J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2010 Dec;18(4):134-138. 10.4250/jcu.2010.18.4.134.
Urine Albumin Creatinine Ratio is Associated with Carotid Atherosclerosis in a Community Based Cohort: Atherosclerosis Risk of Rural Area in Korean General Population Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Devision of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea. kimjy@yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine and Institute of Occupational Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 3Institute of Genomic Cohort, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2177314
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2010.18.4.134
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Albuminuria is a surrogate marker of endothelial dysfunction and a predictor of cardiovascular events. Data are limited with regard to the relationship between albuminuria and subclinical atherosclerosis in a community-based cohort. We determined the association between albuminuria measured by the urine albumin creatinine ratio (UACR) and carotid intima media thickness (CIMT) in a Korean rural population.
METHODS
We enrolled 1,369 healthy subjects older than 40 years (857 males and 518 females) with normal renal function and measured the CIMT. We excluded subjects with overt proteinuria (> 300 mg/day) or with treatment of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and any cardiovascular disease. The subjects were stratified into the quartile value of the UACR (lowest quartile: UACR < 4.8 and highest quartile: UACR > 17.7). And we evaluate the relationship between UACR and CIMT by linear regression and logistic regression analysis.
RESULTS
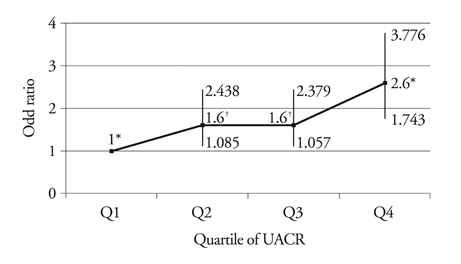
Increasing quartile of the UACR had a stepwise increase in body mass index, blood pressure, cholesterol profile [low density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol and triglyceride], glucose, homeostratic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), and C-reactive protein (all p values < 0.001). Maximal CIMT from the 1st to the 4th quartile values of the UACR were 0.74 +/- 0.17, 0.77 +/- 0.18, 0.78 +/- 0.18, and 0.82 +/- 0.21 mm, respectively (p < 0.001). In a multivariate regression model adjusted for age, sex, systolic blood pressure, triglyceride, LDL-cholesterol, fasting blood sugar, waist circumference, adiponectin, HOMA-IR, high sensitive C-reactive protein, smoking, UACR showed a significant association with maximal CIMT (B = 0.014, R2 = 0.145, p = 0.002).
CONCLUSION
Albuminuria measured by the UACR was significantly associated with both CIMT and traditional risk factors of atherosclerosis except for smoking in healthy Koreans.
MeSH Terms
-
Adiponectin
Albuminuria
Atherosclerosis
Biomarkers
Blood Glucose
Blood Pressure
Body Mass Index
C-Reactive Protein
Cardiovascular Diseases
Carotid Artery Diseases
Carotid Intima-Media Thickness
Cholesterol
Cohort Studies
Creatinine
Diabetes Mellitus
Dyslipidemias
Fasting
Glucose
Humans
Hypertension
Insulin Resistance
Linear Models
Lipoproteins
Logistic Models
Male
Proteinuria
Risk Factors
Smoke
Smoking
Waist Circumference
Adiponectin
Blood Glucose
C-Reactive Protein
Cholesterol
Creatinine
Glucose
Lipoproteins
Smoke
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Relationship between Urinary Albumin Excretion and Carotid Atherosclerosis in General Korean Population
Kye Hun Kim
J Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2010;18(4):146-147. doi: 10.4250/jcu.2010.18.4.146.
Reference
-
1. Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004. 351:1296–1305.
Article2. Hillege HL, Fidler V, Diercks GF, van Gilst WH, de Zeeuw D, van Veldhuisen DJ, Gans RO, Janssen WM, Grobbee DE, de Jong PE. Prevention of Renal and Vascular End Stage Disease (PREVEND) Study Group. Urinary albumin excretion predicts cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality in general population. Circulation. 2002. 106:1777–1782.
Article3. Gerstein HC, Mann JF, Yi Q, Zinman B, Dinneen SF, Hoogwerf B, Hallé JP, Young J, Rashkow A, Joyce C, Nawaz S, Yusuf S. HOPE Study Investigators. Albuminuria and risk of cardiovascular events, death, and heart failure in diabetic and nondiabetic individuals. JAMA. 2001. 286:421–426.
Article4. Viberti GC, Hill RD, Jarrett RJ, Argyropoulos A, Mahmud U, Keen H. Microalbuminuria as a predictor of clinical nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1982. 1:1430–1432.
Article5. Arnlöv J, Evans JC, Meigs JB, Wang TJ, Fox CS, Levy D, Benjamin EJ, D'Agostino RB, Vasan RS. Low-grade albuminuria and incidence of cardiovascular disease events in nonhypertensive and nondiabetic individuals: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2005. 112:969–975.
Article6. Jørgensen L, Jenssen T, Johnsen SH, Mathiesen EB, Heuch I, Joakimsen O, Fosse E, Jacobsen BK. Albuminuria as risk factor for initiation and progression of carotid atherosclerosis in non-diabetic persons: the Tromsø Study. Eur Heart J. 2007. 28:363–369.7. Furtner M, Kiechl S, Mair A, Seppi K, Weger S, Oberhollenzer F, Poewe W, Willeit J. Urinary albumin excretion is independently associated with carotid and femoral artery atherosclerosis in the general population. Eur Heart J. 2005. 26:279–287.
Article8. Ruggenenti P, Gaspari F, Perna A, Remuzzi G. Cross sectional longitudinal study of spot morning urine protein: creatinine ratio, 24 hour urine protein excretion rate, glomerular filtration rate, and end stage renal failure in chronic renal disease in patients without diabetes. BMJ. 1998. 316:504–509.
Article9. O'Leary DH, Polak JF, Kronmal RA, Manolio TA, Burke GL, Wolfson SK Jr. Cardiovascular health study collaborative research group. Carotid-artery intima and media thickness as a risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke in older adults. N Engl J Med. 1999. 340:14–22.10. Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Cifkova R, Fagard R, Germano G, Grassi G, Heagerty AM, Kjeldsen SE, Laurent S, Narkiewicz K, Ruilope L, Rynkiewicz A, Schmieder RE, Struijker Boudier HA, Zanchetti A, Vahanian A, Camm J, De Caterina R, Dean V, Dickstein K, Filippatos G, Funck-Brentano C, Hellemans I, Kristensen SD, McGregor K, Sechtem U, Silber S, Tendera M, Widimsky P, Zamorano JL, Kjeldsen SE, Erdine S, Narkiewicz K, Kiowski W, Agabiti-Rosei E, Ambrosioni E, Cifkova R, Dominiczak A, Fagard R, Heagerty AM, Laurent S, Lindholm LH, Mancia G, Manolis A, Nilsson PM, Redon J, Schmieder RE, Struijker-Boudier HA, Viigimaa M, Filippatos G, Adamopoulos S, Agabiti-Rosei E, Ambrosioni E, Bertomeu V, Clement D, Erdine S, Farsang C, Gaita D, Kiowski W, Lip G, Mallion JM, Manolis AJ, Nilsson PM, O'Brien E, Ponikowski P, Redon J, Ruschitzka F, Tamargo J, van Zwieten P, Viigimaa M, Waeber B, Williams B, Zamorano JL. The task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension. The task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology. 2007 Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2007. 28:1462–1536.
Article11. Liu JE, Robbins DC, Palmieri V, Bella JN, Roman MJ, Fabsitz R, Howard BV, Welty TK, Lee ET, Devereux RB. Association of albuminuria with systolic and diastolic left ventricular dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: the Strong Heart Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003. 41:2022–2028.
Article12. Borch-Johnsen K, Feldt-Rasmussen B, Strandgaard S, Schroll M, Jensen JS. Urinary albumin excretion. An independent predictor of ischemic heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1999. 19:1992–1997.13. Tuttle KR, Puhlman ME, Cooney SK, Short R. Urinary albumin and insulin as predictors of coronary artery disease: An angiographic study. Am J Kidney Dis. 1999. 34:918–925.
Article14. Agewall S, Björn . Microalbuminuria and intima-media thickness of the carotid artery in clinically healthy men. Atherosclerosis. 2002. 164:161–166.
Article15. Jensen JS, Borch-Johnsen K, Jensen G, Feldt-Rasmussen B. Microalbuminuria reflects a generalized transvascular albumin leakiness in clinically healthy subjects. Clin Sci (Lond). 1995. 88:629–633.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Carotid Atherosclerosis as a Marker of Atherosclerosis of the Thoracic Aorta in the Elderly
- The Glycated Albumin to Glycated Hemoglobin Ratio Might Not Be Associated with Carotid Atherosclerosis in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
- General principles of carotid Doppler ultrasonography
- The Ratio of Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Based on Cystatin C and Creatinine Reflecting Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetic Patients
- Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio for Risk Assessment in Coronary Artery Disease and Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis