J Adv Prosthodont.
2012 Aug;4(3):127-133. 10.4047/jap.2012.4.3.127.
Comparison of effect of desensitizing agents on the retention of crowns cemented with luting agents: an in vitro study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthetic Dentistry, Dr. D.Y. Patil Dental College & Hospital, Pimpri, India. shitalsonune@yahoo.com
- KMID: 2176406
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2012.4.3.127
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Many dentists use desensitizing agents to prevent hypersensitivity. This study compared and evaluated the effect of two desensitizing agents on the retention of cast crowns when cemented with various luting agents.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
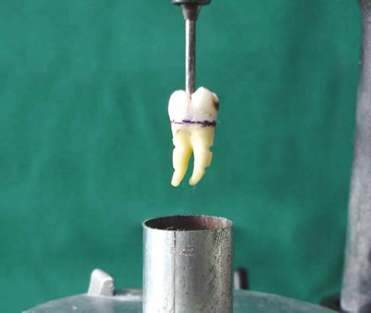
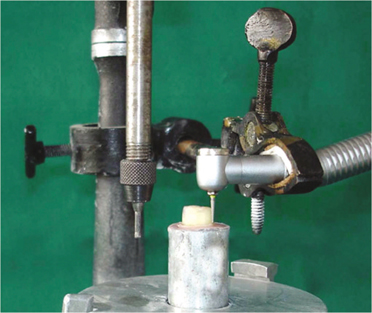
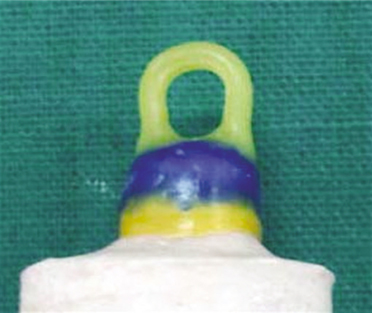
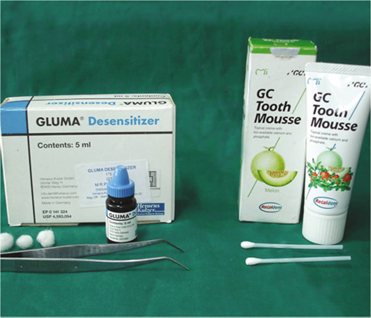
Ninety freshly extracted human molars were prepared with flat occlusal surface, 6 degree taper and approximately 4 mm axial length. The prepared specimens were divided into 3 groups and each group is further divided into 3 subgroups. Desensitizing agents used were GC Tooth Mousse and GLUMA(R) desensitizer. Cementing agents used were zinc phosphate, glass ionomer and resin modified glass ionomer cement. Individual crowns with loop were made from base metal alloy. Desensitizing agents were applied before cementation of crowns except for control group. Under tensional force the crowns were removed using an automated universal testing machine. Statistical analysis included one-way ANOVA followed by Turkey-Kramer post hoc test at a preset alpha of 0.05.
RESULTS
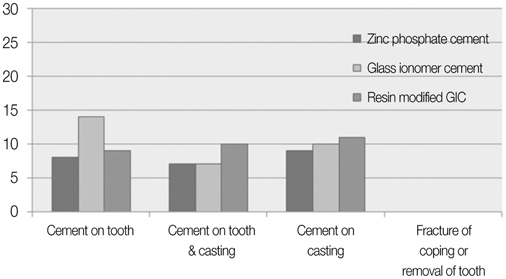
Resin modified glass ionomer cement exhibited the highest retentive strength and all dentin treatments resulted in significantly different retentive values (In Kg.): GLUMA (49.02 +/- 3.32) > Control (48.61 +/- 3.54) > Tooth mousse (48.34 +/- 2.94). Retentive strength for glass ionomer cement were GLUMA (41.14 +/- 2.42) > Tooth mousse (40.32 +/- 3.89) > Control (39.09 +/- 2.80). For zinc phosphate cement the retentive strength were lowest GLUMA (27.92 +/- 3.20) > Control (27.69 +/- 3.39) > Tooth mousse (25.27 +/- 4.60).
CONCLUSION
The use of GLUMA(R) desensitizer has no effect on crown retention. GC Tooth Mousse does not affect the retentive ability of glass ionomer and resin modified glass ionomer cement, but it decreases the retentive ability of zinc phosphate cement.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acrylic Resins
Alloys
Caseins
Cementation
Collodion
Crowns
Dental Cements
Dentin
Dentin Sensitivity
Dentists
Glass
Glass Ionomer Cements
Glutaral
Humans
Hypersensitivity
Molar
Phosphates
Polymethacrylic Acids
Retention (Psychology)
Silicon Dioxide
Tooth
Zinc
Zinc Compounds
Zinc Phosphate Cement
Acrylic Resins
Alloys
Caseins
Collodion
Dental Cements
Glass Ionomer Cements
Glutaral
Phosphates
Polymethacrylic Acids
Silicon Dioxide
Zinc
Zinc Compounds
Zinc Phosphate Cement
Figure
Reference
-
1. Johnston JF, Dykema RW, Goodacre CJ, Phillips RW. Johnston's modern practice in fixed prosthodontics. 1986. 4th ed. Philadelphia: WB saunders Co..2. Addy M. Etiology and clinical implications of dentine hypersensitivity. Dent Clin North Am. 1990. 34:503–514.3. Johnson RH, Zulqar-Nain BJ, Koval JJ. The effectiveness of an electro-ionizing toothbrush in the control of dentinal hypersensitivity. J Periodontol. 1982. 53:353–359.4. Richardson D, Tao L, Pashley DH. Dentin permeability: effects of crown preparation. Int J Prosthodont. 1991. 4:219–225.5. Zaimoglu A, Aydin AK. An evaluation of smear layer with various desensitizing agents after tooth preparation. J Prosthet Dent. 1992. 68:450–457.6. Kaufman EG, Coelho AB, Colin L. Factors influencing the retention of cemented gold castings. J Prosthet Dent. 1961. 11:486–502.7. Malone WFP, Koth DL. Tylman's theory and practice for fixed prosthodontics. 1989. 8th ed. St. Louis: Ishiyaku Euroamerica.8. Yim NH, Rueggeberg FA, Caughman WF, Gardner FM, Pashley DH. Effect of dentin desensitizers and cementing agents on retention of full crowns using standardized crown preparations. J Prosthet Dent. 2000. 83:459–465.9. Johnson GH, Hazelton LR, Bales DJ, Lepe X. The effect of a resin-based sealer on crown retention for three types of cement. J Prosthet Dent. 2004. 91:428–435.10. Palacios RP, Johnson GH, Phillips KM, Raigrodski AJ. Retention of zirconium oxide ceramic crowns with three types of cement. J Prosthet Dent. 2006. 96:104–114.11. Kern M, Kleimeier B, Schaller HG, Strub JR. Clinical comparison of postoperative sensitivity for a glass ionomer and a zinc phosphate luting cement. J Prosthet Dent. 1996. 75:159–162.12. Bebermeyer RD, Berg JH. Comparison of patient-perceived postcementation sensitivity with glass-ionomer and zinc phosphate cements. Quintessence Int. 1994. 25:209–214.13. Mazzaoui SA, Burrow MF, Tyas MJ, Dashper SG, Eakins D, Reynolds EC. Incorporation of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate into a glass-ionomer cement. J Dent Res. 2003. 82:914–918.14. Burwell A. Tubule occlusion of a NovaMin-containing dentrifrice compared to Recaldent-containing dentrifice-a Remin/Demin study in vitro. NovaMin Research Report. 2006. NovaMin Technology Inc..15. Swift EJ Jr, Lloyd AH, Felton DA. The effect of resin desensitizing agents on crown retention. J Am Dent Assoc. 1997. 128:195–200.16. Johnson GH, Lepe X, Bales DJ. Crown retention with use of a 5% glutaraldehyde sealer on prepared dentin. J Prosthet Dent. 1998. 79:671–676.17. Arrais CA, Chan DC, Giannini M. Effects of desensitizing agents on dentinal tubule occlusion. J Appl Oral Sci. 2004. 12:144–148.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of GLUMA desensitizer on the retention of full metal crowns cemented with Rely X U200 self-adhesive cement
- In vitro study of the tensile bond strength of cement-eetained single implant prosthesis by the various provisional luting cements and the surface treatment of abutments
- The selection criteria of temporary or permanent luting agents in implant-supported prostheses: in vitro study
- Effect of hemispherical dimples at titanium implant abutments for the retention of cemented crowns
- In vitro study of compressive fracture strength of Empress 2 crowns cemented with various luting agents