Yonsei Med J.
2013 Nov;54(6):1505-1510. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.6.1505.
Easy Identification of Mechanical Axis during Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. orthomania@gmail.com
- KMID: 1798150
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.6.1505
Abstract
- PURPOSE
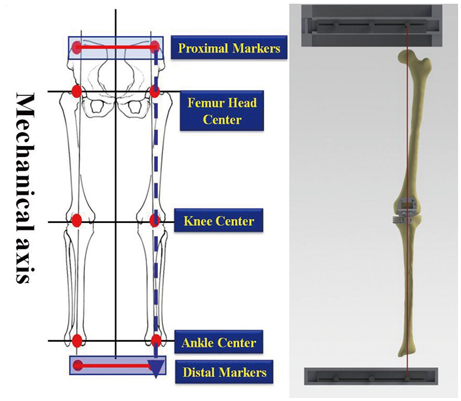
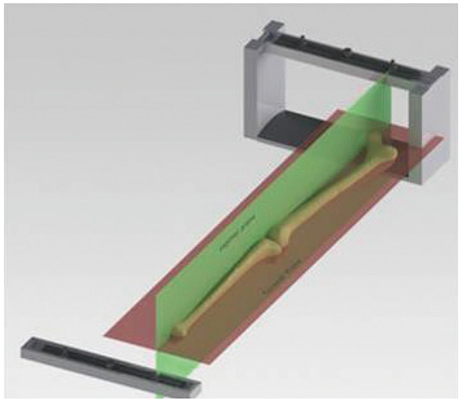
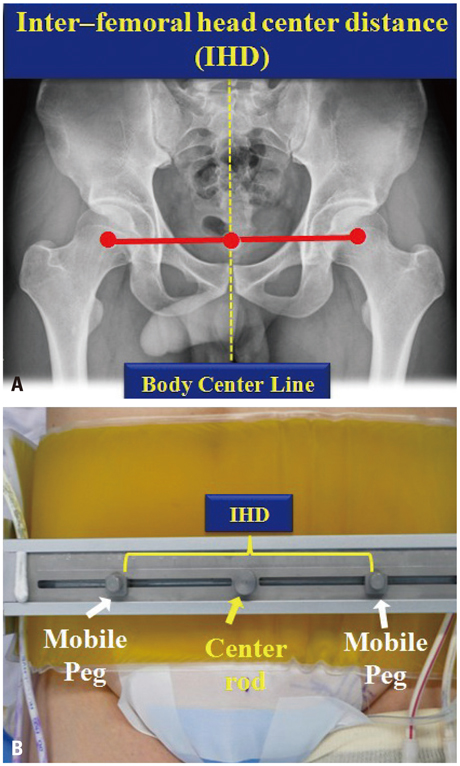
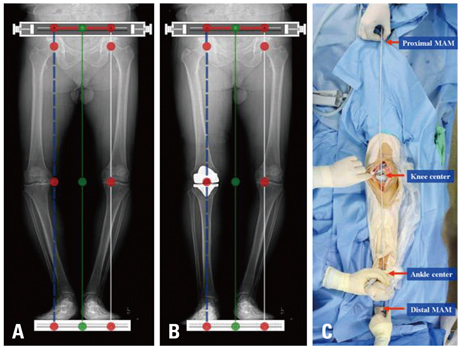
We devised an intraoperatively identifiable mechanical axis (IIMA) as a reference of alignment in total knee arthroplasty (TKA).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between February 2010 and January 2011, primary TKAs were consecutively performed on 672 patients (1007 knees) using an IIMA as a reference in the coronal plane.
RESULTS
The alignment of the lower extremity improved from a mean of 11.4+/-6.7degrees (-10.3-34.4degrees) of varus preop. to 0.7+/-3.5degrees (-5.2-8.6degrees) immediately after surgery. Mean alignment of the femoral component in the coronal plane was 89.3+/-2.3degrees (83.4-97.2degrees) postop. and mean alignment of the tibial component was 90.4+/-2.2degrees (85.1-94.2degrees) postop.
CONCLUSION
This study showed that IIMA could be of considerable value as a new guider of alignment that is easily accessible and highly effective during total knee arthroplasty.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Radiologic Outcomes According to Varus Deformity in Minimally Invasive Surgery Total Knee Arthroplasty
Ju-Hyung Yoo, Sang-Hoon Park, Chang-Dong Han, Hyun-Cheol Oh, Jun-Young Park, Seung-Jin Choi
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(1):225-231. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.1.225.
Reference
-
1. Baldini A, Adravanti P. Less invasive TKA: extramedullary femoral reference without navigation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466:2694–2700.2. Bardakos N, Cil A, Thompson B, Stocks G. Mechanical axis cannot be restored in total knee arthroplasty with a fixed valgus resection angle: a radiographic study. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22:6 Suppl 2. 85–89.
Article3. Berend M. Consequences of Malalignment in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Few if Any-Opposes. Semin Arthroplasty. 2010; 21:99–101.
Article4. Choong PF, Dowsey MM, Stoney JD. Does accurate anatomical alignment result in better function and quality of life? Comparing conventional and computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24:560–569.
Article5. Cooke TD. Definition of axial alignment of the lower extremity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84-A:146–147.
Article6. Werner FW, Ayers DC, Maletsky LP, Rullkoetter PJ. The effect of valgus/varus malalignment on load distribution in total knee replacements. J Biomech. 2005; 38:349–355.
Article7. Ishida K, Matsumoto T, Tsumura N, Kubo S, Kitagawa A, Chin T, et al. Mid-term outcomes of computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011; 19:1107–1112.
Article8. Sikorski JM. Alignment in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008; 90:1121–1127.
Article9. Huang TW, Hsu WH, Peng KT, Hsu RW. Total knee replacement in patients with significant femoral bowing in the coronal plane: a comparison of conventional and computer-assisted surgery in an Asian population. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011; 93:345–350.10. Huang TW, Hsu WH, Peng KT, Hsu RW, Weng YJ, Shen WJ. Total knee arthroplasty with use of computer-assisted navigation compared with conventional guiding systems in the same patient: radiographic results in Asian patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93:1197–1202.
Article11. Jeffery RS, Morris RW, Denham RA. Coronal alignment after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73:709–714.
Article12. Mullaji A, Shetty GM, Kanna R, Sharma A. Variability in the range of inter-anterior superior iliac spine distance and its correlation with femoral head centre. A prospective computed tomography study of 200 adults. Skeletal Radiol. 2010; 39:363–368.
Article13. Mullaji AB, Marawar SV, Mittal V. A comparison of coronal plane axial femoral relationships in Asian patients with varus osteoarthritic knees and healthy knees. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24:861–867.
Article14. Nagamine R, Kondo K, Ikemura S, Shiranita A, Nakashima S, Hara T, et al. Distal femoral cut perpendicular to the mechanical axis may induce varus instability in flexion in medial osteoarthritic knees with varus deformity in total knee arthroplasty: a pitfall of the navigation system. J Orthop Sci. 2004; 9:555–559.
Article15. Parratte S, Pagnano MW, Trousdale RT, Berry DJ. Effect of postoperative mechanical axis alignment on the fifteen-year survival of modern, cemented total knee replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92:2143–2149.
Article16. Lee DH, Seo JG, Moon YW. Synchronisation of tibial rotational alignment with femoral component in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2008; 32:223–227.
Article17. Seo JG, Moon YW, Lim JS, Park SJ, Kim SM. Mechanical axis-derived femoral component rotation in extramedullary total knee arthroplasty: a comparison between femoral transverse axis and transepicondylar axis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012; 20:538–545.
Article18. Seo JG, Moon YW, Park SH, Kang HM, Kim SM. How precise is the identification of the center of the femoral head during total knee arthroplasty? Acta Orthop. 2012; 83:53–58.
Article19. Chin PL, Foo LS, Yang KY, Yeo SJ, Lo NN. Randomized controlled trial comparing the radiologic outcomes of conventional and minimally invasive techniques for total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22:800–806.
Article20. Rolston L, Siewert K. Assessment of knee alignment after bicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24:1111–1114.
Article21. Mihalko WM, Krackow KA. Differences between extramedullary, intramedullary, and computer-aided surgery tibial alignment techniques for total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2006; 19:33–36.
Article22. Catani F, Biasca N, Ensini A, Leardini A, Bianchi L, Digennaro V, et al. Alignment deviation between bone resection and final implant positioning in computer-navigated total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90:765–771.
Article23. Catani F, Digennaro V, Ensini A, Leardini A, Giannini S. Navigation-assisted total knee arthroplasty in knees with osteoarthritis due to extra-articular deformity. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012; 20:546–551.
Article24. Zhang GQ, Chen JY, Chai W, Liu M, Wang Y. Comparison between computer-assisted-navigation and conventional total knee arthroplasties in patients undergoing simultaneous bilateral procedures: a randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93:1190–1196.
Article25. Sawant MR, Murty A, Ireland J. A clinical method for locating the femoral head centre during total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2004; 11:209–212.
Article26. Harvie P, Sloan K, Beaver RJ. Three-dimensional component alignment and functional outcome in computer-navigated total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized study comparing two navigation systems. J Arthroplasty. 2011; 26:1285–1290.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bony Landmarks for Determining the Mechanical Axis of the Femur in the Sagittal Plane during Total Knee Arthroplasty
- The Discrepancy between Eipcondylar and Posterior Condylar Axis of Femur in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Radiographic Analysis of the Tibial Axis on the Antero-posterior and Lateral view of Knee
- An Extramedullary Femoral Alignment System in Total Knee Arthroplasty Using the Inter-Femoral Head Center Distance
- Radiological Results and Assessment of Navigation-Guided Total Knee Arthroplasty