J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2007 Aug;42(4):523-529. 10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.4.523.
Availability of D-dimer Test for the Diagnosis ofDeep Vein Thrombosis after Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Center for Joint Disease, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Jeonnam, Korea. cjssudbghs@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2186515
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.4.523
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To investigate the prevalence of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) after Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and evaluate the availability of D-dimer test for the diagnosis of DVT after TKA.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From April 2006 to July 2006, 140 consecutive patients, who had degenerative osteoarthritic knees and underwent primary total knee arthroplasty, were enrolled in this study. General and hematological risk factors were compared between DVT positive and negative patients. D-dimer level was checked preoperatively, and at 1, 7 and 14 days after surgery. A diagnosis of DVT was established by computed tomography venography.
RESULTS
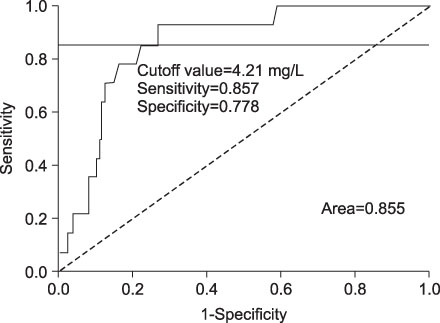
DVT was found in 48 (34%) patients and only 5 (10.4%) showed symptoms of DVT. Regarding the risk factors, only obesity was significantly associated with an increased incidence of DVT (p=0.049). Seven days after surgery, the average D-dimer level in the DVT positive and negative patients was 4.90 mg/L and 3.12 mg/L, respectively (p=0.000).
CONCLUSION
In our study patients, the incidence of symptomatic DVT was lower than in the Western population. We recommend obesity, clinical symptoms and D-dimer value at 7 days after surgery as a valuable screening tests for detecting DVT.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bates SM, Grand'Maison A, Johnston M, et al. A latex Ddimer reliably excludes venous thromboembolism. Arch Intern Med. 2001. 161:447–453.
Article2. Bounameaux H, Miron MJ, Blanchard J, de Moerloose P, Hoffmeyer P, Leyvraz PF. Measurement of plasma D-dimer is not useful in the prediction or diagnosis of postoperative deep vein thrombosis in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1998. 9:749–752.
Article3. Cohen SH, Ehrlich GE, Kauffman MS, Cope C. Thrombophlebitis following knee surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973. 55:106–112.
Article4. Elias A, Aptel I, Huc B, et al. D-dimer test and diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis: a comparative study of 7 assays. Thromb Haemost. 1996. 76:518–522.
Article5. Geerts WH, Heit JA, Clagett GP, et al. Prevention of venous thromboembolism. Chest. 2001. 119:Suppl 1. S132–S175.
Article6. Haake DA, Berkman SA. Venous thromboembolic disease after hip surgery. Risk factors, prophylaxis, and diagnosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989. 242:212–231.7. Heit JA, O'Fallon WM, Petterson TM, et al. Relative impact of risk factors for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a population-based study. Arch Intern Med. 2002. 162:1245–1248.8. Jick H, Slone D, Westerholm B, et al. Venous thromboembolic disease and ABO blood type. A cooperative study. Lancet. 1969. 1:539–542.
Article9. Khaw FM, Moran CG, Pinder IM, Smith SR. The incidence of fatal pulmonary embolism after knee replacement with no prophylactic anticoagulation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993. 75:940–941.
Article10. Kim V, Spandorfer J. Epidemiology of venous thromboembolic disease. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2001. 19:839–859.
Article11. Kim YH. The incidence of deep vein thrombosis after cementless and cemented knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990. 72:779–783.
Article12. Kim YH, Kim JS. Incidence and natural history of deep-vein thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty. A prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002. 84:566–570.13. Kim YH, Suh JS. Low incidence of deep-vein thrombosis after cementless total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988. 70:878–882.
Article14. Ko PS, Chan WF, Siu TH, Khoo J, Wu WC, Lam JJ. Deep venous thrombosis after total hip or knee arthroplasty in a "low-risk" Chinese population. J Arthroplasty. 2003. 18:174–179.
Article15. Koster T, Blann AD, Briet E, Vandenbroucke JP, Rosendaal FR. Role of clotting factor VIII in effect of von Willebrand factor on occurrence of deep-vein thrombosis. Lancet. 1995. 345:152–155.
Article16. Koster T, Rosendaal FR, Briët E, et al. Protein C deficiency in a controlled series of unselected outpatients: an infrequent but clear risk factor for venous thrombosis (Leiden Thrombophilia Study). Blood. 1995. 85:2756–2761.17. Kyrle PA, Minar E, Hirschl M, et al. High plasma levels of factor VIII and risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med. 2000. 343:457–462.18. Lane DA, Grant PJ. Role of hemostatic gene polymorphisms in venous and arterial thrombotic disease. Blood. 2000. 95:1517–1532.
Article19. Lee KB, Song EK, Seon JK, Kim JK. Deep vein thrombosis after joint arthroplasty in lower extremity: venography versus color Doppler ultrasonography. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1999. 34:31–36.
Article20. Lee YG, Kim MK, Cho KJ, et al. The diagnostic availability of multidetector-row computed tomography (MDCT) in deep vein thrombosis developed after joint arthroplasty. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2006. 41:134–139.21. Lieberman JR, Geerts WH. Prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994. 76:1239–1250.
Article22. Leyvraz PF, Richard J, Bachmann F, et al. Adjusted versus fixed-dose subcutaneous heparin in the prevention of deep-vein thrombosis after total hip replacement. N Engl J Med. 1983. 309:954–958.
Article23. Meijers JC, Tekelenburg WL, Bouma BN, Bertina RM, Rosendaal FR. High levels of coagulation factor XI as a risk factor for venous thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2000. 342:696–701.
Article24. Mont MA, Jones LC, Rajadhyaksha AD, et al. Risk factors for pulmonary emboli after total hip or knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. 422:154–163.
Article25. Morrey BF, Adams RA, Ilstrup DM, Bryan RS. Complications and mortality associated with bilateral or unilateral total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987. 69:484–488.
Article26. Moser KM. Pulmonary embolism. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977. 115:829–852.27. Oger E. Incidence of venous thromboembolism: a community-based study in Western France. EPI-GETBP Study Group. Groupe d'Etude de la Thrombose de Bretagne Occidentale. Thromb Haemost. 2000. 83:657–660.28. Patterson BM, Marchand R, Ranawat C. Complications of heparin therapy after total joint arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989. 71:1130–1134.
Article29. Perrier A, Bounameaux H. Cost-effective diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Thromb Haemost. 2001. 86:475–487.
Article30. Rosendaal FR. Risk factors for venous thrombosis: prevalence, risk and interaction. Semin Hematol. 1997. 34:171–187.31. Sharrock NE, Brien WW, Salvati EA, Mineo R, Garvin K, Sculco TP. The effect of intravenous fixed-dose heparin during total hip arthroplasty on the incidence of deep-vein thrombosis. A randomized, double-blind trial in patients operated on with epidural anesthesia and controlled hypotension. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990. 72:1456–1461.
Article32. Shiota N, Sato T, Nishida K, et al. Changes in LPIA D-dimer levels after total hip or knee arthroplasty relevant to deep-vein thrombosis diagnosed by bilateral ascending venography. J Orthop Sci. 2002. 7:444–450.
Article33. Tait RC, Walker ID, Perry DJ, et al. Prevalence of antithrombin deficiency in the healthy population. Br J Haematol. 1994. 87:106–112.
Article34. Tait RC, Walker ID, Reitsma PH, et al. Prevalence of protein C deficiency in the healthy population. Thromb Haemost. 1995. 73:87–93.
Article35. van Boven HH, Vandenbroucke JP, Briët E, Rosendaal FR. Gene-gene and gene-environment interactions determine risk of thrombosis in families with inherited antithrombin deficiency. Blood. 1999. 94:2590–2594.
Article36. van Hylckama Vlieg A, van der Linden IK, Bertina RM, Rosendaal FR. High levels of factor IX increase the risk of venous thrombosis. Blood. 2000. 95:3678–3682.37. Warwick DJ, Whitehouse S. Symptomatic venous thromboembolism after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997. 79:780–786.
Article38. Weijl NI, Rutten MF, Zwinderman AH, et al. Thromboembolic events during chemotherapy for germ cell cancer: a cohort study and review of the literature. J Clin Oncol. 2000. 18:2169–2178.
Article39. White RH, Henderson MC. Risk factors for venous thromboembolism after total hip and knee replacement surgery. Curr Opini Pulm Med. 2002. 8:365–371.
Article40. Yoo MC, Cho YJ, Kim KI, Im YJ, Cho KY, Ryu KN. Incidence of deep vein thrombosis after major hip surgery and diagnostic value of D-dimer. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2006. 41:103–109.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Foot Pump on Prevention of Deep Vein Thrombosis Following Total Knee Arthroplasty
- May–Thurner Syndrome after Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Quantification and Comparison of D-dimer after Pneumatic Tourniquet Release in Patients Undergoing Arthroscopic Knee Surgery on General Anesthesia and Epidural Anesthesia
- Diagnosis of the Deep Vein Thrombosis with Multidetector-Row Computed Tomographic Venography after Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Deep Vein Thrombosis after Total Knee Replacement: Incidence and correlation with clinical risk factors