J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2009 Jun;44(3):344-349. 10.4055/jkoa.2009.44.3.344.
Does a Radiolucent Zone Surrounding the Pedicle Screws mean Nonunion?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea. hyparkys@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2186343
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2009.44.3.344
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: We wanted to retrospectively evaluate the clinical significance of radiolucent zones surrounding the pedicle screws after spinal fusion.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Spinal surgery was performed between May 2003 and December 2005 on elective patients with degenerative lumbar disorders and they underwent transpedicular screw fixation and posterolateral fusion and these patients were the subjects of the study. There were 124 cases with more than 2 years of follow up. Determination of the radiolucent zones around pedicle screws was done using simple x-rays and the cases were divided in to 4 different groups: segmental fixation with short (2 or less segments) or, long (3 or more segments) segmental fixation and those cases with or without sacral fixation. Comparative analysis was done according to osteoporosis, the location of the pedicle screws, the degree of bony-union and fixation of the anterior cortex of the sacrum.
RESULTS
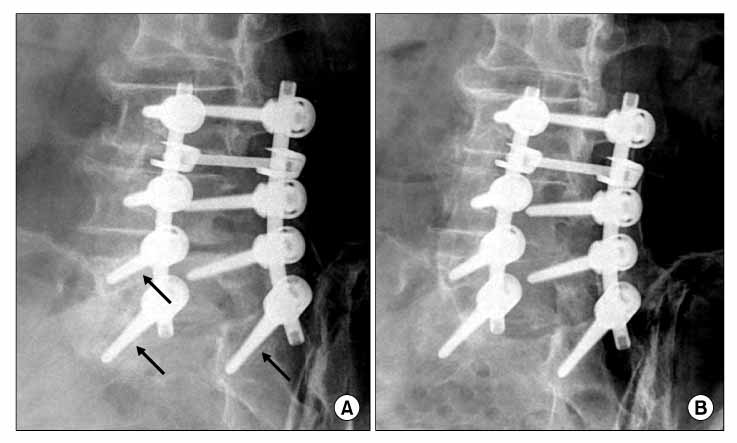
Among the 124 cases and 846 pedicle screws, 189 pedicle screws (22%) had radiolucent zones; 151 of the 189 pedicle screws with a radiolucent zone (27%) were in the sacral fixed group, while 38 of the 189 pedicle screws with a radiolucent zone (13%) were in the non-sacral fixed group, and the difference was significant (p=0.001). In the case of anterior cortical fixation in the sacral fixed group and the complete bony-union, the radiolucent zones had a significantly lower incidence, while the group of patients with osteoporosis (a T score lower than -2.5) had a higher incidence of radiolucent zones.
CONCLUSION
The radiolucent zones surrounding the pedicle screws after spinal fusion were closely related to spinal fusion with sacral fixation and pseudarthrosis, and these radiolucent zones mostly occurred before complete bony-union. The existence of osteoporosis and the techniques of sacral fixation and many different contributing factors must be considered, and careful monitoring is needed even if the radiolucent zone progressive after complete bony-union.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Comparative Study between Combined and Posterior Surgical Treatments for Post-traumatic Kyphosis
Ye-Soo Park, Young-Seok Lee, Seung-Wook Back, Jae-Hoon Kim, Doo-Yeon Lee
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2011;46(3):200-204. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2011.46.3.200.
Reference
-
1. Alanay A, Vyas R, Shamie AN, Sciocia T, Randolph G, Wang JC. Safety and efficacy of implant removal for patients with recurrent back pain after a failed degenerative lumbar spine surgery. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007. 20:271–277.
Article2. Bae SW, Kwak HY, Song BY, Yoo JC, An YJ. Radiolucent zones surrounding transpedicular screws after lumbar spinal instrumented fusion. J Korean Spine Sug. 2005. 12:115–122.
Article3. Diwan AD, Parvartaneni H, Cammisa F. Failed degenerative lumbar spine surgery. Orthop Clin N Am. 2003. 34:309–324.
Article4. Esses SI, Sachs BL, Dreyzin V. Complications associated with the technique of pedicle screw fixation. A selected survey of ABS members. Spine. 1993. 18:2231–2238.
Article5. Gibson JN, Waddell G. Surgery for degenerative lumbar spondylosis: updated cochrane review. Spine. 2005. 30:2312–2320.
Article6. Hsu CC, Chao CK, Wang JL, Hou SM, Tsai YT, Lin J. Increase of pullout strength of spinal pedicle screws with conical core: biomechamical tests and finite element analyses. J Orthop Res. 2005. 23:788–794.7. Kim YJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Rinella AS, Edwards C 2nd. Pseudarthrosis in primary fusions for adult idiopathic scoliosis: incidence, risk factors, and outcome analysis. Spine. 2005. 30:468–474.
Article8. Korovessis P, Parazisis Z, Koureas G, Lambiris E. Rigid, semirigid Versus dynamic instrumentation for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: a correlative radiological and clinical analysis of short-term results. Spine. 2004. 29:735–742.9. Kumar MN, Baklanov A, Chopin D. Correlation between sagittal plane changes and adjacent segment degeneration following lumbar spine fusion. Eur Spine J. 2001. 10:314–319.
Article10. Larsen JM, Capen DA. Pseudarthrosis of the lumbar spine. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1997. 5:153–162.
Article11. Lauerman WC, Bradford DS, Transfeldt EE, Ogilvie JW. Management of pseudarthrosis after arthrodesis of the spine for idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991. 73:222–236.
Article12. Malter AD, McNeney B, Loeser JD, Devo RA. 5-year reoperation rates after different types of lumbar spine surgery. Spine. 1998. 23:814–820.
Article13. Okuyama K, Abe E, Suzuki T, Tamura Y, Chiba M, Sato K. Influence of bone mineral density on pedicle screw fixation: a study of pedicle screw fixation augmenting posterior lumbar interbody fusion in elderly patients. Spine J. 2001. 1:402–407.14. Ozawa T, Takahashi K, Yamagata M, et al. Insertional torque of the lumbar pedicle screw during surgery. J Orthop Sci. 2005. 10:133–136.
Article15. Pihlajamaki H, Myllynen P, Böstman O. Complications of transpedicular lumbosacral fixation for non-traumatic disorders. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997. 79:183–189.16. Sandén B, Olerud C, Petren-Mallmin M, Johansson C, Larsson S. The significance of radiolucent zones surrouding pedicle screws. Definition of screw loosenins in spinal instrumentation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004. 86:457–461.17. Schatzker J, Horne JG, Sumner-Smith G. The effect of movement on the holding power of screws in bone. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1975. 111:257–262.
Article18. Wetzel FT, Brustein M, Phillips FM, Trott S. Hardware failure in an unconstrained lumbar pedicle screw system. A 2-year follow-up study. Spine. 1999. 24:1138–1143.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Radiolucent Zones Surrounding Transpedicular Screws After Lumbar Spinal Instrumented Fusion
- Clinical Significance of the Radiolucent Zone Around the Pedicle Screws in the Lumbar Degenerative Disease
- Pseudarthrosis at L5-S1 after Posterolateral Lumbar Fusion
- Bone Resorption Around Pedicle Screws After Pedicle Screw Plate Fixation
- Clear Zone Formation around Screws in the Early Postoperative Stages after Posterior Lumbar Fusion Using the Cortical Bone Trajectory Technique