Diabetes Metab J.
2013 Aug;37(4):252-261. 10.4093/dmj.2013.37.4.252.
Serum Adiponectin and Type 2 Diabetes: A 6-Year Follow-Up Cohort Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute for Health Promotion, Department of Epidemiology and Health Promotion, Yonsei University Graduate School of Public Health, Seoul, Korea. jsunha@yuhs.ac
- 2Division of Endocrinology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Cardiovascular Center, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Cardiology Division, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Food and Nutrition, Sungshin Women's University College of Human Ecology, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Family Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 10Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, and Cardiac and Vascular Center, Center for Health Promotion, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 11Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 12Division of Public Health Nutrition, Seoul National University School of Public Health and Institute of Health and Environment, Seoul, Korea.
- 13Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 14Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 15Department of Family Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 16Department of Family Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 17National Health Insurance Service, Seoul, Korea.
- 18Huh's Diabetes Center and the 21th Century Diabetes and Vascular Research Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2174266
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.4.252
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Studies on factors which may predict the risk of diabetes are scarce. This prospective cohort study was conducted to determine the association between adiponectin and type 2 diabetes among Korean men and women.
METHODS
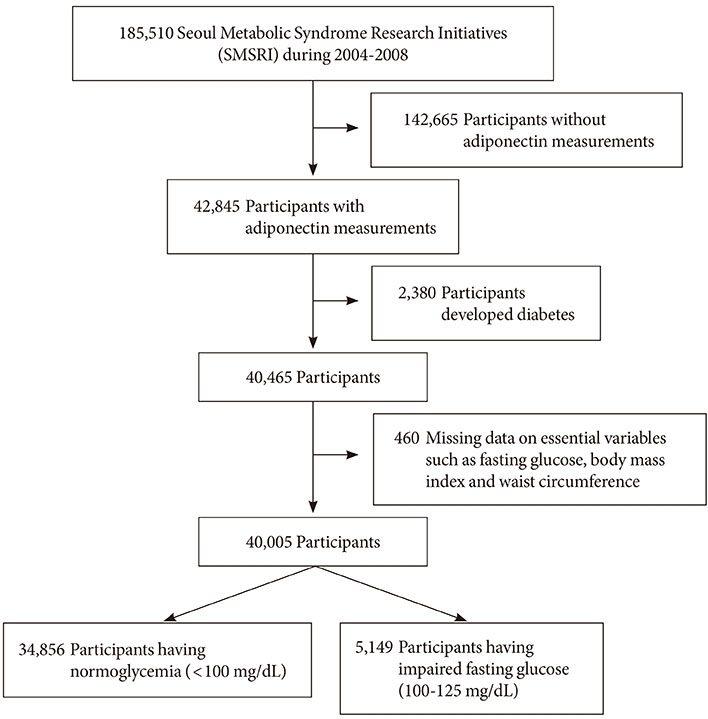
A total of 42,845 participants who visited one of seven health examination centers located in Seoul and Gyeonggi province, Republic of Korea between 2004 and 2008 were included in this study. The incidence rates of diabetes were determined through December 2011. To evaluate the effects of adiponectin on type 2 diabetes, the Cox proportional hazard model was used.
RESULTS
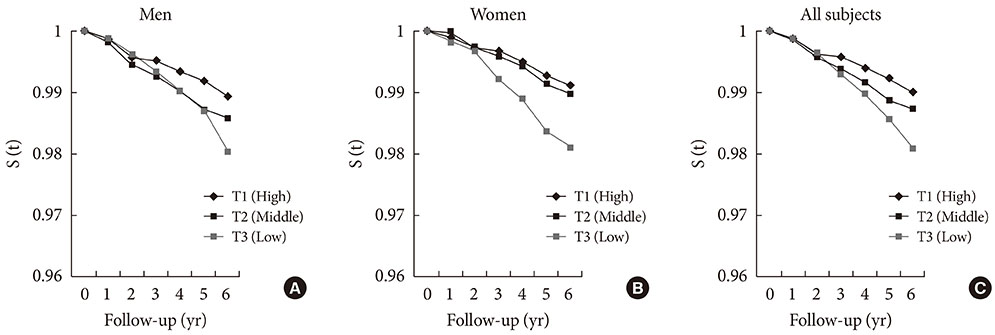
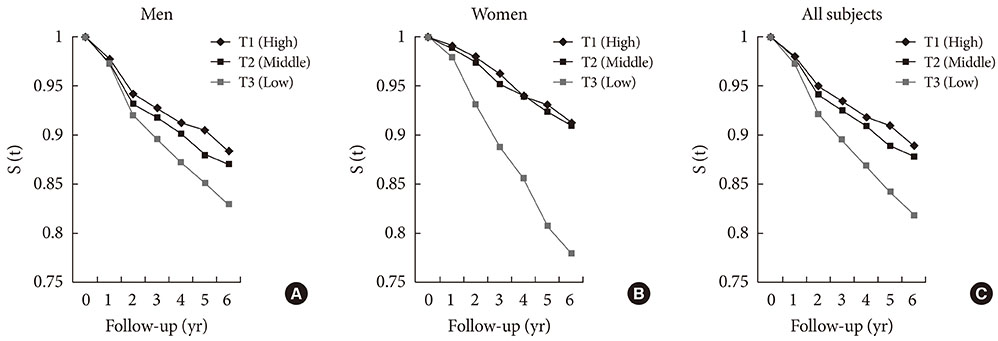
Of the 40,005 participants, 959 developed type 2 diabetes during a 6-year follow-up. After the adjustment for age, body mass index (BMI), and waist circumference, the risks for type 2 diabetes in participants with normoglycemia had a 1.70-fold (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.21 to 2.38) increase in men and a 1.83-fold (95% CI, 1.17 to 2.86) increase in women with the lowest tertile of adiponectin when compared to the highest tertile of adiponectin. For participants with impaired fasting glucose (IFG), the risk for type 2 diabetes had a 1.46-fold (95% CI, 1.17 to 1.83) increase in men and a 2.52-fold (95% CI, 1.57 to 4.06) increase in women with the lowest tertile of adiponectin. Except for female participants with normoglycemia, all the risks remained significant after the adjustment for fasting glucose and other confounding variables. Surprisingly, BMI and waist circumference were not predictors of type 2 diabetes in men or women with IFG after adjustment for fasting glucose and other confounders.
CONCLUSION
A strong association between adiponectin and diabetes was observed. The use of adiponectin as a predictor of type 2 diabetes is considered to be useful.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Levitzky YS, Pencina MJ, D'Agostino RB, Meigs JB, Murabito JM, Vasan RS, Fox CS. Impact of impaired fasting glucose on cardiovascular disease: the Framingham Heart Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008. 51:264–270.2. Kim HK, Kim CH, Kim EH, Bae SJ, Choe J, Park JY, Park SW, Yun YD, Baek SJ, Mok Y, Jee SH. Impaired fasting glucose and risk of cardiovascular disease in Korean men and women: the Korean Heart Study. Diabetes Care. 2013. 36:328–335.3. Stefan N, Vozarova B, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Weyer C, Lindsay RS, Youngren JF, Havel PJ, Pratley RE, Bogardus C, Tataranni PA. Plasma adiponectin concentration is associated with skeletal muscle insulin receptor tyrosine phosphorylation, and low plasma concentration precedes a decrease in whole-body insulin sensitivity in humans. Diabetes. 2002. 51:1884–1888.4. Filippi E, Sentinelli F, Trischitta V, Romeo S, Arca M, Leonetti F, Di Mario U, Baroni MG. Association of the human adiponectin gene and insulin resistance. Eur J Hum Genet. 2004. 12:199–205.5. Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Waki H, Terauchi Y, Kubota N, Hara K, Mori Y, Ide T, Murakami K, Tsuboyama-Kasaoka N, Ezaki O, Akanuma Y, Gavrilova O, Vinson C, Reitman ML, Kagechika H, Shudo K, Yoda M, Nakano Y, Tobe K, Nagai R, Kimura S, Tomita M, Froguel P, Kadowaki T. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat Med. 2001. 7:941–946.6. Yoon SJ, Lee HS, Lee SW, Yun JE, Kim SY, Cho ER, Lee SJ, Jee EJ, Lee HY, Park J, Kim HS, Jee SH. The association between adiponectin and diabetes in the Korean population. Metabolism. 2008. 57:853–857.7. Hotta K, Funahashi T, Arita Y, Takahashi M, Matsuda M, Okamoto Y, Iwahashi H, Kuriyama H, Ouchi N, Maeda K, Nishida M, Kihara S, Sakai N, Nakajima T, Hasegawa K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Hanafusa T, Matsuzawa Y. Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000. 20:1595–1599.8. Li S, Shin HJ, Ding EL, van Dam RM. Adiponectin levels and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2009. 302:179–188.9. Chen KT, Chen CJ, Gregg EW, Imperatore G, Narayan KM. Impaired fasting glucose and risk of diabetes in Taiwan: follow-up over 3 years. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2003. 60:177–182.10. Vazquez G, Duval S, Jacobs DR Jr, Silventoinen K. Comparison of body mass index, waist circumference, and waist/hip ratio in predicting incident diabetes: a meta-analysis. Epidemiol Rev. 2007. 29:115–128.11. Cnop M, Havel PJ, Utzschneider KM, Carr DB, Sinha MK, Boyko EJ, Retzlaff BM, Knopp RH, Brunzell JD, Kahn SE. Relationship of adiponectin to body fat distribution, insulin sensitivity and plasma lipoproteins: evidence for independent roles of age and sex. Diabetologia. 2003. 46:459–469.12. Snehalatha C, Mukesh B, Simon M, Viswanathan V, Haffner SM, Ramachandran A. Plasma adiponectin is an independent predictor of type 2 diabetes in Asian indians. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:3226–3229.13. Kita A, Yamasaki H, Kuwahara H, Moriuchi A, Fukushima K, Kobayashi M, Fukushima T, Takahashi R, Abiru N, Uotani S, Kawasaki E, Eguchi K. Identification of the promoter region required for human adiponectin gene transcription: association with CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005. 331:484–490.14. Gavrila A, Chan JL, Yiannakouris N, Kontogianni M, Miller LC, Orlova C, Mantzoros CS. Serum adiponectin levels are inversely associated with overall and central fat distribution but are not directly regulated by acute fasting or leptin administration in humans: cross-sectional and interventional studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003. 88:4823–4831.15. Kim HS, Jo J, Lim JE, Yun YD, Baek SJ, Lee TY, Huh KB, Jee SH. Adiponectin as predictor for diabetes among pre-diabetic groups. Endocrine. 2013. 02. 06. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12020-013-9890-5.16. Rabe K, Lehrke M, Parhofer KG, Broedl UC. Adipokines and insulin resistance. Mol Med. 2008. 14:741–751.17. Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T, Kubota N, Hara K, Ueki K, Tobe K. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2006. 116:1784–1792.18. Weyer C, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Hotta K, Matsuzawa Y, Pratley RE, Tataranni PA. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 86:1930–1935.19. Tschritter O, Fritsche A, Thamer C, Haap M, Shirkavand F, Rahe S, Staiger H, Maerker E, Haring H, Stumvoll M. Plasma adiponectin concentrations predict insulin sensitivity of both glucose and lipid metabolism. Diabetes. 2003. 52:239–243.20. Menzaghi C, Trischitta V, Doria A. Genetic influences of adiponectin on insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes. 2007. 56:1198–1209.21. Du W, Li Q, Lu Y, Yu X, Ye X, Gao Y, Ma J, Cheng J, Cao Y, Du J, Shi H, Zhou L. Genetic variants in ADIPOQ gene and the risk of type 2 diabetes: a case-control study of Chinese Han population. Endocrine. 2011. 40:413–422.22. Pischon T, Hotamisligil GS, Rimm EB. Adiponectin: stability in plasma over 36 hours and within-person variation over 1 year. Clin Chem. 2003. 49:650–652.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of Plasma Adiponectin and Polymorphism of Adiponectin Gene in the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- The Plasma Adiponectin Levels in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes
- Impact of the Serum Adiponectin Concentration on the Progression of Carotid Atherosclerosis in Patient with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- The Plasma Adiponectin Levels in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes
- Impact of Serum Adiponectin Concentration on Progression of Carotid Atherosclerosis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus