J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2010 Jun;36(3):172-176. 10.5125/jkaoms.2010.36.3.172.
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in osteogenic sarcoma of the neck following oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral Pathology, Oral Cancer Research Institute, College of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, College of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea. kimoms@yuhs.ac
- 3Department of Advanced General Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2189944
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2010.36.3.172
Abstract
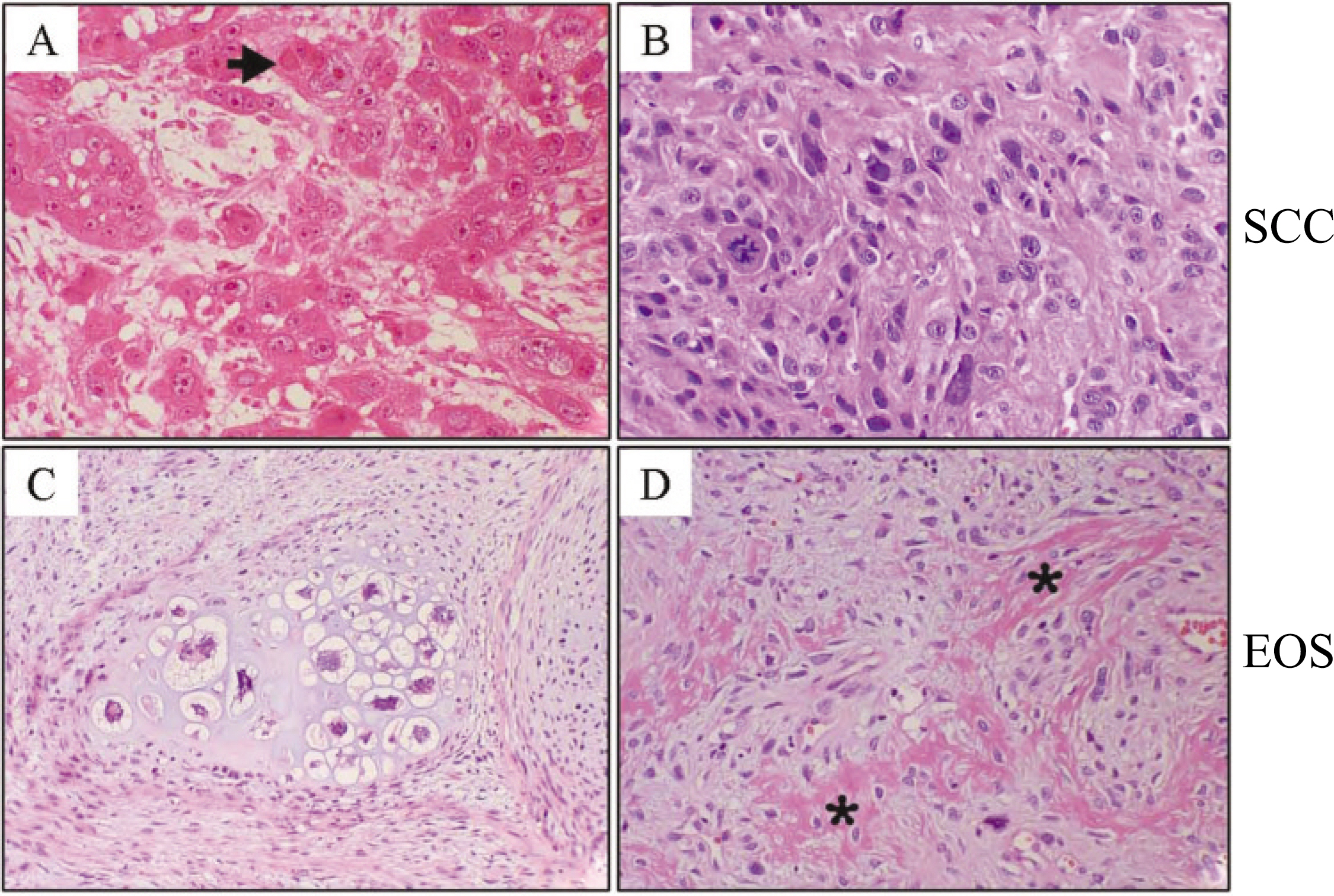
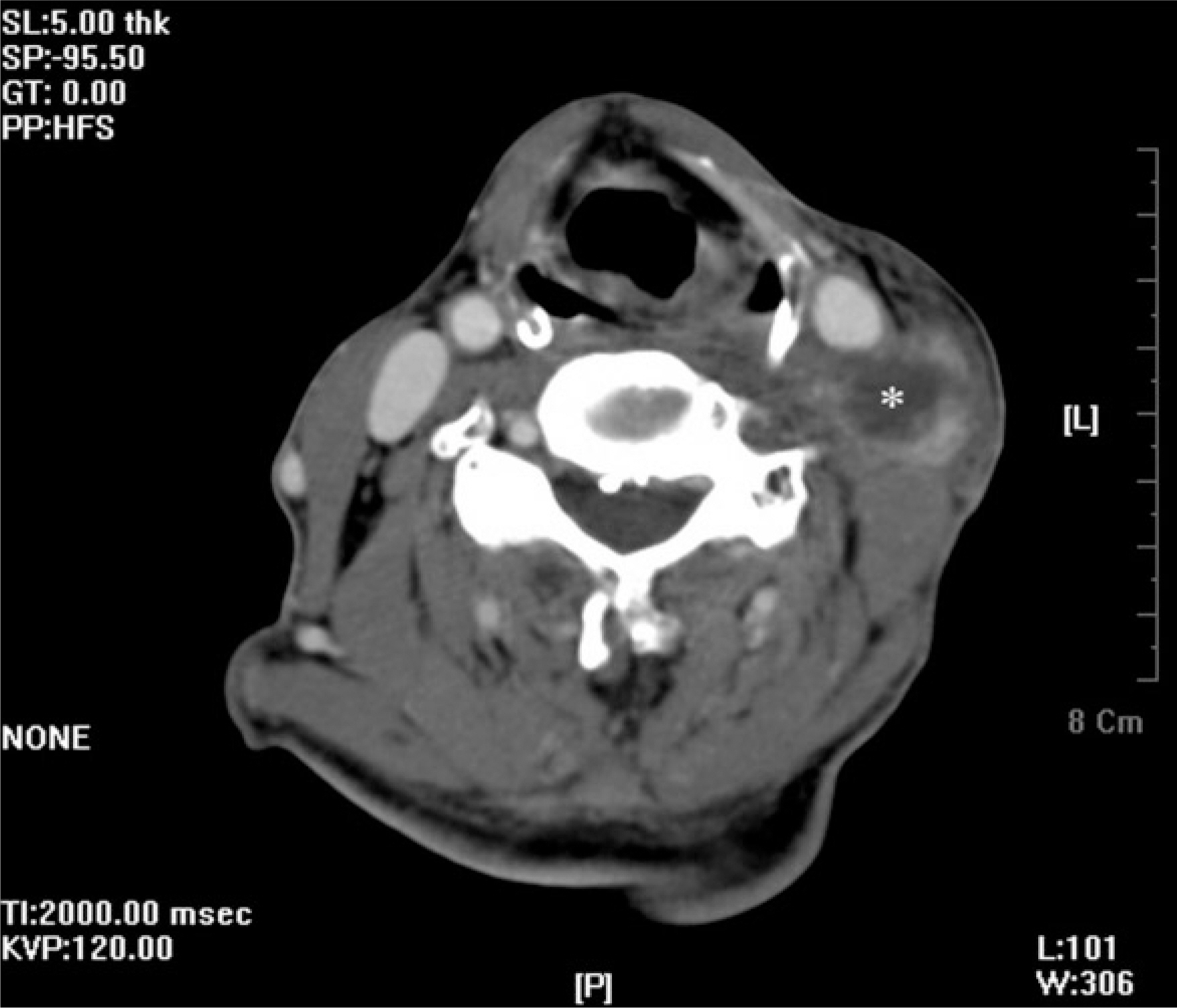
- Postirradiation extraosseous osteogenic sarcomas are uncommon in the head and neck, despite the extensive use of high-dose radiation. It has been described as de novo radiation-induced neoplasm. We present a 73-year-old male who had been treated by radiotherapy for gingival cancer 7 years earlier and later developed extraosseous osteogenic sarcomas (EOSs) of the neck. Microscopically, the neck mass was composed with mesenchymal malignant cells with cartilaginous and osteogenic differentiation. Immunohistochemical stain demonstrated strong positivity of tumor cells for Snail, the one of major epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) inducer. The E-cadherin expression was scarce, showing inverse relationship to Snail expression. Compared with previous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the gingiva, the present EOS sample revealed the remained epithelial cells on cytokeratin immunohistochemistry, suggesting the tumor arise from the cells of epithelial origin. We have also reviewed the previous 6 cases of head and neck EOSs carefully. The clinicopathologic features of the unusual lesion suggest that it is an incomplete EMT of precedent epithelial malignancy rather than de novo pathology.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Lin SY, Chen WM, Wu HH, Chen WY, Chen TH. Extraosseous osteogenic sarcoma. J Chin Med Assoc. 2005; 68:542–5.
Article2. Rao U, Cheng A, Didolkar MS. Extraosseous osteogenic sarcoma: clinicopathological study of eight cases and review of literature. Cancer. 1978; 41:1488–96.3. Sordillo PP, Hajdu SI, Magill GB, Golbey RB. Extraosseous osteogenic sarcoma. A review of 48 patients. Cancer. 1983; 51:727–34.
Article4. Manning JT, Raymond AK, Batsakis JG. Extraosseous osteogenic sarcoma of the parotid gland. J Laryngol Otol. 1986; 100:239–42.
Article5. Das Gupta TK, Hajdu SI, Foote FW Jr. Extraosseous osteogenic sarcoma. Ann Surg. 1968; 168:1011–22.
Article6. Jussawalla DJ, Desai JG. Primary osteogenic sarcoma arising in extraskeletal soft tissues of the neck. Br J Surg. 1964; 51:504–5.
Article7. Parsons WH, Henthorne JC. Extraskeletal osteogenic sarcoma: report of a case of osteogenic sarcoma of the lip. Ann Surg. 1944; 119:595–601.
Article8. Shanoff LB, Spira M, Hardy SB. Myositis ossificans: evolution to osteogenic sarcoma. Report of a histologically verified case. Am J Surg. 1967; 113:537–41.9. Yook JI, Li XY, Ota I, Fearon ER, Weiss SJ. Wnt-dependent regulation of the E-cadherin repressor snail. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280:11740–8.
Article10. Yook JI, Li XY, Ota I, Hu C, Kim HS, Kim NH, et al. A Wnt-Axin2-GSK3beta cascade regulates Snail1 activity in breast cancer cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2006; 8:1398–406.11. Allan CJ, Soule EH. Osteogenic sarcoma of the somatic soft tissues. Clinicopathologic study of 26 cases and review of literature. Cancer. 1971; 27:1121–33.12. Kauffman SL, Stout AP. Extraskeletal osteogenic sarcomas and chondrosarcomas in children. Cancer. 1963; 16:432–9.
Article13. Wurlitzer F, Ayala L, Romsdahl M. Extraosseous osteogenic sarcoma. Arch Surg. 1972; 105:691–5.
Article14. Kalra S, Grimer RJ, Spooner D, Carter SR, Tillman RM, Abudu A. Radiation-induced sarcomas of bone: factors that affect outcome. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007; 89:808–13.15. Tan A, Ngan SY, Choong PF. Postradiation sarcoma of the neck treated with re-irradiation followed by wide excision. World J Surg Oncol. 2006; 4:69.
Article16. Oda H, Tsukita S, Takeichi M. Dynamic behavior of the cadherin-based cell-cell adhesion system during Drosophila gastrulation. Dev Biol. 1998; 203:435–50.17. Peinado H, Olmeda D, Cano A. Snail, Zeb and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 2007; 7:415–28.
Article18. Thiery JP. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002; 2:442–54.
Article19. Becker KF, Rosivatz E, Blechschmidt K, Kremmer E, Sarbia M, Ho ¨fler H. Analysis of the E-cadherin repressor Snail in primary human cancers. Cells Tissues Organs. 2007; 185:204–12.
Article20. Franc l′C, Takkunen M, Dave N, Alameda F, Go′mez S, Rodr l′guez R, et al. Expression of Snail protein in tumor-stroma interface. Oncogene. 2006; 25:5134–44.
Article21. Fine G, Stout AP. Osteogenic sarcoma of the extraskeletal soft tissues. Cancer. 1956; 9:1027–43.
Article22. Brabletz T, Hlubek F, Spaderna S, Schmalhofer O, Hiendlmeyer E, Jung A, et al. Invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer: epithelial-mesenchymal transition, mesenchymal-epithelial transition, stem cells and beta-catenin. Cells Tissues Organs. 2005; 179:56–65.23. Jeschke U, Mylonas I, Kuhn C, Shabani N, Kunert-Keil C, Schindlbeck C, et al. Expression of E-cadherin in human ductal breast cancer carcinoma in situ, invasive carcinomas, their lymph node metastases, their distant metastases, carcinomas with recurrence and in recurrence. Anticancer Res. 2007; 27:1969–74.24. Liu J, Ikeguchi M, Nakamura S, Kaibara N. Re-expression of the cadherin-catenin complex in lymph nodes with metastasis in advanced gastric cancer: the relationship with patient survival. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2002; 21:65–71.25. Park D, Ka � resen R, Axcrona U, Noren T, Sauer T. Expression pattern of adhesion molecules (E-cadherin, alpha-, beta-, gamma-catenin and claudin-7), their influence on survival in primary breast carcinoma, and their corresponding axillary lymph node metastasis. APMIS. 2007; 115:52–65.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and E-cadherin and Vimentin Expression in Basal Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Head and Neck Cancer
- A spindle cell squamous cell carcinoma on the cheek presenting with in-transit metastases and a satellite lesion
- Targeting epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma arising in an odontogenic cyst