Blood Res.
2016 Mar;51(1):50-57. 10.5045/br.2016.51.1.50.
Influence of genetic polymorphisms in the folate pathway on toxicity after high-dose methotrexate treatment in pediatric osteosarcoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University Children's Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hyshin@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2172745
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2016.51.1.50
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Methotrexate (MTX), one of the main drugs used to treat osteosarcoma, is a representative folic acid antagonist. Polymorphisms of various enzymes involved in the metabolism of MTX could contribute to differences in response to MTX in pediatric osteosarcoma patients.
METHODS
Blood and tissue samples were obtained from 37 pediatric osteosarcoma patients who were treated with high-dose MTX therapy. The following 4 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were analyzed: ATIC 347C>G, MTHFR 677C>T, MTHFR 1298A>C and SLC19A1 80G>A. Serial plasma MTX concentrations after high-dose MTX therapy and MTX-induced toxicities were evaluated. Correlations among polymorphisms, MTX concentrations and treatment-induced toxicities were assessed.
RESULTS
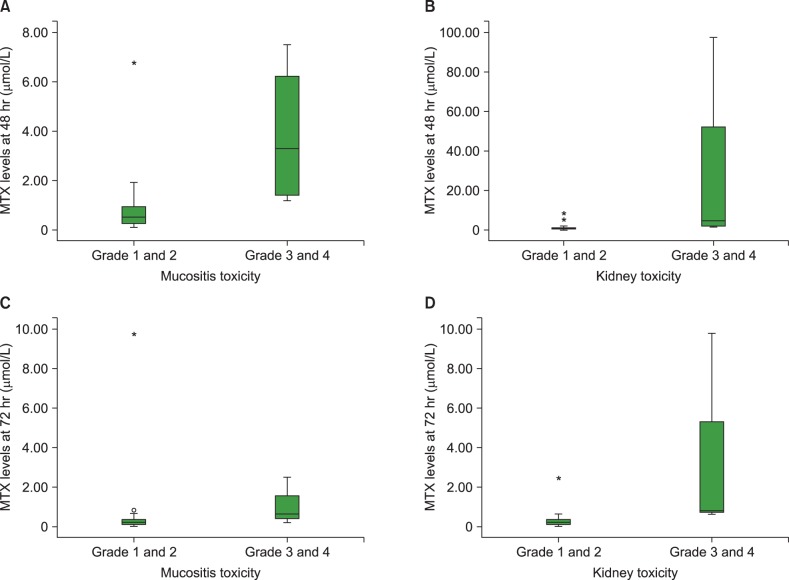
Plasma MTX levels at 48 hours after high-dose MTX infusion were significantly associated with SLC19A1 80G>A (P=0.031). Higher plasma levels of MTX at 48 and 72 hours were significantly associated with MTX-induced mucositis (P=0.007 and P=0.046) and renal toxicity (P=0.002), respectively. SNP of SLC19A1 gene was associated with development of severe mucositis (P=0.026).
CONCLUSION
This study suggests that plasma levels of MTX are associated with GI and renal toxicities after high-dose MTX therapy, and genetic polymorphisms that affect the metabolism of MTX may influence drug concentrations and development of significant side effects in pediatric patients treated with high-dose MTX.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Relling MV, Fairclough D, Ayers D, et al. Patient characteristics associated with high-risk methotrexate concentrations and toxicity. J Clin Oncol. 1994; 12:1667–1672. PMID: 8040679.
Article2. Rask C, Albertioni F, Bentzen SM, Schroeder H, Peterson C. Clinical and pharmacokinetic risk factors for high-dose methotrexate-induced toxicity in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia-a logistic regression analysis. Acta Oncol. 1998; 37:277–284. PMID: 9677100.3. Johansson ÅM, Hill N, Perisoglou M, Whelan J, Karlsson MO, Standing JF. A population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model of methotrexate and mucositis scores in osteosarcoma. Ther Drug Monit. 2011; 33:711–718. PMID: 22105588.
Article4. de Jonge R, Tissing WJ, Hooijberg JH, et al. Polymorphisms in folate-related genes and risk of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2009; 113:2284–2289. PMID: 19020309.
Article5. Gorlick R, Goker E, Trippett T, Waltham M, Banerjee D, Bertino JR. Intrinsic and acquired resistance to methotrexate in acute leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1996; 335:1041–1048. PMID: 8793930.
Article6. Stamp LK, Roberts RL. Effect of genetic polymorphisms in the folate pathway on methotrexate therapy in rheumatic diseases. Pharmacogenomics. 2011; 12:1449–1463. PMID: 22008049.
Article7. Meyers PA, Schwartz CL, Krailo M, et al. Osteosarcoma: a randomized, prospective trial of the addition of ifosfamide and/or muramyl tripeptide to cisplatin, doxorubicin, and high-dose methotrexate. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:2004–2011. PMID: 15774791.
Article8. Marina N, Bielack S, Whelan J, et al. International collaboration is feasible in trials for rare conditions: the EURAMOS experience. Cancer Treat Res. 2009; 152:339–353. PMID: 20213400.
Article9. Trotti A, Colevas AD, Setser A, et al. CTCAE v3.0: development of a comprehensive grading system for the adverse effects of cancer treatment. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2003; 13:176–181. PMID: 12903007.
Article10. Perez C, Wang YM, Sutow WW, Herson J. Significance of the 48-hour plasma level in high-dose methotrexate regimens. Cancer Clin Trials. 1978; 1:107–111. PMID: 316368.11. Shimasaki N, Mori T, Samejima H, et al. Effects of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase and reduced folate carrier 1 polymorphisms on high-dose methotrexate-induced toxicities in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia or lymphoma. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2006; 28:64–68. PMID: 16462575.
Article12. Imanishi H, Okamura N, Yagi M, et al. Genetic polymorphisms associated with adverse events and elimination of methotrexate in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and malignant lymphoma. J Hum Genet. 2007; 52:166–171. PMID: 17180579.
Article13. Laverdière C, Chiasson S, Costea I, Moghrabi A, Krajinovic M. Polymorphism G80A in the reduced folate carrier gene and its relationship to methotrexate plasma levels and outcome of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2002; 100:3832–3834. PMID: 12411325.14. Huang L, Tissing WJ, de Jonge R, van Zelst BD, Pieters R. Polymorphisms in folate-related genes: association with side effects of high-dose methotrexate in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2008; 22:1798–1800. PMID: 18368069.
Article15. Zhao R, Seither R, Brigle KE, Sharina IG, Wang PJ, Goldman ID. Impact of overexpression of the reduced folate carrier (RFC1), an anion exchanger, on concentrative transport in murine L1210 leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272:21207–21212. PMID: 9261128.
Article16. Matherly LH, Goldman DI. Membrane transport of folates. Vitam Horm. 2003; 66:403–456. PMID: 12852262.
Article17. Holmboe L, Andersen AM, Mørkrid L, Slørdal L, Hall KS. High dose methotrexate chemotherapy: pharmacokinetics, folate and toxicity in osteosarcoma patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012; 73:106–114. PMID: 21707700.
Article18. Widemann BC, Adamson PC. Understanding and managing methotrexate nephrotoxicity. Oncologist. 2006; 11:694–703. PMID: 16794248.
Article19. Evans WE, Pratt CB, Taylor RH, Barker LF, Crom WR. Pharmacokinetic monitoring of high-dose methotrexate. Early recognition of high-risk patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1979; 3:161–166. PMID: 316744.20. Stoller RG, Hande KR, Jacobs SA, Rosenberg SA, Chabner BA. Use of plasma pharmacokinetics to predict and prevent methotrexate toxicity. N Engl J Med. 1977; 297:630–634. PMID: 302412.
Article21. Bernard S, Etienne MC, Fischel JL, Formento P, Milano G. Critical factors for the reversal of methotrexate cytotoxicity by folinic acid. Br J Cancer. 1991; 63:303–307. PMID: 1997110.
Article22. Fabre I, Fabre G, Goldman ID. Polyglutamylation, an important element in methotrexate cytotoxicity and selectivity in tumor versus murine granulocytic progenitor cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 1984; 44:3190–3195. PMID: 6204743.23. Gervasini G. Polymorphisms in methotrexate pathways: what is clinically relevant, what is not, and what is promising. Curr Drug Metab. 2009; 10:547–566. PMID: 19702537.
Article24. Schmiegelow K. Advances in individual prediction of methotrexate toxicity: a review. Br J Haematol. 2009; 146:489–503. PMID: 19538530.
Article25. Ross CJ, Visscher H, Rassekh SR, et al. Pharmacogenomics of serious adverse drug reactions in pediatric oncology. J Popul Ther Clin Pharmacol. 2011; 18:e134–e151. PMID: 21467604.26. Stringer AM, Gibson RJ, Bowen JM, Keefe DM. Chemotherapy-induced modifications to gastrointestinal microflora: evidence and implications of change. Curr Drug Metab. 2009; 10:79–83. PMID: 19149515.
Article27. Pico JL, Avila-Garavito A, Naccache P. Mucositis: Its occurrence, consequences, and treatment in the oncology setting. Oncologist. 1998; 3:446–451. PMID: 10388137.
Article28. Epstein JB. Mucositis in the cancer patient and immunosuppressed host. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2007; 21:503–522. viiPMID: 17561080.
Article29. de Koning BA, van Dieren JM, Lindenbergh-Kortleve DJ, et al. Contributions of mucosal immune cells to methotrexate-induced mucositis. Int Immunol. 2006; 18:941–949. PMID: 16636014.
Article30. Gregers J, Christensen IJ, Dalhoff K, et al. The association of reduced folate carrier 80G>A polymorphism to outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia interacts with chromosome 21 copy number. Blood. 2010; 115:4671–4677. PMID: 20335220.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Study on Administration of High-Dose Methotrexate in Children with Osteosarcoma
- Influence of low dose folic acid replacement treatment on plasm homocysteine level in korean coronary artery disease patients.
- Pathological responses to preoperative high-dose methotrexate chemotherapy in osteosarcoma: experience in Korea cancer hospital
- Two Pediatric Osteosarcoma Cases with Delayed Methotrexate Excretion: Its Clinical Course and Management
- A Case of Osteosarcoma after Treatment of Endodermal Sinus Tumor