J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2012 Jun;51(6):343-349. 10.3340/jkns.2012.51.6.343.
NFlex Dynamic Stabilization System : Two-Year Clinical Outcomes of Multi-Center Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Silicon Valley Spine Institute, Campbell, CA, USA.
- 2Orthopedic Spine Associates, Eugene, OR, USA.
- 3BG-Clinic Bergmannstrost, Halle, Germany.
- 4Tallahassee Orthopedic Clinic, Tallahassee, FL, USA.
- 5Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. taj@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2190488
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2012.51.6.343
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
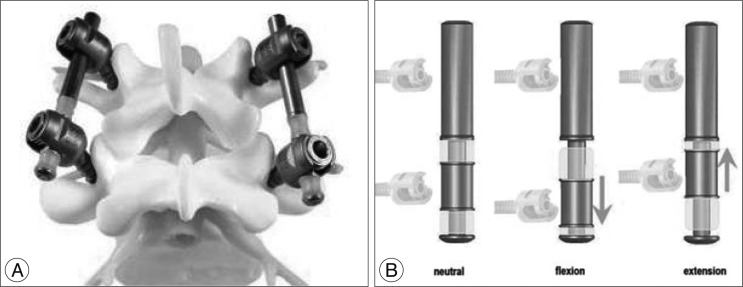
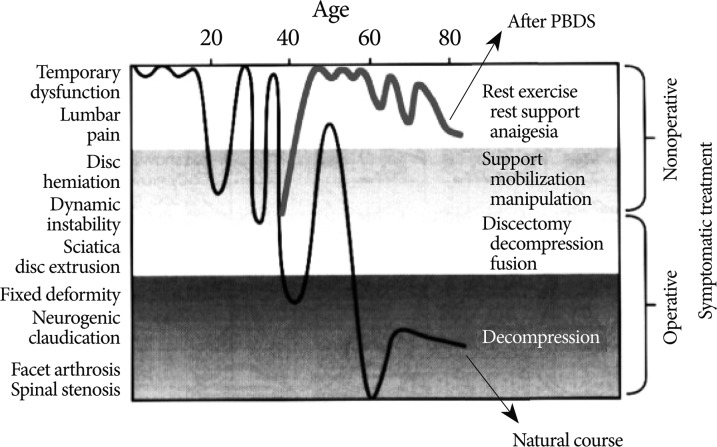
Pedicle-based dynamic stabilization systems, in which semi-rigid rods or cords are used to restrict or control spinal segmental motion, aim to reduce or eliminate the drawbacks associated with rigid fusion. In this study, we analyzed the two-year clinical outcomes of patients treated with the NFlex (Synthes Spine, Inc.), a pedicle-based dynamic stabilization system.
METHODS
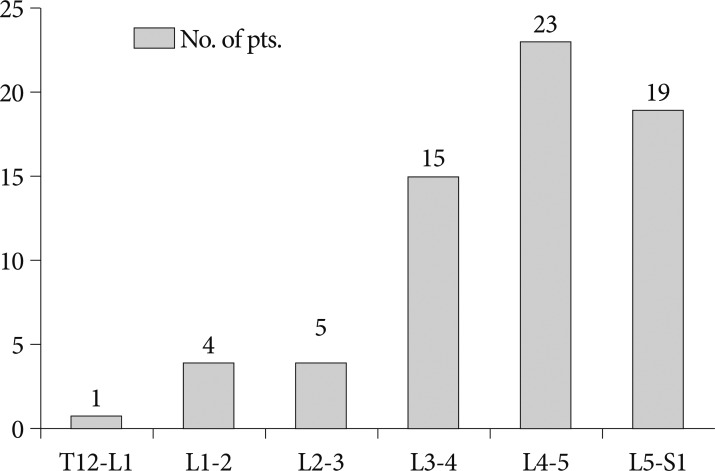
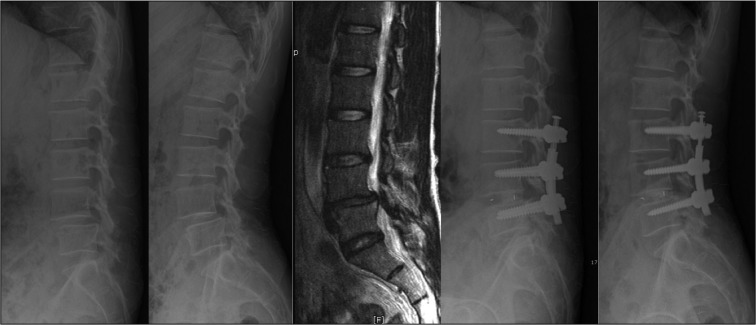
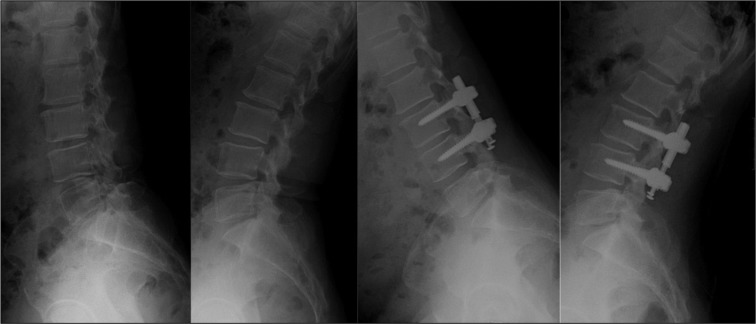
Five sites participated in a retrospective study of 72 consecutive patients who underwent NFlex stabilization. Of these 72 patients, 65 were available for 2-year follow-up. Patients were included based on the presence of degenerative disc disease (29 patients), degenerative spondylolisthesis (16 patients), lumbar stenosis (9 patients), adjacent segment degeneration (6 patients), and degenerative lumbar scoliosis (5 patients). The clinical outcome measures at each assessment were Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) to measure back pain, and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) to measure functional status. Radiographic assessments included evidence of instrumentation failure or screw loosening.
RESULTS
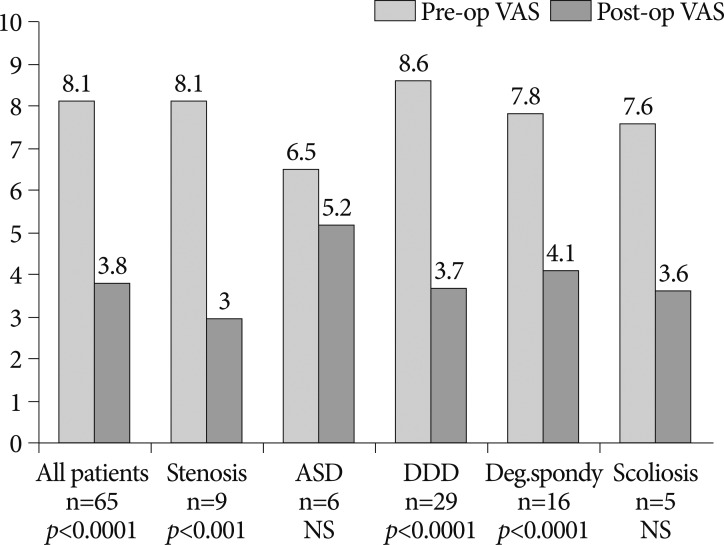
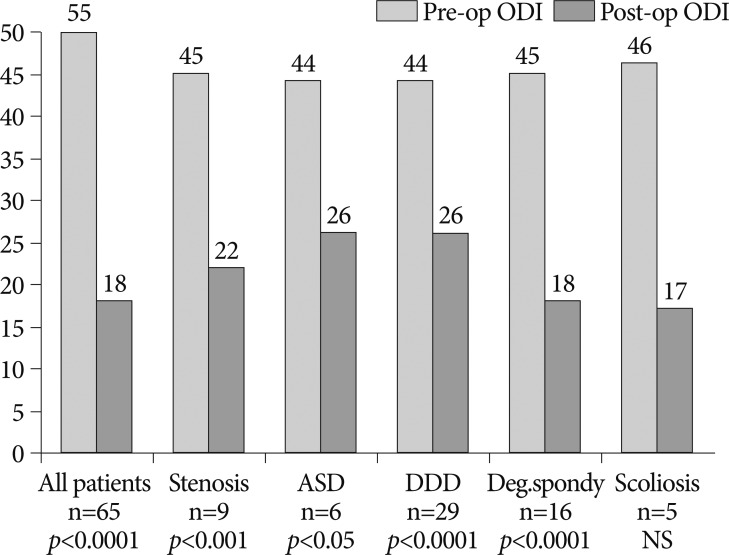
Sixty-five patients (26 men and 39 women) with a mean age of 54.5 years were included. Mean follow-up was 25.6 months. The mean VAS score improved from 8.1 preoperatively to 3.8 postoperatively, representing a 53% improvement, and the ODI score from 44.5 to 21.8, representing a 51% improvement. Improvements in pain and disability scores were statistically significant. Three implant-related complications were observed.
CONCLUSION
Posterior pedicle-based dynamic stabilization using the NFlex system seems effective in improving pain and functional scores, with sustained clinical improvement after two years. With appropriate patient selection, it may be considered an effective alternative to rigid fusion.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Acosta FL, Christensen FB, Coe JD, Jahng TA, Kitchel SH, Meiser HJ, et al. Early clinical and radiograhic results of NFix II posterior dynamic stabilization system. SAS Journal. 2008; 2:69–75.
Article2. Bastian L, Lange U, Knop C, Tusch G, Blauth M. Evaluation of the mobility of adjacent segments after posterior thoracolumbar fixation: a biomechanical study. Eur Spine J. 2001; 10:295–300. PMID: 11563614.
Article3. Bono CM, Kadaba M, Vaccaro AR. Posterior pedicle fixation-based dynamic stabilization devices for the treatment of degenerative diseases of the lumbar spine. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2009; 22:376–383. PMID: 19525796.
Article4. Boos N, Webb JK. Pedicle screw fixation in spinal disorders : a European view. Eur Spine J. 1997; 6:2–18. PMID: 9093822.
Article5. Chou WY, Hsu CJ, Chang WN, Wong CY. Adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar spinal posterolateral fusion with instrumentation in elderly patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2002; 122:39–43. PMID: 11995879.
Article6. Crawford NR, Reyes PM, Senoglu M, Yim J. Motion Characteristics of the NFlex Pedicle Screw Based Dynamic Stabilization System : A Human Cadaver. Spine Arthroplasty Society Annual Meeting. 2008. Miami USA:7. Etebar S, Cahill DW. Risk factors for adjacent-segment failure following lumbar fixation with rigid instrumentation for degenerative instability. J Neurosurg. 1999; 90:163–169. PMID: 10199244.
Article8. Fritzell P, Hägg O, Wessberg P, Nordwall A. Chronic low back pain and fusion : a comparison of three surgical techniques : a prospective multicenter randomized study from the Swedish lumbar spine study group. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27:1131–1141. PMID: 12045508.
Article9. Fritzell P, Hägg O, Nordwall A. Complications in lumbar fusion surgery for chronic low back pain : comparison of three surgical techniques used in a prospective randomized study. A report from the Swedish Lumbar Spine Study Group. Eur Spine J. 2003; 12:178–189. PMID: 12709856.
Article10. Galbusera F, Bellini CM, Anasetti F, Ciavarro C, Lovi A, Brayda-Bruno M. Rigid and flexible spinal stabilization devices : a biomechanical comparison. Med Eng Phys. 2011; 33:490–496. PMID: 21177135.
Article11. Grob D, Benini A, Junge A, Mannion AF. Clinical experience with the Dynesys semirigid fixation system for the lumbar spine : surgical and patient-oriented outcome in 50 cases after an average of 2 years. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:324–331. PMID: 15682014.
Article12. Guigui P, Wodecki P, Bizot P, Lambert P, Chaumeil G, Deburge A. [Long-term influence of associated arthrodesis on adjacent segments in the treatment of lumbar stenosis : a series of 127 cases with 9-year follow-up]. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2000; 86:546–557. PMID: 11060428.13. Highsmith JM, Tumialán LM, Rodts GE Jr. Flexible rods and the case for dynamic stabilization. Neurosurg Focus. 2007; 22:E11. PMID: 17608332.
Article14. Hilibrand AS, Robbins M. Adjacent segment degeneration and adjacent segment disease : the consequences of spinal fusion? Spine J. 2004; 4:190S–194S. PMID: 15541666.15. Khoueir P, Kim KA, Wang MY. Classification of posterior dynamic stabilization devices. Neurosurg Focus. 2007; 22:E3. PMID: 17608337.
Article16. Lee SE, Park SB, Jahng TA, Chung CK, Kim HJ. Clinical experience of the dynamic stabilization system for the degenerative spine disease. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008; 43:221–226. PMID: 19096600.
Article17. Lehmann TR, Spratt KF, Tozzi JE, Weinstein JN, Reinarz SJ, el-Khoury GY, et al. Long-term follow-up of lower lumbar fusion patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1987; 12:97–104. PMID: 2954220.
Article18. Markwalder TM, Wenger M. Adjacent-segment morbidity. J Neurosurg. 2002; 96:139–140. PMID: 11795706.19. Mulholland RC, Sengupta DK. Rationale, principles and experimental evaluation of the concept of soft stabilization. Eur Spine J. 2002; 11:S198–S205. PMID: 12384745.
Article20. Putzier M, Schneider SV, Funk JF, Tohtz SW, Perka C. The surgical treatment of the lumbar disc prolapse : nucleotomy with additional transpedicular dynamic stabilization versus nucleotomy alone. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:E109–E114. PMID: 15738772.21. Resnick DK, Choudhri TF, Dailey AT, Groff MW, Khoo L, Matz PG, et al. Guidelines for the performance of fusion procedures for degenerative disease of the lumbar spine. Part 5 : correlation between radiographic and functional outcome. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005; 2:658–661. PMID: 16028733.
Article22. Reyes-Sánchez A, Zárate-Kalfópulos B, Ramírez-Mora I, Rosales-Olivarez LM, Alpizar-Aguirre A, Sánchez-Bringas G. Posterior dynamic stabilization of the lumbar spine with the Accuflex rod system as a stand-alone device : experience in 20 patients with 2-year follow-up. Eur Spine J. 2010; 19:2164–2170. PMID: 20496039.
Article23. Schnake KJ, Schaeren S, Jeanneret B. Dynamic stabilization in addition to decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31:442–449. PMID: 16481955.
Article24. Schwarzenbach O, Berlemann U, Stoll TM, Dubois G. Posterior dynamic stabilization systems : DYNESYS. Orthop Clin North Am. 2005; 36:363–372. PMID: 15950696.25. Sengupta DK, Mulholland RC. Fulcrum assisted soft stabilization system : a new concept in the surgical treatment of degenerative low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:1019–1029. discussion 1030. PMID: 15864153.26. Stoffel M, Behr M, Reinke A, Stüer C, Ringel F, Meyer B. Pedicle screw-based dynamic stabilization of the thoracolumbar spine with the Cosmic-system : a prospective observation. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2010; 152:835–843. PMID: 20084412.
Article27. Stoll TM, Dubois G, Schwarzenbach O. The dynamic neutralization system for the spine : a multi-center study of a novel non-fusion system. Eur Spine J. 2002; 11:S170–S178. PMID: 12384741.28. Wallach CJ, Teng AL, Wang JC. Yue JJ, Bertagnoli R, McAfee PC, An HS, editors. NFlex. Motion preservation surgery of the spine. 2008. Philadelphia: Saunders;p. 505–510.
Article29. Welch WC, Cheng BC, Awad TE, Davis R, Maxwell JH, Delamarter R, et al. Clinical outcomes of the Dynesys dynamic neutralization system : 1-year preliminary results. Neurosurg Focus. 2007; 22:E8. PMID: 17608342.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pedicle Screw-based Dynamic Stabilization with a Hinged Screw Head System in the Treatment of Lumbar Degenerative Disorders
- The Incidence of Adjacent Segment Degeneration after the Use of a Versatile Dynamic Hybrid Stabilization Device in Lumbar Stenosis: Results of a 5–8-Year Follow-up
- Change of Lumbar Motion after Multi-Level Posterior Dynamic Stabilization with Bioflex System : 1 Year Follow Up
- Lumbar Single-Level Dynamic Stabilization with Semi-Rigid and Full Dynamic Systems: A Retrospective Clinical and Radiological Analysis of 71 Patients
- Does the Addition of a Dynamic Pedicle Screw to a Fusion Segment Prevent Adjacent Segment Pathology in the Lumbar Spine?