J Adv Prosthodont.
2017 Feb;9(1):31-37. 10.4047/jap.2017.9.1.31.
Three-dimensional finite element analysis of platform switched implant
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
- 2Dental Research Institute and Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea. proskwon@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2368209
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2017.9.1.31
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to analyze the influence of the platform switching concept on an implant system and peri-implant bone using three-dimensional finite element analysis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
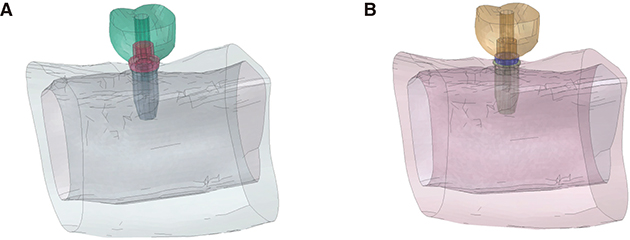
Two three-dimensional finite element models for wide platform and platform switching were created. In the wide platform model, a wide platform abutment was connected to a wide platform implant. In the platform switching model, the wide platform abutment of the wide platform model was replaced by a regular platform abutment. A contact condition was set between the implant components. A vertical load of 300 N was applied to the crown. The maximum von Mises stress values and displacements of the two models were compared to analyze the biomechanical behavior of the models.
RESULTS
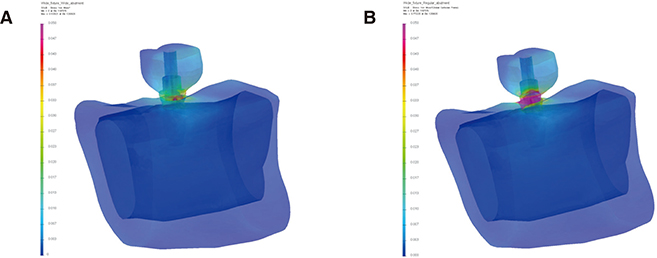
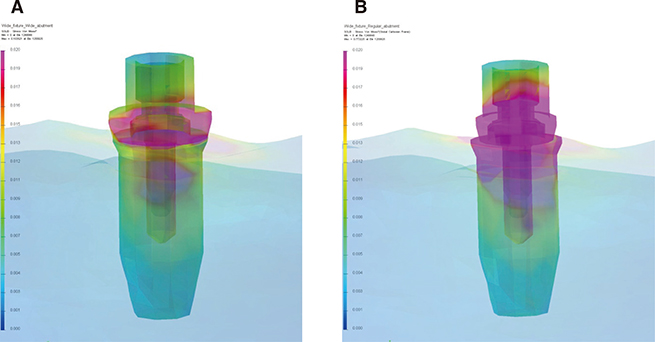
In the two models, the stress was mainly concentrated at the bottom of the abutment and the top surface of the implant in both models. However, the von Mises stress values were much higher in the platform switching model in most of the components, except for the bone. The highest von Mises values and stress distribution pattern of the bone were similar in the two models. The components of the platform switching model showed greater displacement than those of the wide platform model.
CONCLUSION
Due to the stress concentration generated in the implant and the prosthodontic components of the platform switched implant, the mechanical complications might occur when platform switching concept is used.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pellizzer EP, Verri FR, Falcón-Antenucci RM, Júnior JF, de Carvalho PS, de Moraes SL, Noritomi PY. Stress analysis in platform-switching implants: a 3-dimensional finite element study. J Oral Implantol. 2012; 38:587–594.2. Lazzara RJ, Porter SS. Platform switching: a new concept in implant dentistry for controlling postrestorative crestal bone levels. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2006; 26:9–17.3. Schrotenboer J, Tsao YP, Kinariwala V, Wang HL. Effect of microthreads and platform switching on crestal bone stress levels: a finite element analysis. J Periodontol. 2008; 79:2166–2172.4. Duyck J, Slaets E, Sasaguri K, Vandamme K, Naert I. Effect of intermittent loading and surface roughness on peri-implant bone formation in a bone chamber model. J Clin Periodontol. 2007; 34:998–1006.5. Li T, Kong L, Wang Y, Hu K, Song L, Liu B, Li D, Shao J, Ding Y. Selection of optimal dental implant diameter and length in type IV bone: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 38:1077–1083.6. Enkling N, Jöhren P, Klimberg T, Mericske-Stern R, Jervøe-Storm PM, Bayer S, Gülden N, Jepsen S. Open or submerged healing of implants with platform switching: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol. 2011; 38:374–384.7. Cocchetto R, Traini T, Caddeo F, Celletti R. Evaluation of hard tissue response around wider platform-switched implants. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2010; 30:163–171.8. Bilhan H, Mumcu E, Erol S, Kutay O. Influence of platform-switching on marginal bone levels for implants with mandibular overdentures: a retrospective clinical study. Implant Dent. 2010; 19:250–258.9. Canullo L, Iurlaro G, Iannello G. Double-blind randomized controlled trial study on post-extraction immediately restored implants using the switching platform concept: soft tissue response. Preliminary report. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009; 20:414–420.10. Luongo R, Traini T, Guidone PC, Bianco G, Cocchetto R, Celletti R. Hard and soft tissue responses to the platform-switching technique. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2008; 28:551–557.11. Prosper L, Redaelli S, Pasi M, Zarone F, Radaelli G, Gherlone EF. A randomized prospective multicenter trial evaluating the platform-switching technique for the prevention of postrestorative crestal bone loss. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009; 24:299–308.12. Trammell K, Geurs NC, O'Neal SJ, Liu PR, Haigh SJ, McNeal S, Kenealy JN, Reddy MS. A prospective, randomized, controlled comparison of platform-switched and matched-abutment implants in short-span partial denture situations. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2009; 29:599–605.13. Wagenberg B, Froum SJ. Prospective study of 94 platform-switched implants observed from 1992 to 2006. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2010; 30:9–17.14. Calvo-Guirado JL, Ortiz-Ruiz AJ, López-Marí L, Delgado-Ruiz R, Maté-Sánchez J, Bravo Gonzalez LA. Immediate maxillary restoration of single-tooth implants using platform switching for crestal bone preservation: a 12-month study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009; 24:275–281.15. Cumbo C, Marigo L, Somma F, La Torre G, Minciacchi I, D'Addona A. Implant platform switching concept: a literature review. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013; 17:392–397.16. Broggini N, McManus LM, Hermann JS, Medina RU, Oates TW, Schenk RK, Buser D, Mellonig JT, Cochran DL. Persistent acute inflammation at the implant-abutment interface. J Dent Res. 2003; 82:232–237.17. Rodríguez-Ciurana X, Vela-Nebot X, Segalà-Torres M, Calvo-Guirado JL, Cambra J, Méndez-Blanco V, Tarnow DP. The effect of interimplant distance on the height of the interimplant bone crest when using platform-switched implants. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2009; 29:141–151.18. Al-Nsour MM, Chan HL, Wang HL. Effect of the platform-switching technique on preservation of peri-implant marginal bone: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012; 27:138–145.19. Maeda Y, Miura J, Taki I, Sogo M. Biomechanical analysis on platform switching: is there any biomechanical rationale? Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007; 18:581–584.20. Hsu JT, Fuh LJ, Lin DJ, Shen YW, Huang HL. Bone strain and interfacial sliding analyses of platform switching and implant diameter on an immediately loaded implant: experimental and three-dimensional finite element analyses. J Periodontol. 2009; 80:1125–1132.21. Wu AY, Lung H, Huang HL, Chee W. Biomechanical investigations of the expanded platform-switching concept in immediately loaded small diameter implants. J Prosthet Dent. 2016; 115:20–25.22. Pessoa RS, Bezerra FJ, Sousa RM, Vander Sloten J, Casati MZ, Jaecques SV. Biomechanical evaluation of platform switching: different mismatch sizes, connection types, and implant protocols. J Periodontol. 2014; 85:1161–1171.23. Baggi L, Cappelloni I, Di Girolamo M, Maceri F, Vairo G. The influence of implant diameter and length on stress distribution of osseointegrated implants related to crestal bone geometry: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Prosthet Dent. 2008; 100:422–431.24. Tabata LF, Assunção WG, Adelino Ricardo BarÃo V, de Sousa EA, Gomes EA, Delben JA. Implant platform switching: biomechanical approach using two-dimensional finite element analysis. J Craniofac Surg. 2010; 21:182–187.25. Himmlová L, Dostálová T, Kácovský A, Konvicková S. Influence of implant length and diameter on stress distribution: a finite element analysis. J Prosthet Dent. 2004; 91:20–25.26. Canay S, Akça K. Biomechanical aspects of bone-level diameter shifting at implant-abutment interface. Implant Dent. 2009; 18:239–248.27. Pessoa RS, Vaz LG, Marcantonio E Jr, Vander Sloten J, Duyck J, Jaecques SV. Biomechanical evaluation of platform switching in different implant protocols: computed tomography-based three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010; 25:911–919.28. Geng JP, Tan KB, Liu GR. Application of finite element analysis in implant dentistry: a review of the literature. J Prosthet Dent. 2001; 85:585–598.29. Djebbar N, Serier B, Bouiadjra BB, Benbarek S, Drai A. Analysis of the effect of load direction on the stress distribution in dental implant. Mater Des. 2010; 31:2097–2101.30. Quaresma SE, Cury PR, Sendyk WR, Sendyk C. A finite element analysis of two different dental implants: stress distribution in the prosthesis, abutment, implant, and supporting bone. J Oral Implantol. 2008; 34:1–6.31. Eskitascioglu G, Usumez A, Sevimay M, Soykan E, Unsal E. The influence of occlusal loading location on stresses transferred to implant-supported prostheses and supporting bone: A three-dimensional finite element study. J Prosthet Dent. 2004; 91:144–150.32. Bouazza-Juanes K, Martínez-González A, Peiró G, Ródenas JJ, López-Mollá MV. Effect of platform switching on the peri-implant bone: A finite element study. J Clin Exp Dent. 2015; 7:e483–e488.33. Sato Y, Teixeira ER, Tsuga K, Shindoi N. The effectiveness of a new algorithm on a three-dimensional finite element model construction of bone trabeculae in implant biomechanics. J Oral Rehabil. 1999; 26:640–643.34. Barbier L, Vander Sloten J, Krzesinski G, Schepers E, Van der Perre G. Finite element analysis of non-axial versus axial loading of oral implants in the mandible of the dog. J Oral Rehabil. 1998; 25:847–858.35. Rho JY, Ashman RB, Turner CH. Young's modulus of trabecular and cortical bone material: ultrasonic and microtensile measurements. J Biomech. 1993; 26:111–119.36. Wang RF, Kang B, Lang LA, Razzoog ME. The dynamic natures of implant loading. J Prosthet Dent. 2009; 101:359–371.37. Mericske-Stern R, Zarb GA. In vivo measurements of some functional aspects with mandibular fixed prostheses supported by implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1996; 7:153–161.38. Hermann F, Lerner H, Palti A. Factors influencing the preservation of the periimplant marginal bone. Implant Dent. 2007; 16:165–175.39. Abrahamsson I, Berglundh T, Lindhe J. The mucosal barrier following abutment dis/reconnection. An experimental study in dogs. J Clin Periodontol. 1997; 24:568–572.40. Kitamura E, Stegaroiu R, Nomura S, Miyakawa O. Biomechanical aspects of marginal bone resorption around osseointegrated implants: considerations based on a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004; 15:401–412.41. Hoshaw SJ, Fyhrie DP, Takano Y, Burr DB, Milgrom C. A method suitable for in vivo measurement of bone strain in humans. J Biomech. 1997; 30:521–524.42. Khraisat A. Influence of abutment screw preload on stress distribution in marginal bone. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012; 27:303–307.43. Huang HL, Chang CH, Hsu JT, Fallgatter AM, Ko CC. Comparison of implant body designs and threaded designs of dental implants: a 3-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2007; 22:551–562.44. Verri FR, Cruz RS, de Souza Batista VE, Almeida DA, Verri AC, Lemos CA, Santiago Júnior JF, Pellizzer EP. Can the modeling for simplification of a dental implant surface affect the accuracy of 3D finite element analysis? Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2016; 19:1665–1672.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Application of finite element analysis to evaluate platform switching
- ANALYSIS OF THE FIT IN THE IMPLANT PROSTHESIS USING LASER DISPLACEMENT METER AND THREE-DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
- Three-dimensional finite element analysis according to the insertion depth of an immediately loaded implant in the anterior maxilla
- Finite element stress analysis of implant prosthesis according to platform width of fixture
- The effect of implant system with reverse beveled platform design on marginal bone stress distribution