J Adv Prosthodont.
2013 Nov;5(4):374-381. 10.4047/jap.2013.5.4.374.
Effect of alendronate on bone remodeling around implant in the rat
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Oral Science Research Center, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Republic of Korea. hsm5@yuhs.ac
- 2Division in Anatomy and Developmental Biology, Department of Oral Biology, Oral Science Research Center, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
- KMID: 2176523
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2013.5.4.374
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of alendronates on bone remodeling around titanium implant in the maxilla of rats.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
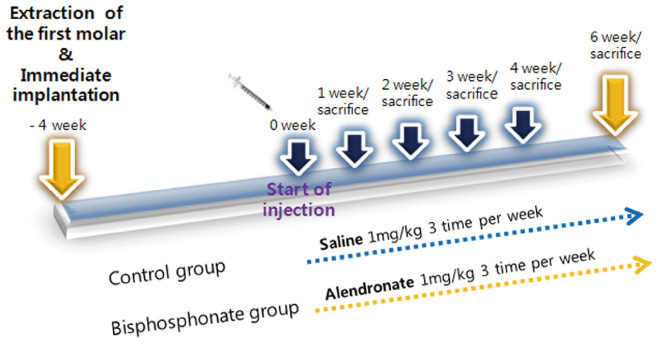
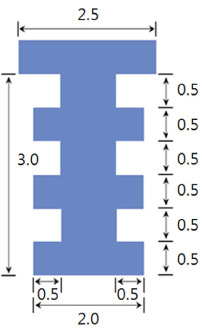
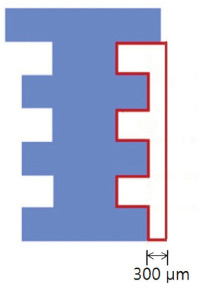
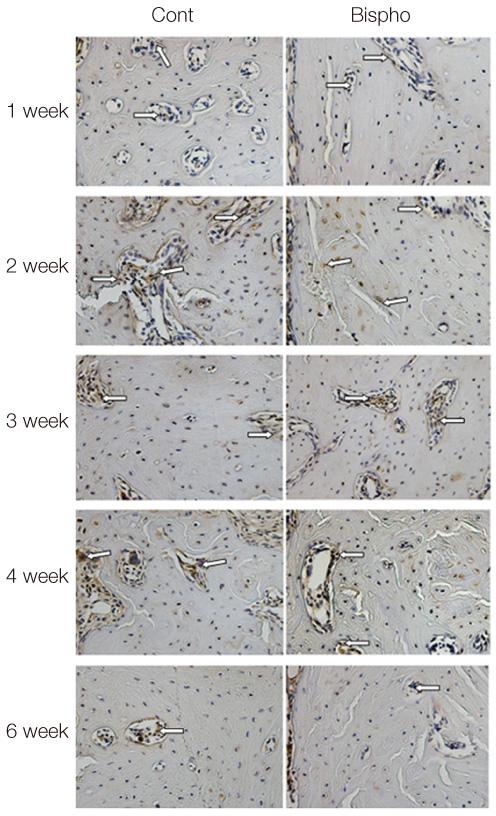
The maxillary first molars were extracted and customized-titanium implants were placed immediately in thirty male Sprague-Dawley rats. The rats were divided into experimental (bisphosphonate) group and control group. At 4 weeks after implantation, the rats in the bisphosphonate group were subcutaneously injected with alendronate three times a week for 6 weeks where as the rats in control group were injected with saline. The rats were sacrificed at 1, 2, 3, 4, or 6 weeks after starting of injection and maxillary bones were collected subsequently. Alveolar bone remodeling around the implants were evaluated by radiographic and histologic analysis. Microarray analysis and immunohistomorphologic analysis were also performed on one rat, sacrificed at 6 weeks after starting of injection, from each group. Statistical analysis was performed using repeated measures analysis of variance and independent t test at a significance level of 5%.
RESULTS
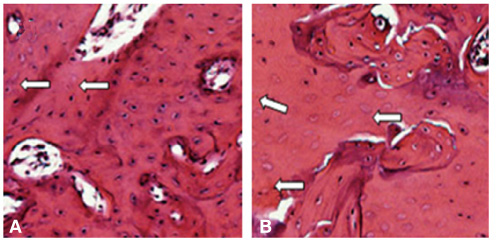
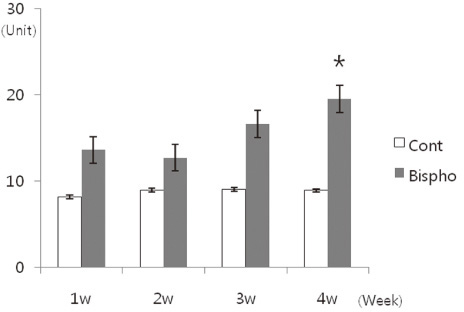
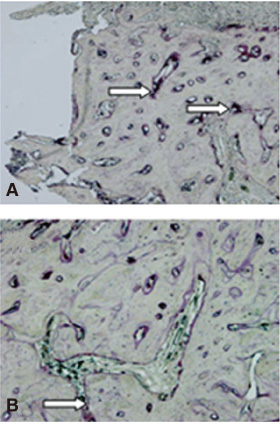
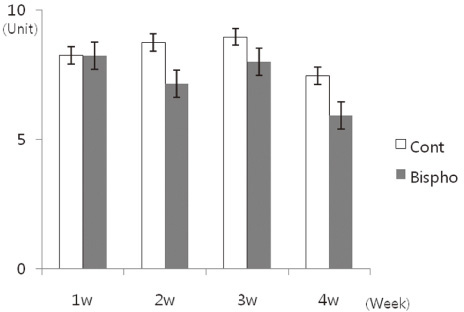
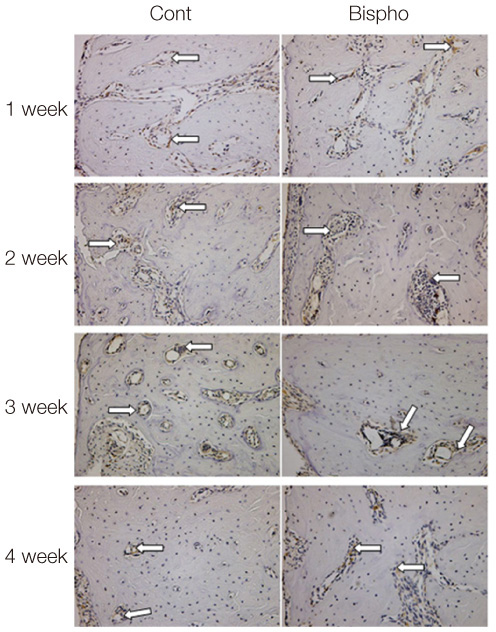
There was no statistically significant difference in the bone area (%) around implant between the bisphosphonate group and the control group. However, the amount of empty lacuna was significantly increased in the bisphosphonate group, especially in the rats sacrificed at 4 weeks after starting of injection compared to that of the corresponding control group. The bisphosphonate group showed the same level of TRAP positive cell count, osteocalcin and angiopoietin 1 as the control group.
CONCLUSION
Alendronate may not decrease the amount of osteoclast. However, the significantly increased amount of empty lacuna in the bisphosphonate group may explain the suppression of bone remodeling in the bisphosphonate group.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Drake MT, Clarke BL, Khosla S. Bisphosphonates: mechanism of action and role in clinical practice. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008; 83:1032–1045.2. Marx RE. Pamidronate (Aredia) and zoledronate (Zometa) induced avascular necrosis of the jaws: a growing epidemic. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 61:1115–1117.3. Ruggiero SL, Mehrotra B, Rosenberg TJ, Engroff SL. Osteonecrosis of the jaws associated with the use of bisphosphonates: a review of 63 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004; 62:527–534.4. Allen MR, Burr DB. The pathogenesis of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: so many hypotheses, so few data. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 67:61–70.5. Hikita H, Miyazawa K, Tabuchi M, Kimura M, Goto S. Bisphosphonate administration prior to tooth extraction delays initial healing of the extraction socket in rats. J Bone Miner Metab. 2009; 27:663–672.6. Kobayashi Y, Hiraga T, Ueda A, Wang L, Matsumoto-Nakano M, Hata K, Yatani H, Yoneda T. Zoledronic acid delays wound healing of the tooth extraction socket, inhibits oral epithelial cell migration, and promotes proliferation and adhesion to hydroxyapatite of oral bacteria, without causing osteonecrosis of the jaw, in mice. J Bone Miner Metab. 2010; 28:165–175.7. Lazarovici TS, Yahalom R, Taicher S, Schwartz-Arad D, Peleg O, Yarom N. Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw associated with dental implants. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 68:790–796.8. Grant BT, Amenedo C, Freeman K, Kraut RA. Outcomes of placing dental implants in patients taking oral bisphosphonates: a review of 115 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 66:223–230.9. Smith SY, Recker RR, Hannan M, Müller R, Bauss F. Intermittent intravenous administration of the bisphosphonate ibandronate prevents bone loss and maintains bone strength and quality in ovariectomized cynomolgus monkeys. Bone. 2003; 32:45–55.10. Allen MR, Kubek DJ, Burr DB. Cancer treatment dosing regimens of zoledronic acid result in near-complete suppression of mandible intracortical bone remodeling in beagle dogs. J Bone Miner Res. 2010; 25:98–105.11. Ruggiero SL, Drew SJ. Osteonecrosis of the jaws and bisphosphonate therapy. J Dent Res. 2007; 86:1013–1021.12. Futami T, Fujii N, Ohnishi H, Taguchi N, Kusakari H, Ohshima H, Maeda T. Tissue response to titanium implants in the rat maxilla: ultrastructural and histochemical observations of the bone-titanium interface. J Periodontol. 2000; 71:287–298.13. Listgarten MA. Soft and hard tissue response to endosseous dental implants. Anat Rec. 1996; 245:410–425.14. Masuda T, Yliheikkilä PK, Felton DA, Cooper LF. Generalizations regarding the process and phenomenon of osseointegration. Part I. In vivo studies. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1998; 13:17–29.15. Pereira MC, Zecchin KG, Campagnoli EB, Jorge J. Ovariectomy delays alveolar wound healing after molar extractions in rats. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 65:2248–2253.16. Fujii N, Kusakari H, Maeda T. A histological study on tissue responses to titanium implantation in rat maxilla: the process of epithelial regeneration and bone reaction. J Periodontol. 1998; 69:485–495.17. Karimbux NY, Sirakian A, Weber HP, Nishimura I. A new animal model for molecular biological analysis of the implant-tissue interface: spatial expression of type XII collagen mRNA around a titanium oral implant. J Oral Implantol. 1995; 21:107–113. discussion 114-5.18. Shimizu M, Sasaki T, Ishihara A, Furuya R, Kawawa T. Bone wound healing after maxillary molar extraction in ovariectomized aged rats. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo). 1998; 47:517–526.19. Bi Y, Gao Y, Ehirchiou D, Cao C, Kikuiri T, Le A, Shi S, Zhang L. Bisphosphonates cause osteonecrosis of the jaw-like disease in mice. Am J Pathol. 2010; 177:280–290.20. Kikuiri T, Kim I, Yamaza T, Akiyama K, Zhang Q, Li Y, Chen C, Chen W, Wang S, Le AD, Shi S. Cell-based immunotherapy with mesenchymal stem cells cures bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw-like disease in mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2010; 25:1668–1679.21. Mashiba T, Turner CH, Hirano T, Forwood MR, Jacob DS, Johnston CC, Burr DB. Effects of high-dose etidronate treatment on microdamage accumulation and biomechanical properties in beagle bone before occurrence of spontaneous fractures. Bone. 2001; 29:271–278.22. Mashiba T, Turner CH, Hirano T, Forwood MR, Johnston CC, Burr DB. Effects of suppressed bone turnover by bisphosphonates on microdamage accumulation and biomechanical properties in clinically relevant skeletal sites in beagles. Bone. 2001; 28:524–531.23. Whyte MP, Wenkert D, Clements KL, McAlister WH, Mumm S. Bisphosphonate-induced osteopetrosis. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349:457–463.24. Odvina CV, Zerwekh JE, Rao DS, Maalouf N, Gottschalk FA, Pak CY. Severely suppressed bone turnover: a potential complication of alendronate therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005; 90:1294–1301.25. Visekruna M, Wilson D, McKiernan FE. Severely suppressed bone turnover and atypical skeletal fragility. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 93:2948–2952.26. Rogers MJ, Gordon S, Benford HL, Coxon FP, Luckman SP, Monkkonen J, Frith JC. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates. Cancer. 2000; 88:2961–2978.27. Russell RG. Bisphosphonates: mode of action and pharmacology. Pediatrics. 2007; 119:S150–S162.28. Fleisch H. Bisphosphonates: mechanisms of action. Endocr Rev. 1998; 19:80–100.29. Balena R, Toolan BC, Shea M, Markatos A, Myers ER, Lee SC, Opas EE, Seedor JG, Klein H, Frankenfield D. The effects of 2-year treatment with the aminobisphosphonate alendronate on bone metabolism, bone histomorphometry, and bone strength in ovariectomized nonhuman primates. J Clin Invest. 1993; 92:2577–2586.30. Chavassieux PM, Arlot ME, Reda C, Wei L, Yates AJ, Meunier PJ. Histomorphometric assessment of the long-term effects of alendronate on bone quality and remodeling in patients with osteoporosis. J Clin Invest. 1997; 100:1475–1480.31. Yang Li C, Majeska RJ, Laudier DM, Mann R, Schaffler MB. High-dose risedronate treatment partially preserves cancellous bone mass and microarchitecture during long-term disuse. Bone. 2005; 37:287–295.32. Weinstein RS, Roberson PK, Manolagas SC. Giant osteoclast formation and long-term oral bisphosphonate therapy. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:53–62.33. Hauge EM, Qvesel D, Eriksen EF, Mosekilde L, Melsen F. Cancellous bone remodeling occurs in specialized compartments lined by cells expressing osteoblastic markers. J Bone Miner Res. 2001; 16:1575–1582.34. Hirao M, Hashimoto J, Ando W, Ono T, Yoshikawa H. Response of serum carboxylated and undercarboxylated osteocalcin to alendronate monotherapy and combined therapy with vitamin K2 in postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Metab. 2008; 26:260–264.35. Wood J, Bonjean K, Ruetz S, Bellahcène A, Devy L, Foidart JM, Castronovo V, Green JR. Novel antiangiogenic effects of the bisphosphonate compound zoledronic acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002; 302:1055–1061.36. Rubin CT, Bain SD, McLeod KJ. Suppression of the osteogenic response in the aging skeleton. Calcif Tissue Int. 1992; 50:306–313.37. Klein-Nulend J, Sterck JG, Semeins CM, Lips P, Joldersma M, Baart JA, Burger EH. Donor age and mechanosensitivity of human bone cells. Osteoporos Int. 2002; 13:137–146.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Alendronate on Bone Regeneration in Defect of Rat Calvaria
- Morphometric analysis of bone in the ovariectomized rat using in vivo micro-CT
- Effect of a Long-term, Oral Fixed Dose with a Combination of Aledronate and Cacitriol on the Cancellous Bone Microarchitecture in Ovariectomized Rats
- The Effects of various Regeneration techniques on Bone Regeneration around Dental Implant
- Factors and Mechanisms Involved in the Coupling from Bone Resorption to Formation: How Osteoclasts Talk to Osteoblasts