Ann Dermatol.
2015 Oct;27(5):593-596. 10.5021/ad.2015.27.5.593.
Folliculocystic and Collagen Hamartoma: A New Entity?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea. shlee@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2171459
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2015.27.5.593
Abstract
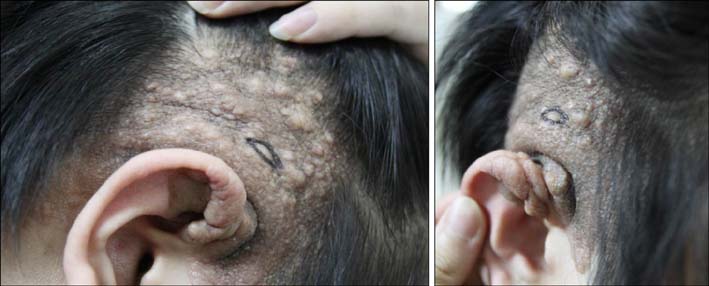
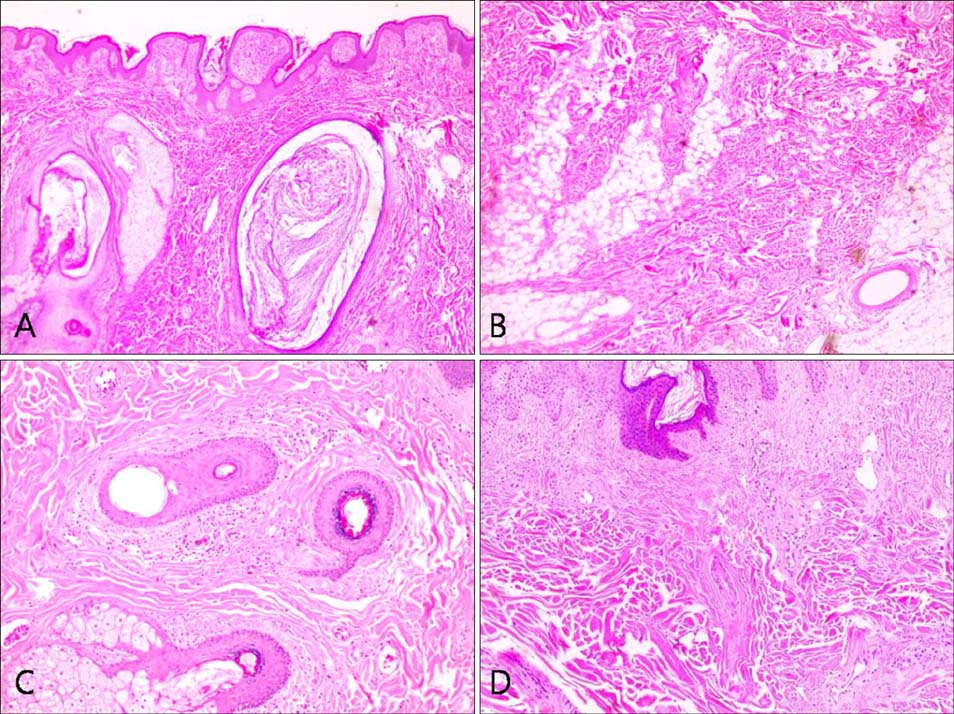
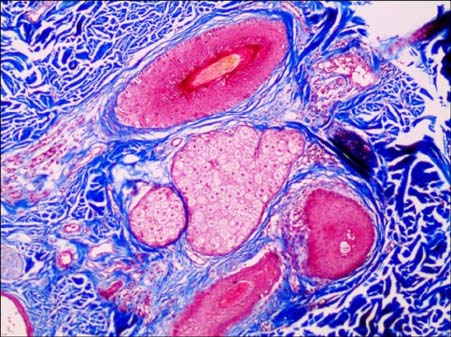
- Folliculocystic and collagen hamartoma is a newly described complex hamartoma characterized by abundant collagen deposition, concentric perifollicular fibrosis, and keratin- filled infundibular cysts that are visible on histopathological examination. Here, we report the case of a 19-year-old Korean man who had large brownish infiltrated plaques with numerous follicular comedo-like openings and subcutaneous cystic masses on his right temporal scalp and ear since birth. Histopathological examination showed abundant collagen deposition in the dermis that extended up to the subcutaneous fat layer, multifocal infundibular cysts packed with keratin, and perifollicular inflammation and fibrosis. Hence, we describe a new type of hamartoma with folliculocystic and collagen components but without tuberous sclerosis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Torrelo A, Hadj-Rabia S, Colmenero I, Piston R, Sybert VP, Hilari-Carbonell H, et al. Folliculocystic and collagen hamartoma of tuberous sclerosis complex. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012; 66:617–621.
Article2. Uitto J, Santa Cruz DJ, Eisen AZ. Connective tissue nevi of the skin. Clinical, genetic, and histopathologic classification of hamartomas of the collagen, elastin, and proteoglycan type. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1980; 3:441–461.3. Wataya-Kaneda M, Tanaka M, Hamasaki T, Katayama I. Trends in the prevalence of tuberous sclerosis complex manifestations: an epidemiological study of 166 Japanese patients. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e63910.
Article4. Nickel WR, Reed WB. Tuberous sclerosis. Special reference to the microscopic alterations in the cutaneous hamartomas. Arch Dermatol. 1962; 85:209–226.5. Morrison JG, Jones EW, MacDonald DM. Juvenile elastoma and osteopoikilosis (the Buschke--Ollendorff syndrome). Br J Dermatol. 1977; 97:417–422.
Article6. Umaretiya PJ, Miest RY, Tollefson MM. A 5-year-old with connective tissue nevi: Buschke-Ollendorff syndrome. J Pediatr. 2014; 165:206.
Article7. Surrenti T, Callea F, De Horatio LT, Diociaiuti A, El Hachem M. Buschke-Ollendorff syndrome: sparing unnecessary investigations. Cutis. 2014; 94:97–100.8. Abbas O, Bhawan J. Cutaneous plexiform lesions. J Cutan Pathol. 2010; 37:613–623.
Article9. Ward BA, Gutmann DH. Neurofibromatosis 1: from lab bench to clinic. Pediatr Neurol. 2005; 32:221–228.
Article10. Kantrow SM, Ivan D, Williams MD, Prieto VG, Lazar AJ. Metastasizing adenocarcinoma and multiple neoplastic proliferations arising in a nevus sebaceus. Am J Dermatopathol. 2007; 29:462–466.
Article11. Chi SG, Kim JY, Kim HY, Lee SJ, Kim DW, Lee WJ. Multiple nevus sebaceous occurring on the scalp and on the contralateral side of the face. Ann Dermatol. 2011; 23:389–391.
Article12. Simi CM, Rajalakshmi T, Correa M. Clinicopathologic analysis of 21 cases of nevus sebaceus: a retrospective study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008; 74:625–627.
Article