J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2008 Oct;43(5):567-571. 10.4055/jkoa.2008.43.5.567.
Changes in Vertebral Axial Rotation after Thoracoscopic Scoliosis Correction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. csl@smc.samsung.co.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Sanbon Hospital of Wonkwang University, Gunpo, Korea.
- KMID: 2186417
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2008.43.5.567
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: In this study, we investigated whether thoracoscopic anterior correction can effectively derotates the scoliotic spine and we also evaluated the patterns of derotational changes inside the instrumented area and at the junction between the instrumented and uninstrumented area.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
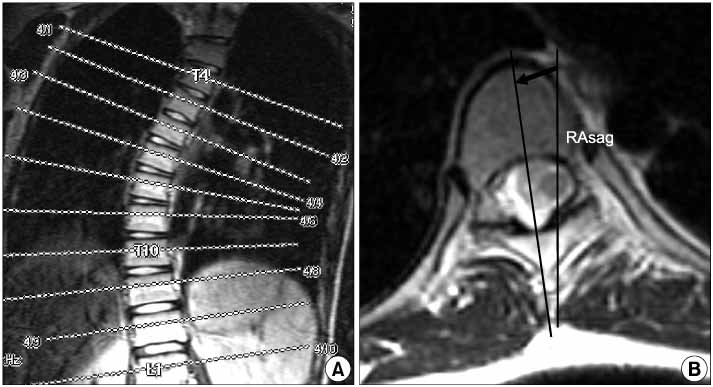
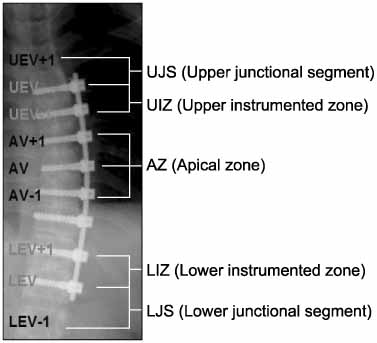
Preoperative and postoperative MR images with single axial cuts through each vertebral level were obtained in 20 patients who underwent thoracoscopic anterior instrumentation. Each vertebral rotation was measured by the use of Aaro's method. Vertebral axial derotation of the apical zone (AZ), upper instrumented zone (UIZ), lower instrumented zone (LIZ) and junctional segment were compared. The amount of segmental rotation and segmental derotation in each zone was calculated. Statistical analysis was performed by the use of by 2-way ANOVA and the Wilcoxon signed ranks test.
RESULTS
The average axial rotations at AZ were 10.1degrees preoperatively and 5.3degrees postoperatively with an average correction rate of 48%. Derotation of the AZ was greater than the UIZ and LIZ. For the LIZ derotation was not significant (p=0.023) while for the UIZ there was a significant derotation (p<0.001). Postoperatively, the first uninstrumented vertebra rotated significantly in the direction of rotation of the instrumented end vertebra. Preoperative and postoperative segmental rotation was higher in the UIZ and LIZ than in the AZ. However, segmental derotation occurred uniformly in the instrumented area. At the junctional segment, preoperative segmental rotation was same as that of the UIZ and LIZ and segmental derotation was not significant.
CONCLUSION
Thoracoscopic scoliosis correction can achieve effective axial correction by causing derotation of each of the vertebral bodies and segmental derotation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aaro S, Dahlborn M, Svensson L. Estimation of vertebral rotation in structural scoliosis by computer tomography. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh). 1978. 19:990–992.
Article2. Betz RR, Harms J, Clements DH 3rd, et al. Comparison of anterior and posterior instrumentation for correction of adolescent thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 1999. 24:225–239.
Article3. Kaneda K, Shono Y, Satoh S, Abumi K. Anterior correction of thoracic scoliosis with Kaneda anterior spinal system. A preliminary report. Spine. 1997. 22:1358–1368.4. Lee SM, Suk SI, Chung ER. Direct vertebral rotation: a new technique of three-dimensional deformity correction with segmental pedicle screw fixation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2004. 29:343–349.
Article5. Picetti GD 3rd, Ertl JP, Bueff HU. Endoscopic instrumentation, correction, and fusion of idiopathic scoliosis. Spine J. 2001. 1:190–197.
Article6. Wood KB, Olsewski JM, Schendel MJ, Boachie-Adjei O, Gupta M. Rotational changes of the vertebral pelvic axis after sublaminar instrumentation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 1997. 22:51–57.
Article7. Wood KB, Transfeldt EE, Ogilvie JW, Schendel MJ, Bradford DS. Rotational changes of the vertebral-pelvic axis following Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation. Spine. 1991. 16:Suppl 8. S404–S408.
Article8. Zielke K. Ventral derotation spondylodesis. Results of treatment of cases of idiopathic lumbar scoliosis (author's (author's transl)). Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 1982. 120:320–329.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Intersegmental Compression on the 3-D Correction of Idiopathic Scoliosis Using Thoracoscopic Surgery
- Comparison of en-bloc direct vertebrae rotation and non-direct vertebrae rotation for the correction of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis Lenke 5C: a retrospective study in Changsha, China
- Expressing Cobb Angle as Linear Measurement in Scoliosis and Its Significance: A Clinical and Geometrical Analysis of Scoliosis
- Direct Vertebral Rotation (DVR): A New Technique of 3-D Deformity Correction with Segmental Pedicle Screw Fixation in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (AIS)
- Pedicle Screw Instrumentation for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: The Insertion Technique, the Fusion Levels and Direct Vertebral Rotation