Infect Chemother.
2012 Oct;44(5):403-406. 10.3947/ic.2012.44.5.403.
A Case of Septic Arthritis Caused by Persistent MRSA Bacteremia with Successful Treatment Through Linezolid
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shhan74@yuhs.ac
- 2AIDS Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2170389
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2012.44.5.403
Abstract
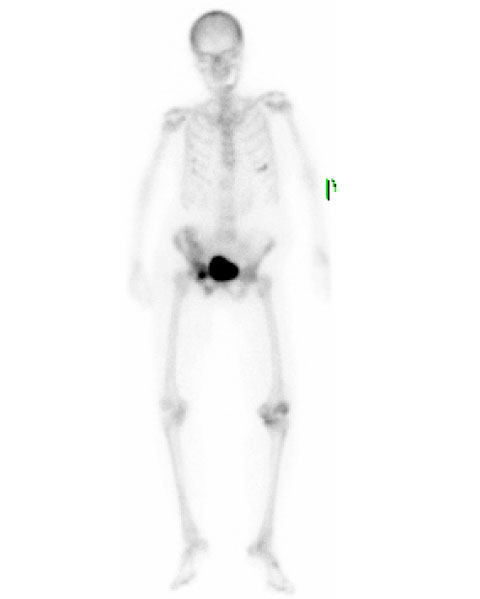
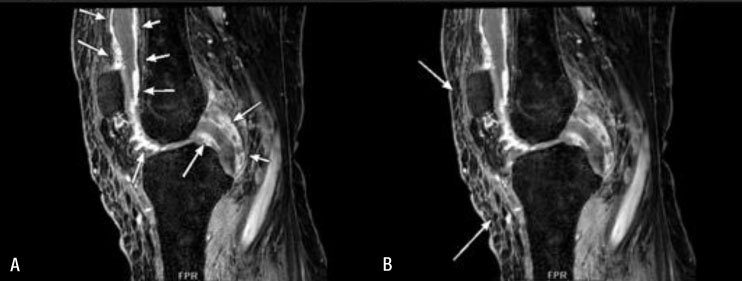
- Vancomycin is the primary antibiotic administered for treatment of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) infection; however, treatment failure of vancomycin is currently not uncommon in patients with in vitro vancomycin susceptibile S. aureus (MIC < or = 2 microg/mL) infection. In this report, we describe a case of septic arthritis caused by persistent MRSA bacteremia and treated successfully with linezolid after failure of initial vancomycin therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Khatib R, Johnson LB, Sharma M, Fakih MG, Ganga R, Riederer K. Persistent Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: incidence and outcome trends over time. Scand J Infect Dis. 2009. 41:4–9.
Article2. Fowler VG Jr, Olsen MK, Corey GR, Woods CW, Cabell CH, Reller LB, Cheng AC, Dudley T, Oddone EZ. Clinical identifiers of complicated Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Arch Intern Med. 2003. 163:2066–2072.
Article3. Yoshida T, Hiramatsu K. Potent in vitro bactericidal activity of polymyxin B against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Microbiol Immunol. 1993. 37:853–859.
Article4. Moellering RC Jr. New treatments for multiply drug-resistant Gram-positive bacteria. J Infect. 2009. 59:Suppl 1. S1–S3.
Article5. Wilcox MH, Tack KJ, Bouza E, Herr DL, Ruf BR, Ijzerman MM, Croos-Dabrera RV, Kunkel MJ, Knirsch C. Complicated skin and skin-structure infections and catheter-related blood-stream infections: noninferiority of linezolid in a phase 3 study. Clin Infect Dis. 2009. 48:203–212.
Article6. Yoon YK, Kim JY, Park DW, Sohn JW, Kim MJ. Predictors of persistent methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia in patients treated with vancomycin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010. 65:1015–1018.
Article7. Tenover FC, Moellering RC Jr. The rationale for revising the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute vancomycin minimal inhibitory concentration interpretive criteria for Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. 44:1208–1215.
Article8. Howden BP, Davies JK, Johnson PD, Stinear TP, Grayson ML. Reduced vancomycin susceptibility in Staphylococcus aureus, including vancomycin-intermediate and heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate strains: resistance mechanisms, laboratory detection, and clinical implications. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010. 23:99–139.
Article9. Sakoulas G, Moise-Broder PA, Schentag J, Forrest A, Moellering RC Jr, Eliopoulos GM. Relationship of MIC and bactericidal activity to efficacy of vancomycin for treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. 42:2398–2402.
Article10. Falagas ME, Siempos II, Papagelopoulos PJ, Vardakas KZ. Linezolid for the treatment of adults with bone and joint infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2007. 29:233–239.
Article11. De Bels D, Garcia-Filoso A, Jeanmaire M, Preseau T, Miendje Deyi VY, Devriendt J. Successful treatment with linezolid of septic shock secondary to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus arthritis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005. 55:812–813.
Article12. Sakoulas G, Moellering RC Jr. Increasing antibiotic resistance among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 46:Suppl 5. S360–S367.13. Jang HC, Kim SH, Kim KH, Kim CJ, Lee S, Song KH, Jeon JH, Park WB, Kim HB, Park SW, Kim NJ, Kim EC, Oh MD, Choe KW. Salvage treatment for persistent methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: efficacy of linezolid with or without carbapenem. Clin Infect Dis. 2009. 49:395–401.
Article14. Falagas ME, Siempos II, Vardakas KZ. Linezolid versus glycopeptide or beta-lactam for treatment of Gram-positive bacterial infections: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet Infect Dis. 2008. 8:53–66.
Article15. Beibei L, Yun C, Mengli C, Nan B, Xuhong Y, Rui W. Linezolid versus vancomycin for the treatment of gram-positive bacterial infections: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2010. 35:3–12.
Article16. Lu PL, Wang JT, Chen CJ, Chen WC, Chen TC, Hwang YC, Chang SC. Compassionate use of linezolid for adult Taiwanese patients with bone and joint infections. Chemotherapy. 2010. 56:429–435.
Article17. Kutscha-Lissberg F, Hebler U, Muhr G, Köller M. Linezolid penetration into bone and joint tissues infected with methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. 47:3964–3966.
Article18. Orrick JJ, Johns T, Janelle J, Ramphal R. Thrombocytopenia secondary to linezolid administration: what is the risk? Clin Infect Dis. 2002. 35:348–349.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Alternating Linezolid-Vancomycin Therapy for Persistent Endovascular Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection: A Case Report
- Septic Arthritis Caused by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron Bacteremia in a Patient with Multiple Myeloma
- A Case of Lactic Acidosis Caused by Linezolid Treatment of Persistent Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Bacteremia
- Successful Treatment of Recurrent Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia and Endocarditis by Linezolid, Valve Replacement, and Excisional Surgery of Limb in a Patient with Complicated Arteriovenous Malformation
- Hematogenous Septic Arthritis of the Hip in Extensive Burn