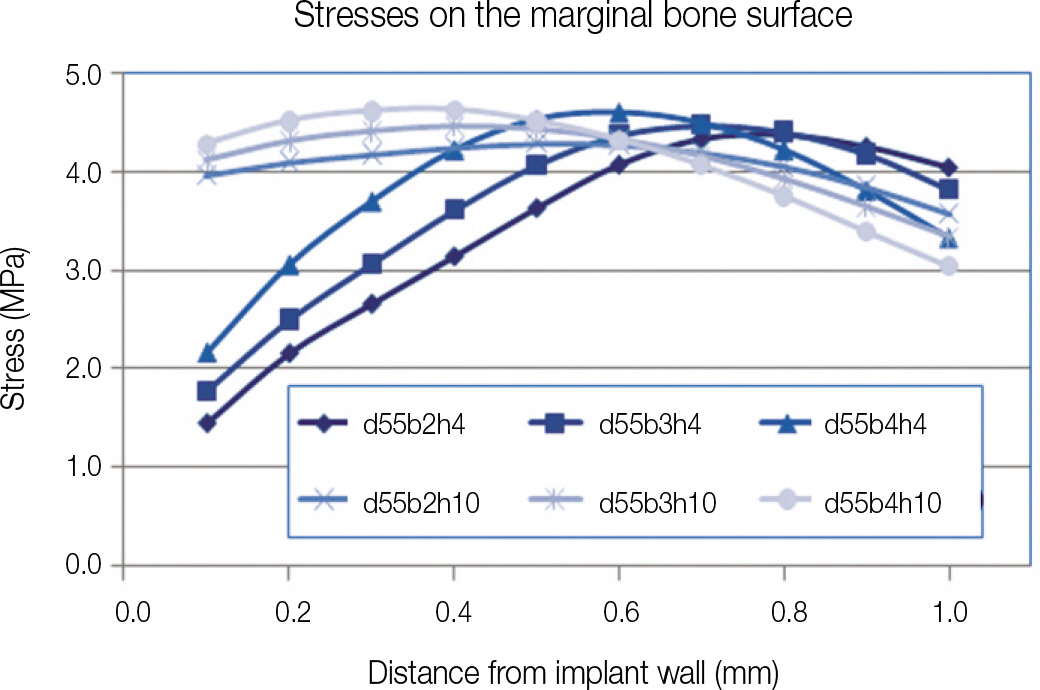
Stress concentration commonly observed around dental implants did not occur in the marginal bone around all six test implant models. Marginal bone stress varied according to the implant neck bevel which had different width and height. The stress was affected more markedly by the difference in height than in width.
CONCLUSION
This result indicates that the implant neck bevel may play an important role in improving stress distribution in the marginal bone area.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Hansson S. The implant neck: smooth or provided with retention elements. A biomechanical approach. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1999. 10:394–405.
Article2.Tada S., Stegaroiu R., Kitamura E., Miyakawa O., Kusakari H. Influence of implant design and bone quality on stress/strain distribution in bone around implants: a 3-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2003. 18:357–68.3.Petrie CS., Williams JL. Comparative evaluation of implant designs: influence of diameter, length, and taper on strains in the alveolar crest. A three-dimensional finite-element analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2005. 16:486–94.4.Holmes DC., Loftus JT. Influence of bone quality on stress distribution for endosseous implants. J Oral Implantol. 1997. 23:104–11.5.Kitagawa T., Tanimoto Y., Nemoto K., Aida M. Influence of cortical bone quality on stress distribution in bone around dental implant. Dent Mater J. 2005. 24:219–24.
Article6.Sevimay M., Turhan F., Kiliçarslan MA., Eskitascioglu G. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the effect of different bone quality on stress distribution in an implant-supported crown. J Prosthet Dent. 2005. 93:227–34.
Article7.Barbier L., Vander Sloten J., Krzesinski G., Schepers E., Van der Perre G. Finite element analysis of non-axial versus axial loading of oral implants in the mandible of the dog. J Oral Rehabil. 1998. 25:847–58.
Article8.Kitamura E., Stegaroiu R., Nomura S., Miyakawa O. Biomechanical aspects of marginal bone resorption around osseointegrated implants: considerations based on a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004. 15:401–12.
Article9.Kitamura E., Stegaroiu R., Nomura S., Miyakawa O. Influence of marginal bone resorption on stress around an implant-a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Oral Rehabil. 2005. 32:279–86.10.Natali AN., Pavan PG., Ruggero AL. Analysis of bone-implant interaction phenomena by using a numerical approach. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006. 17:67–74.
Article11.Chang M., Wennstro ¨m JL., Odman P., Andersson B. Implant supported single-tooth replacements compared to contralateral natural teeth. Crown and soft tissue dimensions. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1999. 10:185–94.
Article12.Albrektsson T., Zarb G., Worthington P., Eriksson AR. The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: a review and proposed criteria of success. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1986. 1:11–25.13.Frost HM. Wolff's Law and bone' s structural adaptations to mechanical usage: an overview for clinicians. Angle Orthod. 1994. 64:175–88.14.Rubin CT., Lanyon LE. Regulation of bone mass by mechanical strain magnitude. Calcif Tissue Int. 1985. 37:411–7.
Article15.Duyck J., R�nold HJ., Van Oosterwyck H., Naert I., Vander Sloten J., Ellingsen JE. The influence of static and dynamic loading on marginal bone reactions around osseointegrated implants: an animal experimental study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2001. 12:207–18.
Article16.Schrotenboer J., Tsao YP., Kinariwala V., Wang HL. Effect of mi-crothreads and platform switching on crestal bone stress levels: a finite element analysis. J Periodontol. 2008. 79:2166–72.
Article17.Lee DW., Choi YS., Park KH., Kim CS., Moon IS. Effect of mi-crothread on the maintenance of marginal bone level: a 3-year prospective study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007. 18:465–70.
Article18.Chung JM., Jo KH., Lee CH., Yu WJ., Lee KB. Finite element analysis of peri-implant bone stress influenced by cervical module configuration of endosseous implant. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2009. 47:394–405.
Article19.Li YF. Comparative and analysis study of peri-implant bone stress around Rescue implant and standard implant using finite element method. Masters thesis, Department of Dentistry, Graduate School, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea,. 2009.20.NISA II/DISPLAY III User' s Manuel, Engineering Mechanics Research Corporation (EMRC). 1998.21.Langer B., Langer L., Herrmann I., Jorneus L. The wide fixture: a solution for special bone situations and a rescue for the compromised implant. Part 1. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1993. 8:400–8.22.Covani U., Bortolaia C., Barone A., Sbordone L. Bucco-lingual cre-stal bone changes after immediate and delayed implant placement. J Periodontol. 2004. 75:1605–12.
Article23.Broggini N., McManus LM., Hermann JS., Medina RU., Oates TW., Schenk RK., Buser D., Mellonig JT., Cochran DL. Persistent acute inflammation at the implant-abutment interface. J Dent Res. 2003. 82:232–7.
Article24.Hermann JS., Buser D., Schenk RK., Cochran DL. Crestal bone changes around titanium implants. A histometric evaluation of unloaded non-submerged and submerged implants in the canine mandible. J Periodontol. 2000. 71:1412–24.
Article25.Piattelli A., Vrespa G., Petrone G., Iezzi G., Annibali S., Scarano A. Role of the microgap between implant and abutment: a retrospective histologic evaluation in monkeys. J Periodontol. 2003. 74:346–52.
Article26.Tarnow DP., Cho SC., Wallace SS. The effect of inter-implant distance on the height of inter-implant bone crest. J Periodontol. 2000. 71:546–9.
Article27.Hartman GA., Cochran DL. Initial implant position determines the magnitude of crestal bone remodeling. J Periodontol. 2004. 75:572–7.
Article28.Sanavi F., Weisgold AS., Rose LF. Biologic width and its relation to periodontal biotypes. J Esthet Dent. 1998. 10:157–63.
Article29.Oh TJ., Yoon J., Misch CE., Wang HL. The causes of early implant bone loss: myth or science? J Periodontol. 2002. 73:322–33.
Article30.Misch CE. Contemporary Implant Dentistry. St. Louis: Mosby;2008. p. 545.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Three-dimensional finite element analysis of platform switched implant
- Influence of crestal module design on marginal bone stress around dental implant
- Effect of implant fixtures with blood pocket designed platforms on crestal bone
- Evaluation of marginal bone loss around platform-switched implants by digital subtraction radiography
- Three-dimensional finite element analysis for influence of marginal bone resorption on stress distribution in internal conical joint type implant fixture