Bony Landmarks for Determining the Mechanical Axis of the Femur in the Sagittal Plane during Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea. orthopaedee@naver.com
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, CHA Gumi Medical Center, CHA University, Gumi, Korea.
- KMID: 999390
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2009.1.3.128
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
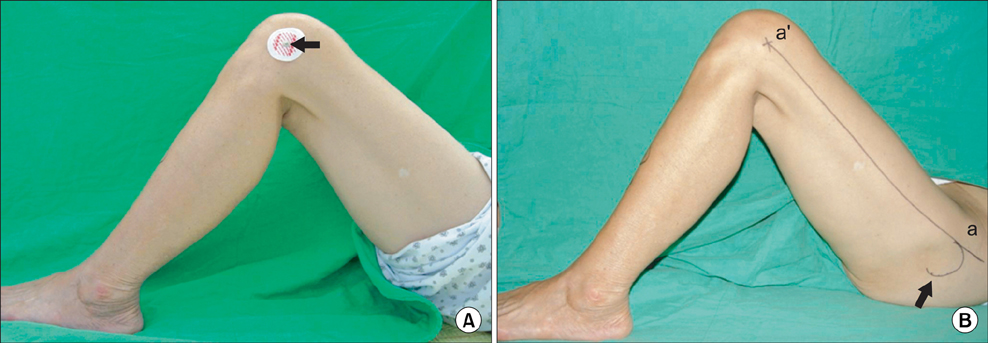
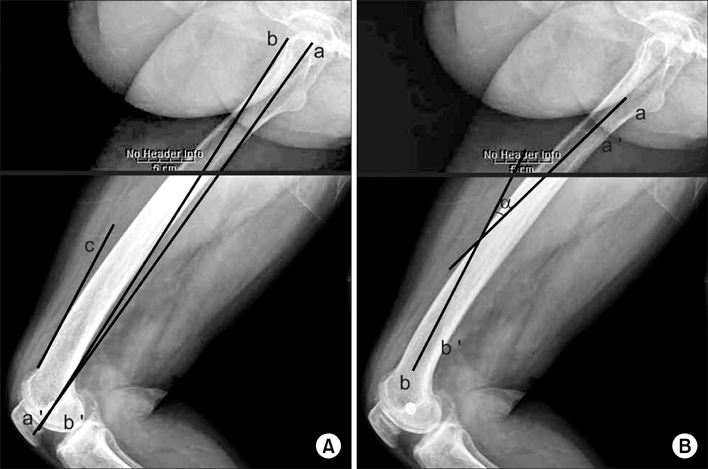
There is no accepted landmark for the mechanical axis of the femoral axis in sagittal plane in conventional total knee arthroplasty. METHODS: As palpable anatomic landmarks of the femur, lateral epicondyle, and anterior margin of the greater trochanter were identified. The line connecting these two landmarks was defined as the "palpable sagittal axis". The mechanical axis of the femur was compared with the palpable sagittal axis and the distal femoral anterior cortex axis. These axes were also compared with sagittal bowing of the femur. RESULTS: The distal femoral anterior cortex axis and the palpable sagittal axis were flexed by 4.1degrees and 2.4degrees more than the sagittal mechanical axes, respectively (p < 0.05). However, the palpable sagittal axis was not correlated with sagittal bowing of the femur (Spearman's rs, 0.17; p = 0.14). CONCLUSIONS: The palpable sagittal axis showed a consistent relationship with the sagittal mechanical femoral axes regardless of the severity of the sagittal bowing of the femur.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
The Analysis of Risk Factors in No Thumb Test in Total Knee Arthroplasty
Jee Hyoung Kim, Song Lee, Dong Oh Ko, Chang Wook Yoo, Tae Hwan Chun, Jung Soo Lee
Clin Orthop Surg. 2011;3(4):274-278. doi: 10.4055/cios.2011.3.4.274.An Extramedullary Femoral Alignment System in Total Knee Arthroplasty Using the Inter-Femoral Head Center Distance
Jai-Gon Seo, Ji-Soon Lim, Hyun-Il Lee, Kyung-Jea Woo
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2010;45(5):347-355. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2010.45.5.347.Measurement of the Weight-bearing Standing Coronal and Sagittal Axial Alignment of Lower Extremity in Young Korean Adults
Seoung-Joon Lee, Ho-Joon Lee, Jin-Il Kim, Kwang-Jun Oh
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2011;46(3):191-199. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2011.46.3.191.Accuracy of Inter Femoral Head Center Distance Measurement and Evaluation for Coronal Alignment of Femoral Component during Total Knee Arthroplasty
Woon Hwa Jung, Dong Hyun Kim, Chung Woo Chun, Jae Heon Jeong, Yong Chan Ha, Jai Gon Seo
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2011;46(4):320-325. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2011.46.4.320.
Reference
-
1. Moreland JR. Mechanisms of failure in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988. (226):49–64.
Article2. Bargren JH, Blaha JD, Freeman MA. Alignment in total knee arthroplasty: correlated biomechanical and clinical observations. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983. (173):178–183.3. Clayton ML, Thompson TR, Mack RP. Correction of alignment deformities during total knee arthroplasties: staged soft-tissue releases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986. (202):117–124.4. Gilbert BM. Anterior femoral curvature: its progably basis and utility as a criterion of racial assessment. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1976. 45(3 pt. 2):601–604.
Article5. Tang WM, Chiu KY, Kwan MF, Ng TP, Yau WP. Sagittal bowing of the distal femur in Chinese patients who require total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Res. 2005. 23(1):41–45.
Article6. Dennis DA, Channer M, Susman MH, Stringer EA. Intramedullary versus extramedullary tibial alignment systems in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1993. 8(1):43–47.
Article7. Engh GA, Petersen TL. Comparative experience with intramedullary and extramedullary alignment in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1990. 5(1):1–8.
Article8. Laskin RS. Intramedullary instrumentation: safer and more accurate than extramedullary instrumentation. Orthopedics. 2001. 24(8):739.
Article9. Hood RW, Vanni M, Insall JN. The correction of knee alignment in 225 consecutive total condylar knee replacements. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1981. (160):94–105.
Article10. Singh SP, Singh S. A study of anterior femoral curvature in Indian subjects. Acta Anat (Basel). 1972. 83(3):416–425.
Article11. Walensky NA. A study of anterior femoral curvature in man. Anat Rec. 1965. 151(4):559–570.
Article12. Callaghan JJ, O'Rourke MR, Goetz DD, Schmalzried TP, Campbell PA, Johnston RC. Tibial post impingement in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002. (404):83–88.
Article13. Puloski SK, McCalden RW, MacDonald SJ, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB. Tibial post wear in posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty: an unrecognized source of polyethylene debris. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. 83(3):390–397.14. Jenny JY, Clemens U, Kohler S, Kiefer H, Konermann W, Miehlke RK. Consistency of implantation of a total knee arthroplasty with a non-image-based navigation system: a case-control study of 235 cases compared with 235 conventionally implanted prostheses. J Arthroplasty. 2005. 20(7):832–839.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Accuracy of Alignment Determined by Patient-Specific Instrumentation System in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Evaluation of Bone Cutting Error of the Total Knee Arthroplasty with Computer-assisted Navigation
- Easy Identification of Mechanical Axis during Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Indirect Measurement of Joint Space Distance using Ladmarks in TKRA
- The Discrepancy between Eipcondylar and Posterior Condylar Axis of Femur in Total Knee Arthroplasty