J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2008 Jul;33(4):405-412. 10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.405.
Is an oxygen inhibition layer essential for the interfacial bonding between resin composite layers?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Korea. inboglee@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2176008
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.405
Abstract
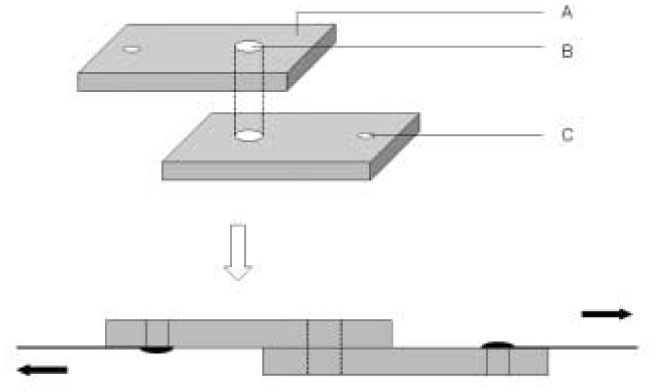
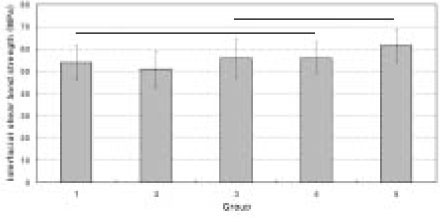
- This study was aimed to investigate whether an oxygen inhibition layer (OIL) is essential for the interfacial bonding between resin composite layers or not. A composite (Z-250, 3M ESPE) was filled in two layers using two aluminum plate molds with a hole of 3.7 mm diameter. The surface of first layer of cured composite was prepared by one of five methods as followings, thereafter second layer of composite was filled and cured: Group 1 - OIL is allowed to remain on the surface of cured composite; Group 2 - OIL was removed by rubbing with acetone-soaked cotton; Group 3 - formation of the OIL was inhibited using a Mylar strip; Group 4 - OIL was covered with glycerin and light-cured; Group 5 (control) - composite was bulk-filled in a layer. The interfacial shear bond strength between two layers was tested and the fracture modes were observed. To investigate the propagation of polymerization reaction from active area having a photo-initiator to inactive area without the initiator, a flowable composite (Aelite Flow) or an adhesive resin (Adhesive of ScotchBond Multipurpose) was placed over an experimental composite (Exp_Com) which does not include a photoinitiator and light-cured. After sectioning the specimen, the cured thickness of the Exp_Com was measured. The bond strength of group 2, 3 and 4 did not show statistically significant difference with group 1. Groups 3 and 4 were not statistically significant different with control group 5. The cured thicknesses of Exp_Com under the flowable resin and adhesive resin were 20.95 (0.90) um and 42.13 (2.09), respectively.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of glycerin on the surface hardness of composites after curing
Hyun-Hee Park, In-Bog Lee
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2011;36(6):483-489. doi: 10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.483.
Reference
-
1. Andrzejewska E, Lindén LÅ, Rabek JF. The role of oxygen in camphorquinone-initiated photopolymerization. Macromol Chem Phys. 1998. 199:441–449.
Article2. Gauthier MA, Stangel I, Ellis TH, Zhu XX. Oxygen inhibition in dental resins. J Dent Res. 2005. 84:725–729.
Article3. Truffier-Boutry D, Place E, Devaux J, Leloup G. Interfacial layer characterization in dental composite. J Oral Rehabil. 2003. 30:74–77.
Article4. Velazquez E, Vaidyanathan J, Vaidyanathan TK, Houpt M, Shey Z, von Hagen S. Effect of primer solvent and curing mode on dentin shear bond strength and interface morphology. Quintessence Int. 2003. 34:548–555.5. Kupiec KA, Barkmeier WW. Laboratory evaluation of surface treatments of composite repair. Oper Dent. 1996. 21:59–62.6. Suh BI. Oxygen-inhibited layer in adhesion dentistry. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2004. 16:316–323.
Article7. Dall'Oca S, Papacchini F, Goracci C, Cury AH, Suh BI, Tay FR, Polimeni A, Ferrari M. Effect of oxygen inhibition on composite repair strength over time. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2007. 81:493–498.8. Finger WJ, Lee KS, Podszun W. Monomers with low oxygen inhibition as enamel/dentin adhesives. Dent Mater. 1996. 12:256–261.
Article9. Rueggeberg FA, Margeson DH. The effect of oxygen inhibition on an unfilled/filled composite system. J Dent Res. 1990. 69:1652–1658.
Article10. Eliades GC, Caputo AA. The strength of layering technique in visible light-cured composites. J Prosthet Dent. 1989. 61:31–38.
Article11. Lewis G, Johnson W, Martin W, Canerdy A, Claburn C, Collier M. Shear bond strength of immediately repaired light-cured composite resin restorations. Oper Dent. 1998. 23:121–127.12. Ruyter IE. Unpolymerized surface layers on sealants. Acta Odontol Scand. 1981. 39:27–32.
Article13. Harry RA, Frederick WL, James EM. Contemporary polymer chemistry. 2003. 3rd Ed. Pearson Education Inc..14. Bala O, Olmez A, Kalayci S. Effect of LED and halogen light curing on polymerization of resin-based composites. J Oral Rehabil. 2005. 32:134–140.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effects of dentin bonding agent thickness on stress distribution of composite-tooth interface : Finite element method
- A Study Of Surface Roughness Of Composite Resin
- Development of anticariogenic composite resin
- Self-adhesion of low-viscosity composites to dentin surface
- Effect of film thickness of resin cement on bonding efficiency in indirect composite restoration