J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2011 Aug;46(4):320-325. 10.4055/jkoa.2011.46.4.320.
Accuracy of Inter Femoral Head Center Distance Measurement and Evaluation for Coronal Alignment of Femoral Component during Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Murup Hospital, Changwon, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. osjjaeheon@naver.com
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2185430
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2011.46.4.320
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Alignment is an important factor in the long-term success of total knee arthroplasty. In the total knee arthroplasty, the conventional extramedullary femoral alignment system has significant error in femoral coronal alignment, since it is difficult to find the femoral head center and it is time consuming to determine during the operation. The purpose of our study was to evaluate the accuracy of the newly-designed marker system for extramedullary femoral alignment that uses radiologic distance between the 2 femoral head centers.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
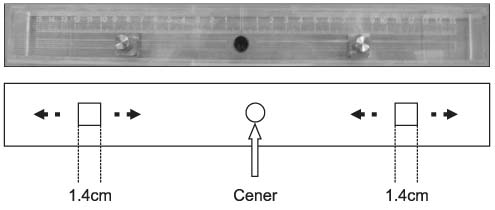
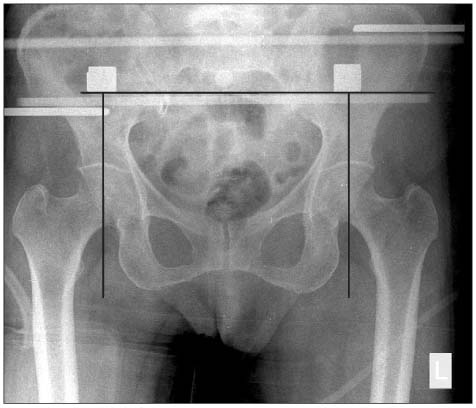
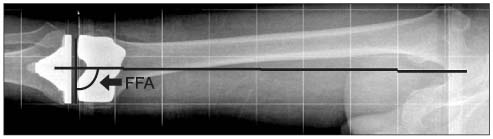
Between July 2008 and July 2009, 90 patients (100 knees) with knee osteoarthritis underwent total knee arthroplasty using the femoral extramedullary femoral guide system. We measured the distance between the femoral head centers using the radiologic picture archiving and communication system (PACS, General Electric, Milwaukee, WI) system preoperatively, then plastic rods and metal pegs were used to simulate the inter femoral head center distance. By placing the center of the plastic rod after marking the inter femoral head center distance on the central body line, we could trace the coronal mechanical axis. We measured the angle between the femoral mechanical axis and the femoral component in standing long leg antero-posterior radiograph to assess radiologically the accuracy of coronal alignment postoperatively.
RESULTS
The average femoral length in the study group was 402.5+/-16.2 mm. The mean distance between the femoral head and the center of the marker was 49.6+/-17.9 mm. The average error in estimation of the distance between the femoral head center and the metal peg of the marker was 3.78+/-3.14 mm. The positional error in alignment was 1degrees or less in 90% and 2degrees or less in 100% of knees. The average angle of femoral component to femoral mechanical axis was 89.9+/-1.5degrees (range 84.4-93.6degrees). The coronal alignment of the femoral components was within 90degrees+/-3degrees in -96% of cases.
CONCLUSION
Our results suggest that the clinical method reported here is a simple and reliable method to localize the center of the femoral head during total knee arthroplasty.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Andriacchi TP. Biomechanics and gait analysis in total knee replacement. Orthop Rev. 1988. 17:470–473.2. Laskin RS. Total knee arthroplasty using an uncemented, polyethylene tibial implant. A seven-year follow-up study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993. (288):270–276.
Article3. Matsuda S, Miura H, Nagamine R, et al. Posterior tibial slope in the normal and varus knee. Am J Knee Surg. 1999. 12:165–168.4. Mihalko WM, Krackow KA. Posterior cruciate ligament effects on the flexion space in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999. (360):243–250.
Article5. Matsuda Y, Ishii Y, Ichimura K. Identifying the center of the femoral head using ultrasonography to assess the higher accuracy of femoral extramedullary guides in TKA. J Orthop Sci. 2004. 9:6–9.
Article6. Brys DA, Lombardi AV Jr, Mallory TH, Vaughn BK. A comparison of intramedullary and extramedullary alignment systems for tibial component placement in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991. (263):175–179.
Article7. Dennis DA, Channer M, Susman MH, Stringer EA. Intramedullary versus extramedullary tibial alignment systems in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1993. 8:43–47.
Article8. Engh GA, Petersen TL. Comparative experience with intramedullary and extramedullary alignment in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1990. 5:1–8.
Article9. Kandel L, Vasili C, Kirsh G. Extramedullary femoral alignment instrumentation reduces blood loss after uncemented total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2006. 19:256–258.
Article10. Kumar N, Saleh J, Gardiner E, Devadoss VG, Howell FR. Plugging the intramedullary canal of the femur in total knee arthroplasty: reduction in postoperative blood loss. J Arthroplasty. 2000. 15:947–949.11. Markel DC, Femino JE, Farkas P, Markel SF. Analysis of lower extremity embolic material after total knee arthroplasty in a canine model. J Arthroplasty. 1999. 14:227–232.
Article12. Seo JG, Kim BK, Moon YW, et al. Bony landmarks for determining the mechanical axis of the femur in the sagittal plane during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Surg. 2009. 1:128–131.
Article13. Bargren JH, Blaha JD, Freeman MA. Alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Correlated biomechanical and clinical observations. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983. (173):178–183.14. Jeffery RS, Morris RW, Denham RA. Coronal alignment after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991. 73:709–714.
Article15. Lotke PA, Ecker ML. Influence of positioning of prosthesis in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977. 59:77–79.
Article16. Rand JA, Coventry MB. Ten-year evaluation of geometric total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988. (232):168–173.
Article17. Cates HE, Ritter MA, Keating EM, Faris PM. Intramedullary versus extramedullary femoral alignment systems in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993. (286):32–39.
Article18. Baldini A, Adravanti P. Less invasive TKA: extramedullary femoral reference without navigation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008. 466:2694–2700.19. Seo JG, Moon YW, Kim YS. A comparison of extramedullary and intramedullary femoral component alignment guide systems in TKA. J Korean Knee Soc. 2006. 18:47–54.20. Samarji RS, Charalambous CP, Waldron S, Noble J. Placement of a palpable marker adjacent to the mid-inguinal point: assessment of a clinical method for detecting the femoral head centre during knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2009. 16:228–230.
Article21. Ritter MA, Campbell ED. A model for easy location of the center of the femoral head during total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1988. 3:Suppl. S59–S61.
Article22. Sawant MR, Murty A, Ireland J. A clinical method for locating the femoral head centre during total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2004. 11:209–212.
Article23. Mullaji A, Shetty GM, Kanna R, Sharma A. Variability in the range of inter-anterior superior iliac spine distance and its correlation with femoral head centre. A prospective computed tomography study of 200 adults. Skeletal Radiol. 2010. 39:363–368.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An Extramedullary Femoral Alignment System in Total Knee Arthroplasty Using the Inter-Femoral Head Center Distance
- Comparison of an Accelerometer-Based Portable Navigation System, Patient-Specific Instrumentation, and Conventional Instrumentation for Femoral Alignment in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- A Comparison of Accuracy between the Sonography-guided Extramedullary and Intramedullary Alignment Systems for the Femoral Component in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Accuracy of Limb Alignment in Total Knee Arthroplasty using Image-Free Navigation System: Comparison with Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Easy Identification of Mechanical Axis during Total Knee Arthroplasty