J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2009 Sep;34(5):442-449. 10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.5.442.
The effects of dentin bonding agent thickness on stress distribution of composite-tooth interface : Finite element method
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Korea. operatys16@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1986607
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.5.442
Abstract
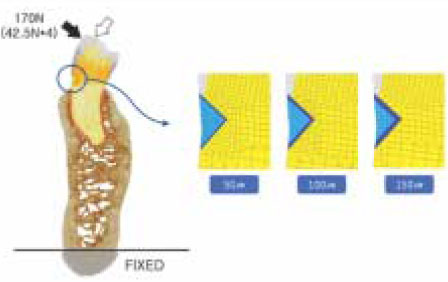
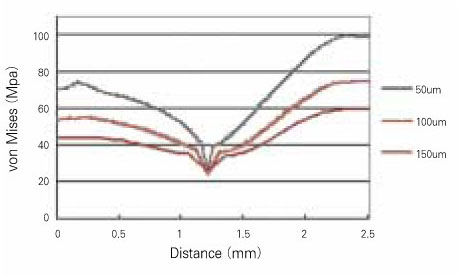
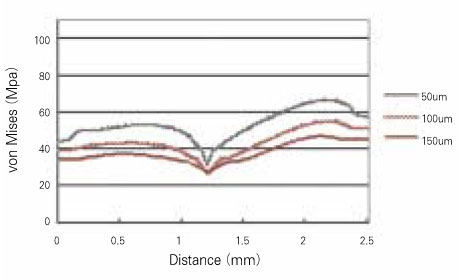
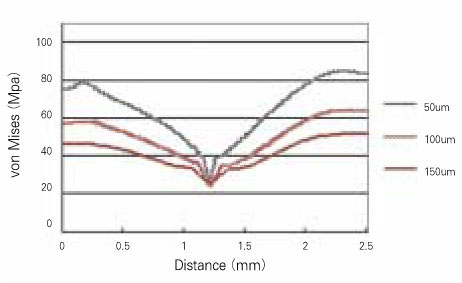
- The aim of this study was to examine that thick dentin bonding agent application or low modulus composite restoration could reduce stresses on dentin bonding agent layer. A mandibular first premolar with abfraction lesion was modeled by finite element method. The lesion was restored by different composite resins with variable dentin bonding agent thickness (50microm, 100microm, 150microm). 170N of occlusal loading was applied buccally or lingually. Von Mises stress on dentin bonding agent layer were measured. When thickness of dentin bonding agent was increased von Mises stresses at dentin bonding agent were decreased in both composites. Lower elastic modulus composite restoration showed decreased von Mises stresses. On root dentin margin more stresses were generated than enamel margin. For occlusal stress relief at dentin boning agent layer to applicate thick dentin bonding agent or to choose low elastic modulus composite is recommended.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Influence of application methods of one-step self-etching adhesives on microtensile bond strength
Chul-Kyu Choi, Sung-Ae Son, Jin-Hee Ha, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Yong-Hun Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2011;36(3):203-210. doi: 10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.203.
Reference
-
1. Grippo JO. Abfractions : a new classification of hard tissue lesions of teeth. J Esthet Dent. 1991. 3:14–19.2. Heymann HO. Examining tooth flexure effects. JADA. 1991. 122:41–47.3. Lee WC, Eakle WS. Possible role of tensile stress in the etiology of cervical erosive lesions of teeth. J Prosthet Dent. 1984. 52:374–380.
Article4. Stewart GP, Balda BA, Norman RD. The effects of mechanical loading on marginal integrity of composite restorations. Dent Mater. 1986. 2:151–152.
Article5. Sturdevant JR, Lundeen TF, Sluder TB, Leinfelder KF. Three-year study of two light-cured posterior composite resins. Dent Mater. 1986. 2:263–268.
Article6. McCoy RB, Anderson MH, Lepe X, Jonson GH. Clinical success of class V composite resin restorations without mechanical retention. JADA. 1998. 129:593–599.
Article7. Mattison GD. Photoelastic stress analysis of cast gold endodontic posts. J Prosthet Dent. 1982. 48:407–411.8. Assif D, Oren E, Marshak BL, Aviv I. Photoelastic analysis of stress transfer by endodontically treated teeth to the supporting structures using different restorative technique. J Prosthet Dent. 1989. 61:535–543.
Article9. Kuroe T, Itoh H, Caputo AA, Konuma M. Biomechanincs of cervical tooth structure lesions and their restoration. Quintessence Int. 2000. 31:267–274.10. Um CM, Kwon HC, Son HH, Cho BH, Rim YI. Finite element analysis of stress distribution according to cavity design of class v composite resin filling. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 1999. 24:67–75.11. Turner MJ, Clough RW, Martin HC, Topp LJ. Stiffness and deflection analysis of complex structure. J Aero Sci. 1956. 23:805–823.12. Ausiello P, Apicella A, Davidson CL. Effect of adhesive layer properties on stress distribution in composite restorations-a 3D finite element analysis. Dent Mater. 2002. 18:295–303.
Article13. Rees JS. The effect of variation in occlusal loading on the development of abfraction lesions : a finite element study. J Oral Rehabil. 2002. 29:188–193.
Article14. Yaman SD, Sahin M, Aydin C. Finite element analysis of strength characteristics of various resin based restorative materials in class V cavities. J Oral Rehabil. 2003. 30:630–641.
Article15. Chon CS, Kim HS, Shim JS, Kim YH. Finite element knalysis for elastic modulus of the periodontal ligament in premolar regions. J Korean Soc Precision Eng. 2005. 22:202–209.16. Van Meerbeek B, Willems G, Celis JP, Roos JR, Braem M, Lambrechts P, Vanherle G. Assesment by nano-indentation of the hardness and elasticity of the resin-dentin bonding area. J Dent Res. 1993. 72:1434–1442.
Article17. Moon PC, Chang YH. Effect of DBA layer thickness on composite resin shrinkage stress. J Dent Res. 1992. 71:275–283.18. Choi KK, Cordon JR, Ferracane JL. The effects of adhesive thickness on polymerization contraction stress of composite. J Dent Res. 2000. 79:812–817.
Article19. Peter A, Paul SJ, Luthy H, Scharer P. Film thickness of various dentin bonding agents. J Oral Rehabil. 1997. 24:568–573.20. Cho BH, Yoo HM, Kim DH. Two-dimensional finite element analysis on the effect of interface condition and retention groove in class v composite resin restoration. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 1998. 23:639–646.21. Rees JS. Abfraction lesion formation in maxillary incisors, canines and premolars: A finite element study. Eur J Oral Sci. 2003. 111:149–154.
Article22. Widmalm SE, Ericsson SG. Maximal bite force with centric and eccentric load. J Oral Rehabil. 1982. 9:445–450.
Article23. Gibbs CH, Mahan PE, Lundeen HC, Brehnan K, Walsh EK, Holbrook WB. Occlusal force during chewing and swallowing as measured by sound transmission. J Prosthet Dent. 1981. 46:443–449.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stress distribution of oval and circular fiber posts in amandibular premolar: a three-dimensional finite element analysis
- A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON THE COMPOSITE RESTORATION DESIGN AND PLACEMENT METHODS USING THREE DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
- Effect of the marginal position of prosthesis on stress distribution of teeth with abfraction lesion using finite element analysis
- The effect of restorative materials on the stress distribution of class V composite resin restorations: a 3D finite element investigation
- Finite element analysis of the influence of esthetic posts on incisors