Blood Res.
2015 Sep;50(3):147-153. 10.5045/br.2015.50.3.147.
Favorable outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation followed by post-transplant treatment with imatinib in children with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology, Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hojim@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2172757
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2015.50.3.147
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is the preferred curative therapy for children with Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). We evaluated the treatment outcomes of children with Ph+ ALL who underwent allogeneic HSCT.
METHODS
Fifteen children diagnosed with Ph+ ALL in Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital between 1998 and 2012 were retrospectively analyzed.
RESULTS
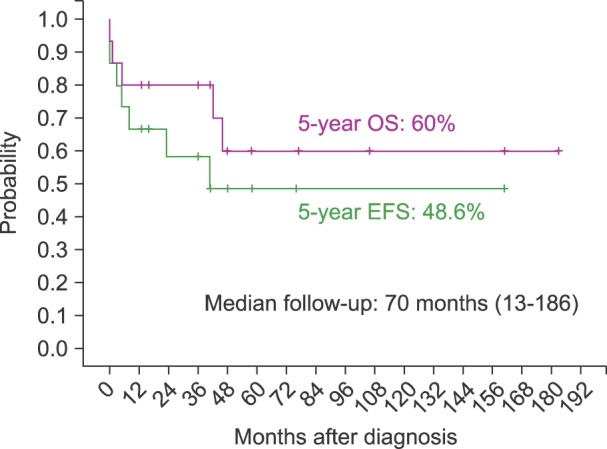
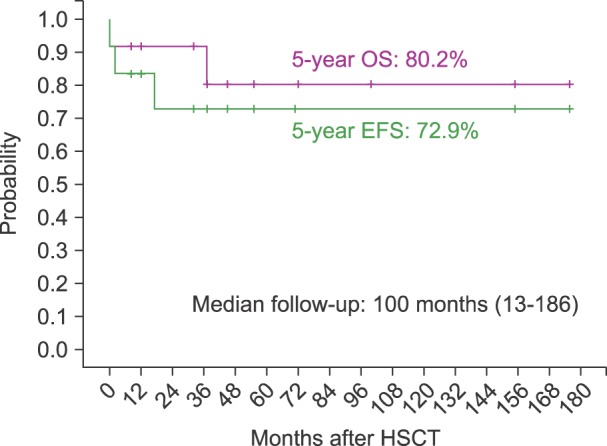
Of 521 children diagnosed with ALL during the study period, 15 had a Philadelphia chromosome. Among these 15 patients, 13 attained complete remission (CR) following induction chemotherapy, and two died of intracerebral hemorrhage during leukapheresis and induction chemotherapy, respectively. Of the 13 patients who attained CR, 12 received allogeneic HSCT, mainly from unrelated donors. Of the 12 patients who received HSCT, one died of a transplant-related cause, one died of relapse after HSCT, and 10 remain in continuous CR. Of the 10 patients who remained in CR longer than six months after HSCT, seven received post-HSCT imatinib. For all 15 patients, the 5-year overall survival, event-free survival, and cumulative incidence of relapse were 60.0%, 48.6%, and 38.8%, respectively, with a median follow-up of 70 months. For the HSCT group, the 5-year overall survival, event-free survival, and cumulative incidence of relapse were 80.2%, 72.9%, and 29.3%, respectively, with a median follow-up of 100 months.
CONCLUSION
Allogeneic HSCT cures a significant proportion of Ph+ ALL patients. Because the use of imatinib appears to be a promising approach, strategies that include tyrosine kinase inhibitors before and after HSCT require further evaluation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Cerebral Hemorrhage
Child*
Chungcheongnam-do
Disease-Free Survival
Follow-Up Studies
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation*
Hematopoietic Stem Cells*
Humans
Incidence
Induction Chemotherapy
Leukapheresis
Philadelphia Chromosome
Precursor Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia-Lymphoma*
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Recurrence
Retrospective Studies
Unrelated Donors
Imatinib Mesylate
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Outcome and prognostic factors of children with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with imatinib followed by allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in first remission
Juae Shin, Na Yeong Lee, Seongkoo Kim, Jae Wook Lee, Pil-Sang Jang, Nack-Gyun Chung, Bin Cho
Blood Res. 2019;54(1):45-51. doi: 10.5045/br.2019.54.1.45.
Reference
-
1. Cytogenetic abnormalities in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: correlations with hematologic findings outcome. A Collaborative Study of the Group Français de Cytogénétique Hématologique. Blood. 1996; 87:3135–3142. PMID: 8605327.2. Aricò M, Schrappe M, Hunger SP, et al. Clinical outcome of children with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated between 1995 and 2005. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:4755–4761. PMID: 20876426.
Article3. Ottmann OG, Pfeifer H. Management of Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL). Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2009; 371–381. PMID: 20008223.
Article4. Ravandi F, Kebriaei P. Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2009; 23:1043–1063. PMID: 19825452.
Article5. Schrappe M, Nachman J, Hunger S, et al. Educational symposium on long-term results of large prospective clinical trials for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (1985-2000). Leukemia. 2010; 24:253–254. PMID: 20145664.
Article6. Fagioli F, Zecca M, Rognoni C, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children and adolescents: a retrospective multicenter study of the Italian Association of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology (AIEOP). Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012; 18:852–860. PMID: 22019726.
Article7. Roy A, Bradburn M, Moorman AV, et al. Early response to induction is predictive of survival in childhood Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: results of the Medical Research Council ALL 97 trial. Br J Haematol. 2005; 129:35–44. PMID: 15801953.
Article8. Schrappe M, Aricò M, Harbott J, et al. Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: good initial steroid response allows early prediction of a favorable treatment outcome. Blood. 1998; 92:2730–2741. PMID: 9763557.9. Mori T, Manabe A, Tsuchida M, et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in first remission rescues children with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Tokyo Children's Cancer Study Group (TCCSG) studies L89-12 and L92-13. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2001; 37:426–431. PMID: 11745870.
Article10. Laport GG, Alvarnas JC, Palmer JM, et al. Long-term remission of Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation from matched sibling donors: a 20-year experience with the fractionated total body irradiation-etoposide regimen. Blood. 2008; 112:903–909. PMID: 18519812.
Article11. Wei G, Rafiyath S, Liu D. First-line treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia: dasatinib, nilotinib, or imatinib. J Hematol Oncol. 2010; 3:47. PMID: 21108851.
Article12. de Labarthe A, Rousselot P, Huguet-Rigal F, et al. Imatinib combined with induction or consolidation chemotherapy in patients with de novo Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of the GRAAPH-2003 study. Blood. 2007; 109:1408–1413. PMID: 17062730.
Article13. Lee S, Kim YJ, Min CK, et al. The effect of first-line imatinib interim therapy on the outcome of allogeneic stem cell transplantation in adults with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2005; 105:3449–3457. PMID: 15657178.
Article14. Yanada M, Takeuchi J, Sugiura I, et al. High complete remission rate and promising outcome by combination of imatinib and chemotherapy for newly diagnosed BCR-ABL-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a phase II study by the Japan Adult Leukemia Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:460–466. PMID: 16344315.
Article15. Druker BJ, Sawyers CL, Kantarjian H, et al. Activity of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in the blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia with the Philadelphia chromosome. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:1038–1042. PMID: 11287973.
Article16. Hoelzer D, Gökbuget N, Ottmann OG. Targeted therapies in the treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Semin Hematol. 2002; 39(4 Supple 3):32–37. PMID: 12447850.
Article17. Ottmann OG, Druker BJ, Sawyers CL, et al. A phase 2 study of imatinib in patients with relapsed or refractory Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoid leukemias. Blood. 2002; 100:1965–1971. PMID: 12200353.
Article18. Chen H, Liu KY, Xu LP, et al. Administration of imatinib after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation may improve disease-free survival for patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphobla stic leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2012; 5:29. PMID: 22682059.
Article19. Aricò M, Valsecchi MG, Camitta B, et al. Outcome of treatment in children with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2000; 342:998–1006. PMID: 10749961.
Article20. Sharathkumar A, Saunders EF, Dror Y, et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation vs chemotherapy for children with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2004; 33:39–45. PMID: 14566329.
Article21. Doki N, Ohashi K, Oshikawa G, Kobayashi T, Kakihana K, Sakamaki H. Clinical outcome of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph + ALL): experience from a single institution. Pathol Oncol Res. 2014; 20:61–66. PMID: 23821455.
Article22. Salami K, Alkayed K, Halalsheh H, Hussein AA, Riziq M, Madanat F. Hematopoietic stem cell transplant versus chemotherapy plus tyrosine kinase inhibitor in the treatment of pediatric Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2013; 6:34–41. PMID: 23664604.
Article23. Rives S, Estella J, Gómez P, et al. Intermediate dose of imatinib in combination with chemotherapy followed by allogeneic stem cell transplantation improves early outcome in paediatric Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL): results of the Spanish Cooperative Group SHOP studies ALL-94, ALL-99 and ALL-2005. Br J Haematol. 2011; 154:600–611. PMID: 21707583.24. Manabe A, Kawasaki H, Shimada H, et al. Imatinib use immediately before stem cell transplantation in children with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Results from Japanese Pediatric Leukemia/Lymphoma Study Group (JPLSG) Study Ph(+) ALL04. Cancer Med. 2015; 4:682–689. PMID: 25641907.25. Nishiwaki S, Miyamura K, Kato C, et al. Impact of post-transplant imatinib administration on Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Anticancer Res. 2010; 30:2415–2418. PMID: 20651401.26. Schultz KR, Bowman WP, Aledo A, et al. Improved early event-free survival with imatinib in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a children's oncology group study. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:5175–5181. PMID: 19805687.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia in childhood
- Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Following Imatinib Plus Idarubicin and High-dose Cytarabine in Children with Philadelphia Chromosome-positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- Three cases of Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome positive acute myeloid leukemia (AML) treated with imatinib mesylate (Glivec, STI571) and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation after induction chemotherapy
- Complete Remission by Imatinib Mesylate (Glivec) in a Child Relapsing with Philadelphia Chromosome Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (Ph (+) ALL) after Unrelated Donor Stem Cell Transplantation
- Outcome and prognostic factors of children with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with imatinib followed by allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in first remission