Endocrinol Metab.
2015 Dec;30(4):469-474. 10.3803/EnM.2015.30.4.469.
Association between Bsm1 Polymorphism in Vitamin D Receptor Gene and Diabetic Retinopathy of Type 2 Diabetes in Korean Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea. endoann@naver.com
- KMID: 2169654
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.4.469
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Type 2 diabetes is one of the most common diseases with devastating complications. However, genetic susceptibility of diabetic complications has not been clarified. The vitamin D endocrine system is related with calcification and lipolysis, insulin secretion, and may be associated with many complicated disease including diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Recent studies reported that single nucleotide polymorphisms of vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene were associated with diabetic complications.
METHODS
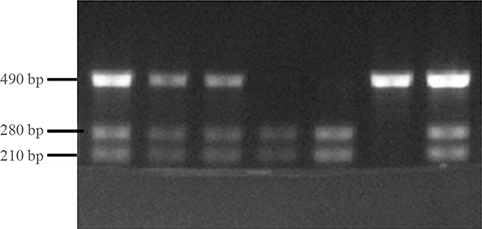
In present study, we evaluated the association of BsmI polymorphism of VDR with diabetic complications in Korean diabetes patients. Total of 537 type 2 diabetic subjects from the Endocrinology Clinic of Chungbuk National University Hospital were investigated. Polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism was used to test the genotype and allele frequency of BsmI (rs1544410; BB, Bb, bb) polymorphisms.
RESULTS
Mean age was 62.44+/-10.64 years and mean disease duration was 13.65+/-7.39 years. Patients with B allele (BB or Bb) was significantly associated with lower risk of diabetic retinopathy (severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy or proliferative retinopathy; 7.4%, 5/68) compared with patients without B allele (bb; 17.3%, 81/469; P=0.035). This association was also significant after adjusting for hemoglobin A1c level, body mass index, age, sex, and diabetes mellitus duration, concurrent dyslipidemia and hypertension (odds ratio, 2.99; 95% confidence interval, 1.08 to 8.29; P=0.035) in logistic regression analysis.
CONCLUSION
Our findings suggest that B allele of Bsm1 polymorphism in VDR gene is associated with lower risk of diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetic patients. Bsm1 genotype could be used as a susceptibility marker to predict the risk of diabetes complication.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Alleles
Body Mass Index
Cardiovascular Diseases
Chungcheongbuk-do
Diabetes Complications
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2
Diabetic Retinopathy*
Dyslipidemias
Endocrine System
Endocrinology
Gene Frequency
Genetic Predisposition to Disease
Genotype
Humans
Hypertension
Insulin
Lipolysis
Logistic Models
Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide
Receptors, Calcitriol*
Vitamin D*
Vitamins*
Insulin
Receptors, Calcitriol
Vitamin D
Vitamins
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tamilselvan B, Seshadri KG, Venkatraman G. Role of vitamin D on the expression of glucose transporters in L6 myotubes. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 17:Suppl 1. S326–S328.2. Kahn BB. Facilitative glucose transporters: regulatory mechanisms and dysregulation in diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1992; 89:1367–1374.3. Vaidya A, Williams JS. The relationship between vitamin D and the renin-angiotensin system in the pathophysiology of hypertension, kidney disease, and diabetes. Metabolism. 2012; 61:450–458.4. Riek AE, Oh J, Sprague JE, Timpson A, de las Fuentes L, Bernal-Mizrachi L, et al. Vitamin D suppression of endoplasmic reticulum stress promotes an antiatherogenic monocyte/macrophage phenotype in type 2 diabetic patients. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287:38482–38494.5. Cyganek K, Mirkiewicz-Sieradzka B, Malecki MT, Wolkow P, Skupien J, Bobrek J, et al. Clinical risk factors and the role of VDR gene polymorphisms in diabetic retinopathy in Polish type 2 diabetes patients. Acta Diabetol. 2006; 43:114–119.6. Nosratabadi R, Arababadi MK, Salehabad VA, Shamsizadeh A, Mahmoodi M, Sayadi AR, et al. Polymorphisms within exon 9 but not intron 8 of the vitamin D receptor are associated with the nephropathic complication of type-2 diabetes. Int J Immunogenet. 2010; 37:493–497.7. Velayoudom-Cephise FL, Larifla L, Donnet JP, Maimaitiming S, Deloumeaux J, Blanchet A, et al. Vitamin D deficiency, vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and cardiovascular risk factors in Caribbean patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2011; 37:540–545.8. Zhang H, Wang J, Yi B, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Zhang K, et al. BsmI polymorphisms in vitamin D receptor gene are associated with diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes in the Han Chinese population. Gene. 2012; 495:183–188.9. Ferrarezi DA, Bellili-Munoz N, Dubois-Laforgue D, Cheurfa N, Lamri A, Reis AF, et al. Allelic variations of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene are associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetics: the DIABHYCAR prospective study. Diabetes Metab. 2013; 39:263–270.10. Yokoyama K, Nakashima A, Urashima M, Suga H, Mimura T, Kimura Y, et al. Interactions between serum vitamin D levels and vitamin D receptor gene FokI polymorphisms for renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e51171.11. Bucan K, Ivanisevic M, Zemunik T, Boraska V, Skrabic V, Vatavuk Z, et al. Retinopathy and nephropathy in type 1 diabetic patients: association with polymorphysms of vitamin D-receptor, TNF, neuro-D and IL-1 receptor 1 genes. Coll Antropol. 2009; 33:Suppl 2. 99–105.12. Capoluongo E, Pitocco D, Concolino P, Santonocito C, Di Stasio E, d'Onofrio G, et al. Slight association between type 1 diabetes and "ff" VDR FokI genotype in patients from the Italian Lazio Region. Lack of association with diabetes complications. Clin Biochem. 2006; 39:888–892.13. Marco MP, Craver L, Betriu A, Fibla J, Fernandez E. Influence of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms on mortality risk in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001; 38:965–974.14. Gyorffy B, Vasarhelyi B, Krikovszky D, Madacsy L, Tordai A, Tulassay T, et al. Gender-specific association of vitamin D receptor polymorphism combinations with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Eur J Endocrinol. 2002; 147:803–808.15. Tawfeek MA, Habib FA, Mouhamed Saultan EE. Vitamin D receptor Bsm1 gene polymorphisms and gestational diabetes mellitus: a Saudi study. Br J Med Med Res. 2011; 1:459–468.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The association of chemokine receptor 5 gene 59029A/G polymorphisms with diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetic patients
- Association of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) 2518A/G Polymorphism with Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy in Korean Type 2 Diabetes
- Association Study of the Peroxisome Proliferators-Activated Receptor gamma2 Pro12Ala Polymorphism with Diabetic Nephropathy
- Clinical Analysis of Diabetic Retinopathy According to the Type of Diabetes Mellitus
- Apolipoprotein E Genetic Polymorphism and Diabetic Microangiopathy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients