J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2011 Jun;37(3):184-194. 10.5125/jkaoms.2011.37.3.184.
Anatomical review of dorsalis pedis artery flap for the oral cavity reconstruction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. leejongh@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Oral Pathology, College of Dentistry, Gangnung-Wonju National University, Gangneung, Korea.
- KMID: 2189771
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2011.37.3.184
Abstract
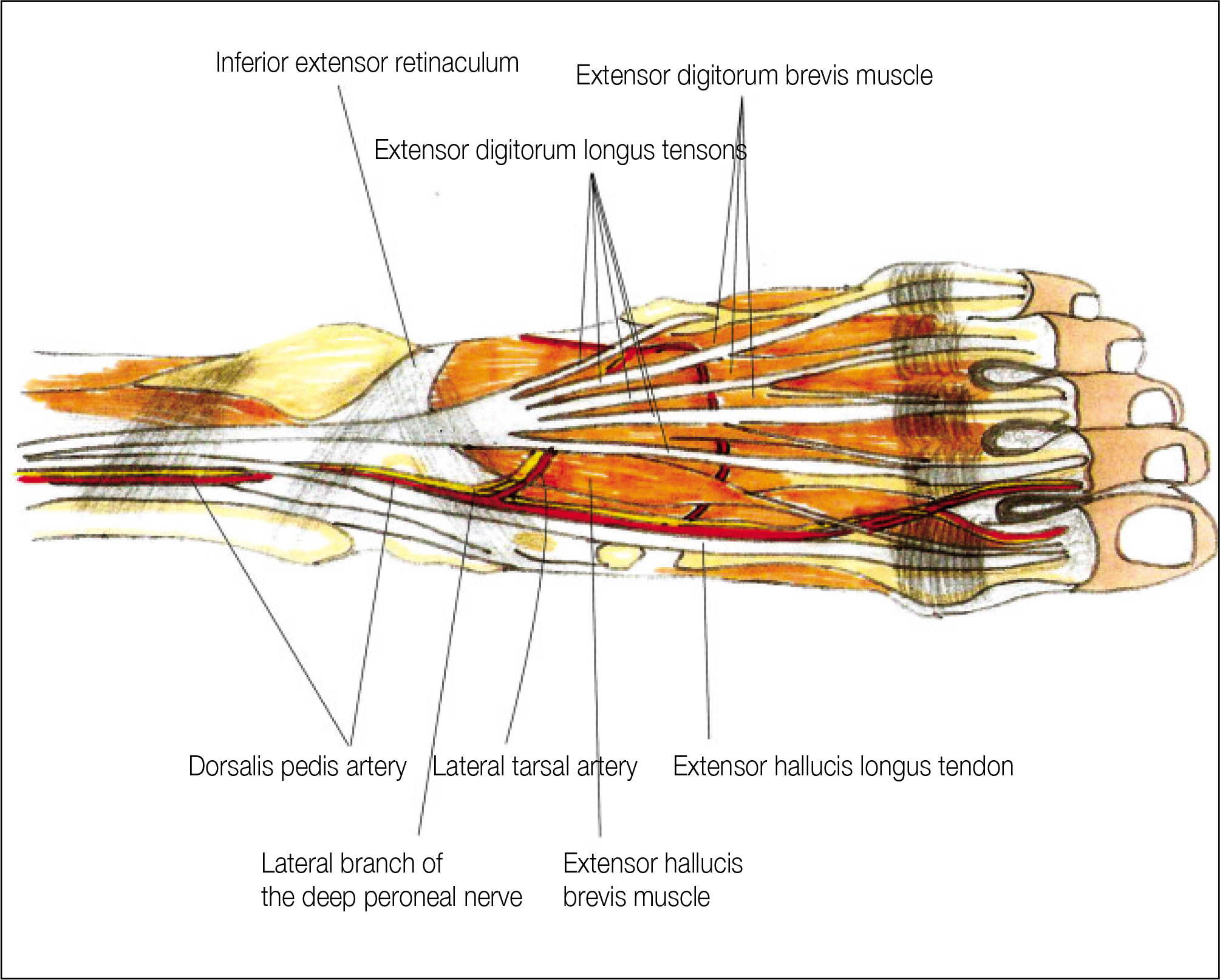
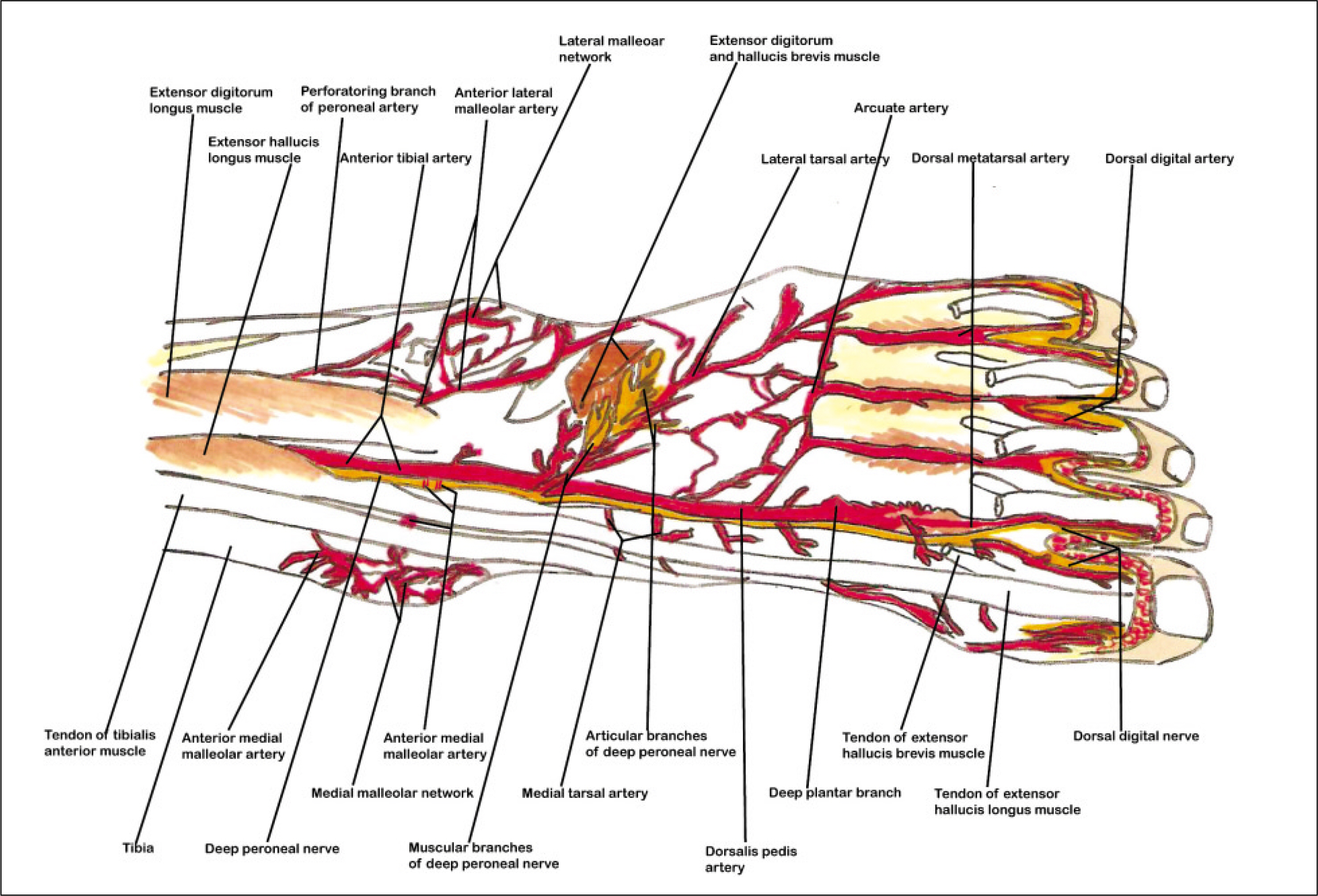
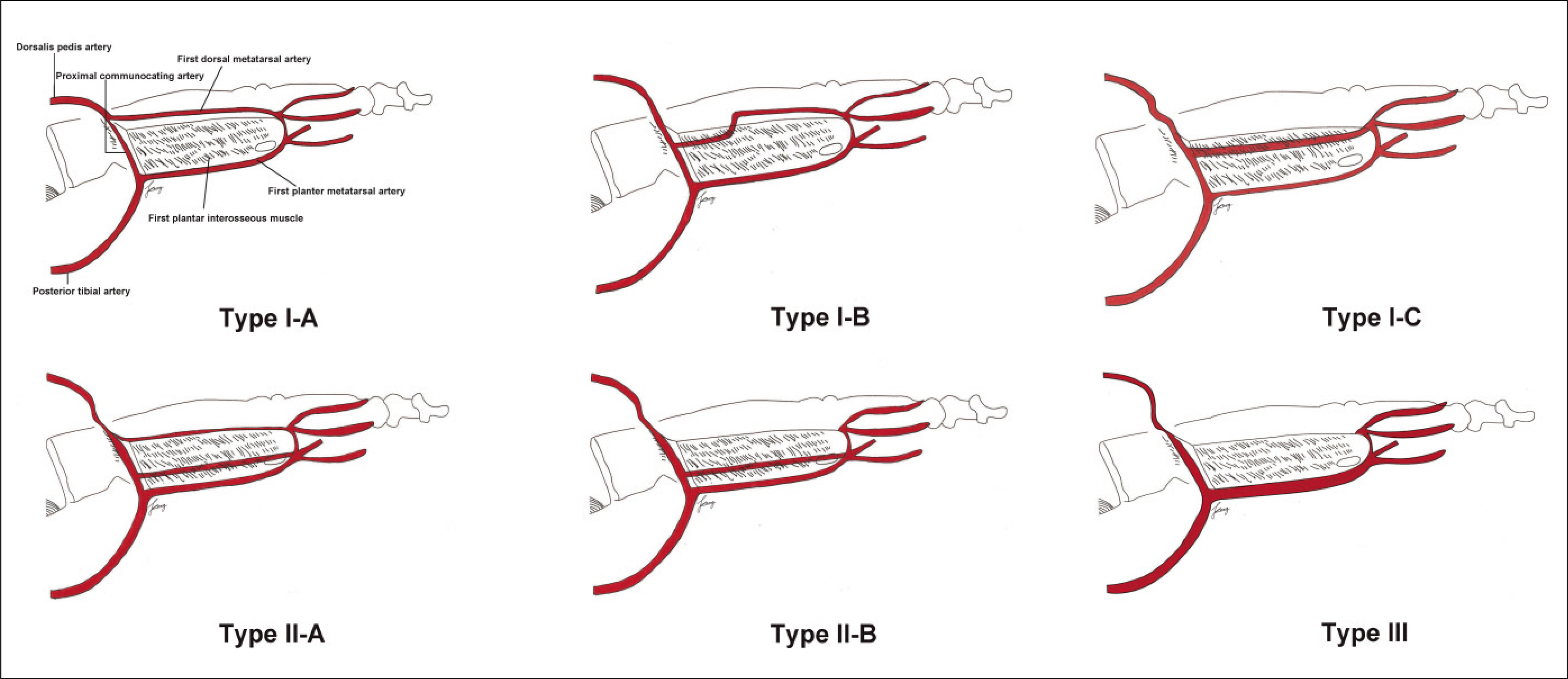
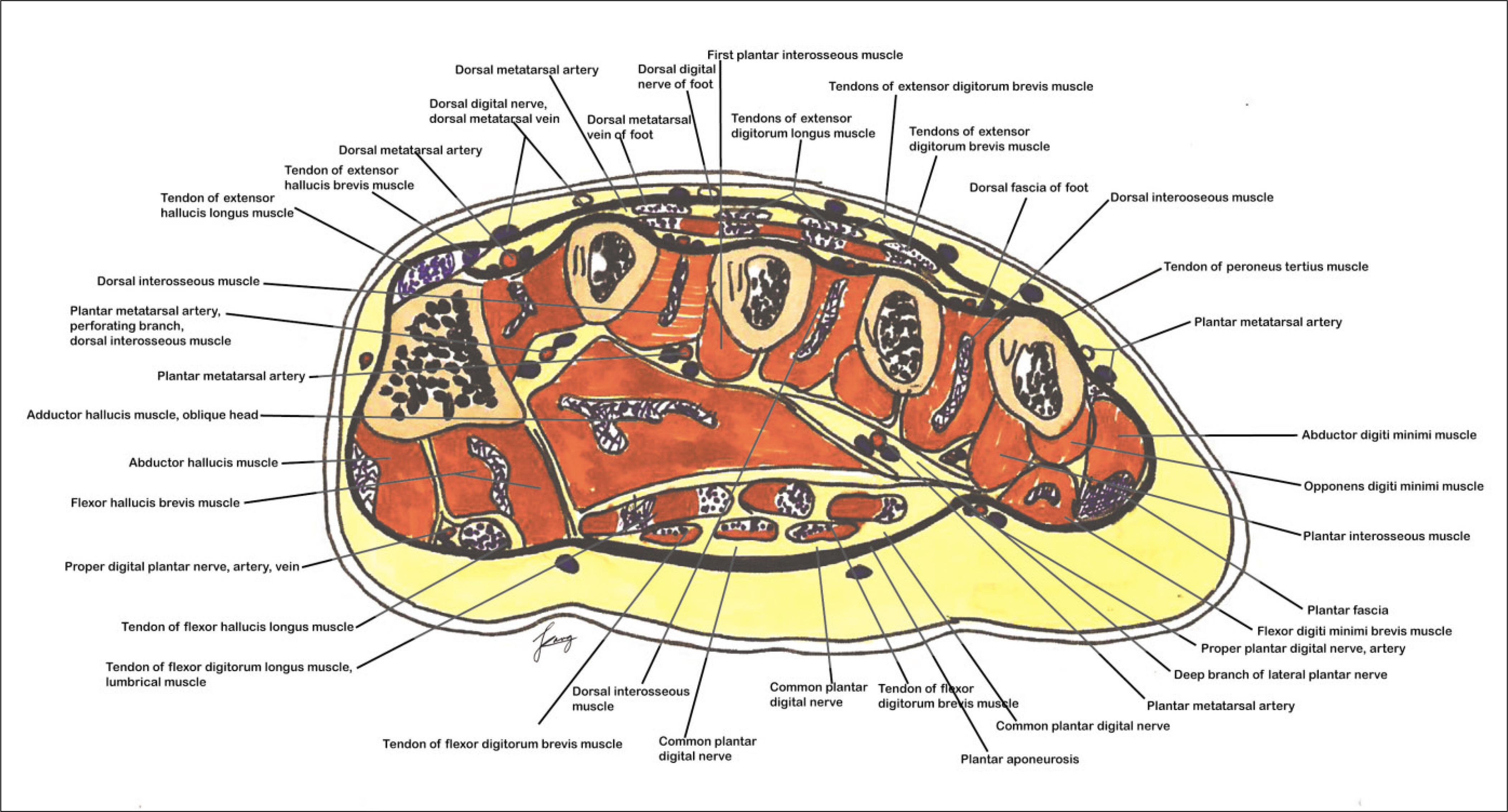
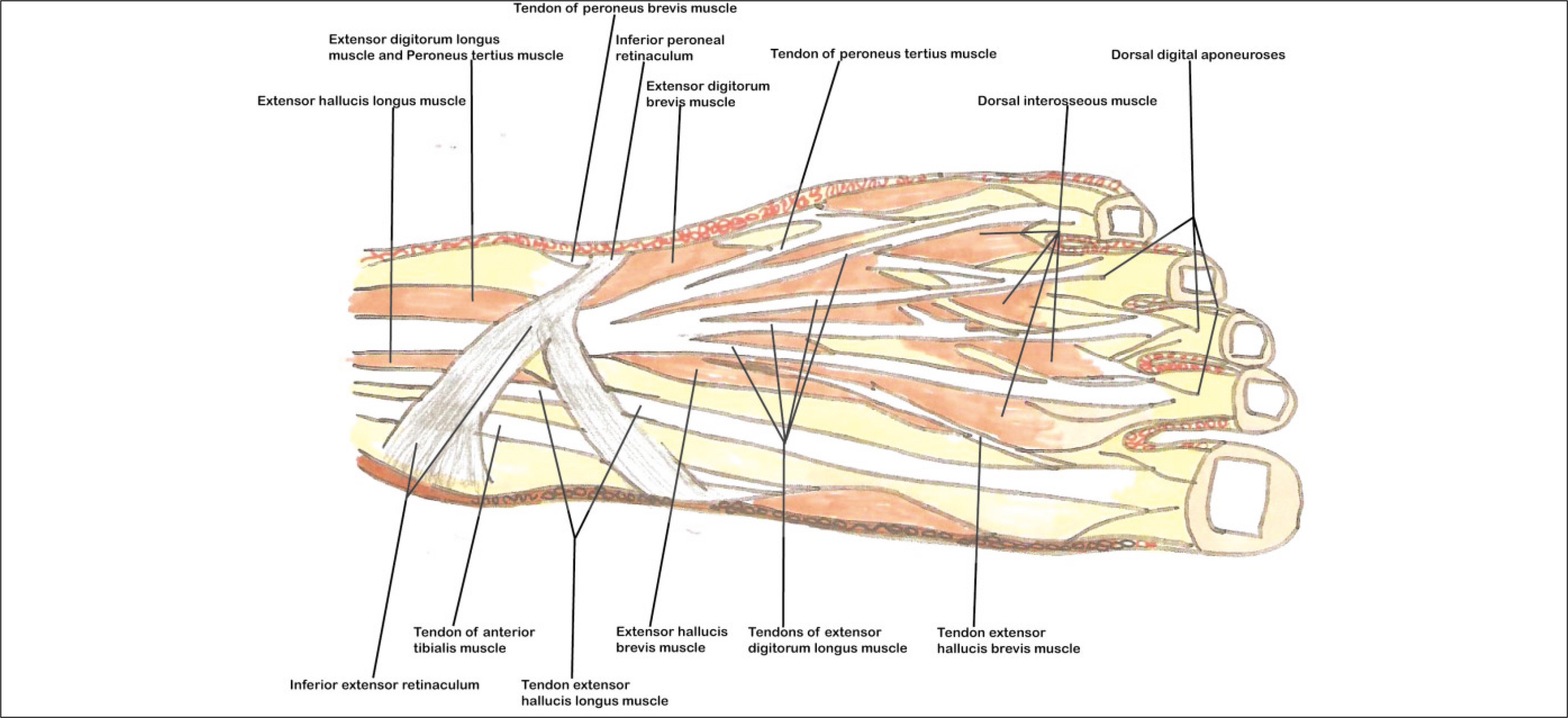
- The dorsalis pedis artery (DPA) was renamed from the anterior tibialis artery after it passed under the extensor retinaculum, and DPA travels between the extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus muscle along the dorsum of the foot. After giving off the proximal and distal tarsal, arcuate and medial tarsal branches, DPA enters the proximal first intermetatarsal space via the first dorsal metatarsal artery (FDMA), which courses over the first dorsal interosseous muscle (FDIM). For detailed knowledge of the neurovascular anatomy of a dorsalis pedis artery flap (DPAF) as a routine reconstructive procedure after the resection of oral malignant tumors, the precise neurovascular anatomy of DPAF must be studied along the DPA courses as above. In this first review article in the Korean language, the anatomical basis of DPAF is summarized and discussed after a delicate investigation of more than 35 recent articles and atlas textbooks. Many advantages of DPAF, such as a consistent flap vascular anatomy, acceptable donor site morbidity, and the ability to perform simultaneous flap harvest using oral cancer ablation procedures, and additional important risks with the pitfalls of DPAF were emphasized. This article will be helpful, particularly for young doctors during the special curriculum periods for the Korean National Board of Specialists in the field of oral and maxillofacial surgery, plastic surgery, otolaryngology, orthopedic surgery, etc.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Azevedo LFL, Zenha H, Rios L, Cunha C, Costa H. Dorsalis pedis free flap in oromandibular reconstruction. Eur J Plast Surg. 2010; 33:355–9.
Article2. O'Brien BM, Shanmugan N. Experimental transfer of composite free flaps with microvascular anastomoses. Aust N Z J Surg. 1973; 43:285–8.3. McCraw JB, Furlow LT Jr. The dorsalis pedis artierialized flap: a clinical study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1975; 55:177–85.4. Ohmori K, Harii K. Free dorsalis pedis sensory flap to the hand, with microvascular anastomoses. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1976; 58:546–54.5. Morrison WA, O'Brien BM, MacLeod AM. The foot as a donor site in reconstructive microsurgery. World J Surg. 1979; 3:43–52.
Article6. Choi TH, Son DG, Han KH. Classification and reconstructive strategies of first web space contracture. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001; 28:522–30.7. Son DG, Kim HJ, Kim JH, Han KH. Dorsalis pedis free flap for hand reconstruction: a technique to minimize donor deformity. Kor J Microsurg. 2004; 13:43–50.8. Alagoz MS, Orbay H, Uysal AC, Comert A, Tuccar E. Vascular anatomy of the metatarsal bones and the interosseous muscles of the foot. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2009; 62:1227–32.
Article9. Kim JK, Chung IH, Lee HY, Yoon KH, Kil YC. Morphological study on the dorsalis pedis and first dorsal metatarsal arteries in Koreans. Korean J Anat. 2001; 34:65–73.10. Li FZ, Yi XG, Liu HS, Wang YX, Wang YK. The blood vessels and nerves of the dorsalis pedis flap. Clin Anat. 1989; 2:9–16.
Article11. Strauch B, Yu HL. Atlas of microvascular surgery; anatomy and operative approaches. 2nd ed.NewYork: Thieme;2006. p. 372–87.12. Sobotta J, Putz R. Sobotta atlas of human anatomy: trunk, viscera, lower limb. 14th ed.Munich: Elsevier Urban & Fischer;13. Gray H, Standring S. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 39th Ed. Edinburgh: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone;2005.14. Lee JH, Dauber W. Anatomic study of the dorsalis pedis-first dorsal metatarsal artery. Ann Plast Surg. 1997; 38:50–5.
Article15. Choi SJ, Jun BH. The extensor digitorum brevis muscle island flap for soft tissue loss around the ankle and distal foot. Kor J Microsurg. 2005; 14:131–7.16. Serafin D. The extensor digitorum brevis flap. Serafin D, editor. Atlas of microsurgical composite tissue transplantation. 1st ed.Philadelphia: WB Saunders;1996. p. 311–20.17. Kalin PJ, Hirsch BE. The origins and function of the interosseous muscles of the foot. J Anat. 1987; 152:83–91.18. Riegger CL. Anatomy of the ankle and foot. Phys Ther. 1988; 68:1802–14.
Article19. Taylor GI, Caddy CM, Watterson PA, Crock JG. The venous territories (venosomes) of the human body: experimental study and clinical implications. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1990; 86:185–213.20. Imanishi N, Kish K, Chang H, Nakajima H, Aiso S. Anatomical study of cutaneous venous flow of the sole. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007; 120:1906–10.
Article21. Robinson DW. Microsurgical transfer of the dorsalis pedis neurovascular island flap. Br J Plast Surg. 1976; 29:209–13.
Article22. Ben-hur N. Reconstruction of the floor of the mouth by a free dorsalis pedis flap with microvascular anastomosis. J Maxillofac Surg. 1980; 8:73–7.
Article23. Acland RD, Flynn MB. Immediate reconstruction of oral cavity and oropharyngeal defects using microvascular free flaps. Am J Surg. 1978; 136:419–23.
Article24. Ohmori K, Sekiguchi J, Ohmori S. Total rhinoplasty with a free osteocutaneous flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1979; 63:387–94.
Article25. Bell MS, Barron PT. A new method or oral reconstruction using a free composite foot flap. Ann Plast Surg. 1980; 5:281–7.26. MacLeod AM, Robinson DW. Reconstruction of defects involving the mandible and floor of mouth by free osteocutaneous flaps derived from the foot. Br J Plast Surg. 1982; 35:239–46.
Article27. Rheiner P. Reconstruction of scrotum with a free flap-late results. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 1983; 15:261–4.28. Ismail TI. The dorslis pedis myofascial flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1990; 86:573–8.29. Banis JC Jr. Thin cutaneous flap for intra oral reconstruction: the dorsalis pedis free flap revisited. Microsurgery. 1988; 9:132–40.
Article30. Zuker RM, Manktelow RT. The dorsalis pedis free flap: technique of elevation, foot closure, and flap application. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1986; 77:93–104.31. Naasan A, Quaba AA. Reconstruction of the oral commissure by vascularized toe web transfer. Br J Plast Surg. 1990; 43:376–8.32. Koshima I, Inagawa K, Urushibara K, Moriguchi T. Combined submental flap with toe web for reconstruction of the lip with oral commissure. Br J Plast Surg. 2000; 53:616–9.
Article33. Oser RF, Picus D, Hicks ME, Darcy MD, Hovsepian DM. Accuracy of DSA in the evaluation of patency of infrapopliteal vessels. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1995; 6:589–94.
Article34. Carpenter JP, Owen RS, Holland GA, Baum RA, Barker CF, Perloff LJ, et al. Magnetic resonance angiography of the aorta, iliac, and femoral arteries. Surgery. 1994; 116:17–23.35. Lee HM, Wang Y, Sostman HD, Schwartz LH, Khilnani NM, Trost DW, et al. Distal lower extremity arteries: evaluation with two-dimensional MR digital subtraction angiography. Radiology. 1998; 207:505–12.
Article36. Lee JM, Kang SG, Byun JN, Kim YC, Choi JY, Kim DH, et al. Evaluation of the pedal artery: comparison of three-dimensional gadolinium-enhanced MR angiography with digital subtraction angiography. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2002; 47:21–26.
Article37. Korean Medical Association. English-Korean. Korean-English Medical Terminology;5th edition. 2008.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Heel Pad Reconstruction using Doresalis Pedis Free Flap or Rotation Flap
- Morphological Study on the Dorsalis Pedis and First Dorsal Metatarsal Arteries in Koreans
- Reverse Dorsalis Pedis Flap Based on the Distal Communicating Artery of the Dorsalis Pedis Artery for the Reconstruction of the Forefoot Defect
- Experience of Microsurgery Using Dorsalis Pedis Artery
- Hinged multiperforator-based extended dorsalis pedis adipofascial flap for dorsal foot defects