Anat Cell Biol.
2010 Sep;43(3):201-210. 10.5115/acb.2010.43.3.201.
Combined actions of Na+/K+-ATPase, NCX1 and glutamate dependent NMDA receptors in ischemic rat brain penumbra
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, College of Medicine, Dongguk University, Gyeongju, Korea. jungyw@dongguk.ac.kr
- KMID: 2168875
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2010.43.3.201
Abstract
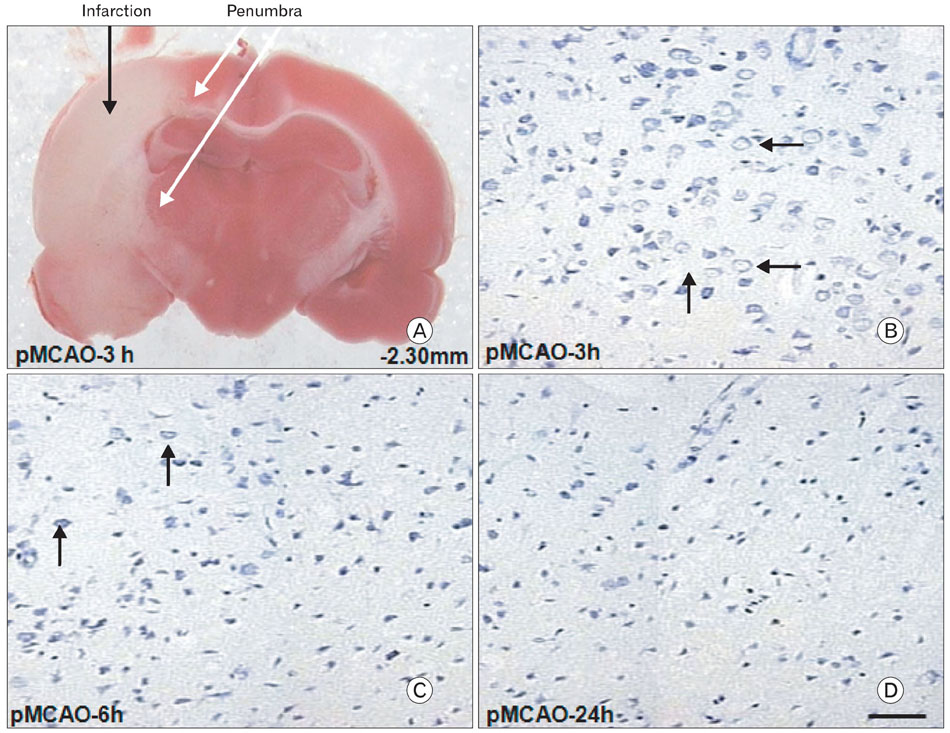
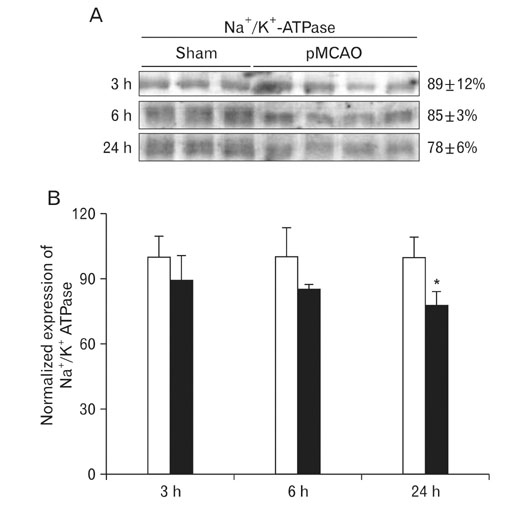
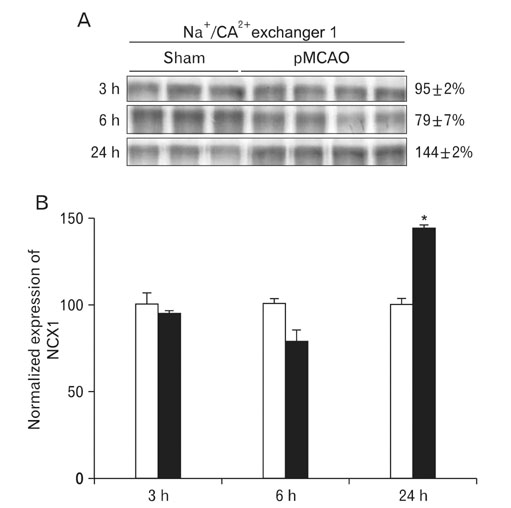
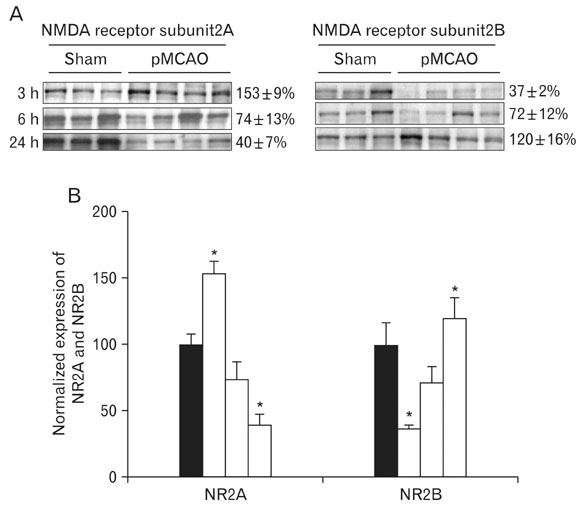
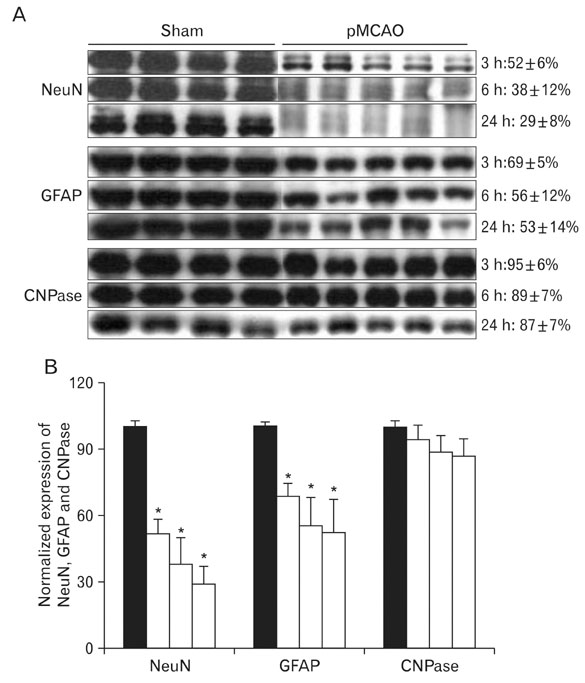
- Instrumental role of Na+ and Ca2+ influx via Na+/K+ adenosine triphosphatase (Na+/K+-ATPase) and Na+/Ca2+ exchanger 1 (NCX1) is examined in the N-Methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor-mediated pathogenesis of penumbra after focal cerebral ischemia. An experimental model of 3, 6, and 24 h focal cerebral ischemia by permanent occlusion of middle cerebral artery was developed in rats. The changes in protein expression of Na+/K+-ATPase and NCX1 as well as functional subunits of NMDA receptor 2A and 2B (NR2A and NR2B) in the penumbra were assessed using by quantitative immunoblottings. The most prominent changes of Na+/K+-ATPase (78+/-6%, n=4, *P<0.05) and NCX1 (144+/-2%, n=4, *P<0.05) in the penumbra were developed 24 h after focal cerebral ischemia. The expression of NR2A in the penumbra was significantly increased (153+/-9%, n=4, *P<0.05) whereas the expression of NR2B was significantly decreased (37+/-2%, n=4, *P<0.05) as compared with sham-operated controls 3 h after focal cerebral ischemia. However, the expression of NR2A and NR2B in the penumbra was reversed 24 h after focal cerebral ischemia (NR2A: 40+/-7%; NR2B: 120+/-16%, n=4, *P<0.05). Moreover, the decreased expression of neuronal nuclei (NeuN) in the penumbra was most prominent than that of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) 24 h after focal cerebral ischemia. These findings imply that intracellular Na+ accumulation via decreased Na+/K+-ATPase exacerbate the Ca2+ overload cooperated by the increased NCX1 and NR2B-containing NMDA receptor which may play an important role in the pathogenesis of the penumbra.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adenosine Triphosphatases
Animals
Brain
Brain Ischemia
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein
Glutamic Acid
Immunoblotting
Middle Cerebral Artery
Models, Theoretical
N-Methylaspartate
Neurons
Rats
Receptors, N-Methyl-D-Aspartate
Adenosine Triphosphatases
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein
Glutamic Acid
N-Methylaspartate
Receptors, N-Methyl-D-Aspartate
Figure
Reference
-
1. Anderson CM, Swanson RA. Astrocyte glutamate transport: review of properties, regulation, and physiological functions. Glia. 2000. 32:1–14.2. Audinat E, Lambolez B, Rossier J, Crépel F. Activity-dependent regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit expression in rat cerebellar granule cells. Eur J Neurosci. 1994. 6:1792–1800.3. Beck T, Weber M, Horváth E, Wree A. Functional cerebral activity during regeneration from entorhinal lesions in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1996. 16:342–352.4. Ben-Ari Y. Modulation of ATP sensitive K+ channels: a novel strategy to reduce the deleterious effects of anoxia. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1990. 268:481–489.5. Benveniste H, Drejer J, Schousboe A, Diemer NH. Elevation of the extracellular concentrations of glutamate and aspartate in rat hippocampus during transient cerebral ischemia monitored by intracerebral microdialysis. J Neurochem. 1984. 43:1369–1374.6. Besancon E, Guo S, Lok J, Tymianski M, Lo EH. Beyond NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors: emerging mechanisms for ionic imbalance and cell death in stroke. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2008. 29:268–275.7. Blaustein MP, Lederer WJ. Sodium/calcium exchange: its physiological implications. Physiol Rev. 1999. 79:763–854.8. Boscia F, Gala R, Pignataro G, et al. Permanent focal brain ischemia induces isoform-dependent changes in the pattern of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger gene expression in the ischemic core, periinfarct area, and intact brain regions. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006. 26:502–517.9. Czyz A, Baranauskas G, Kiedrowski L. Instrumental role of Na+ in NMDA excitotoxicity in glucose-deprived and depolarized cerebellar granule cells. J Neurochem. 2002. 81:379–389.10. D'Ambrosio R, Gordon DS, Winn HR. Differential role of KIR channel and Na(+)/K(+)-pump in the regulation of extracellular K(+) in rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 2002. 87:87–102.11. Fuller W, Parmar V, Eaton P, Bell JR, Shattock MJ. Cardiac ischemia causes inhibition of the Na+/K+ ATPase by a labile cytosolic compound whose production is linked to oxidant stress. Cardiovasc Res. 2003. 57:1044–1051.12. Gegelashvili G, Schousboe A. High affinity glutamate transporters: regulation of expression and activity. Mol Pharmacol. 1997. 52:6–15.13. Hansen AJ, Zeuthen T. Extracellular ion concentrations during spreading depression and ischemia in the rat brain cortex. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981. 113:437–445.14. Hardingham GE, Fukunaga Y, Bading H. Extrasynaptic NMDARs oppose synaptic NMDARs by triggering CREB shut-off and cell death pathways. Nat Neurosci. 2002. 5:405–414.15. Hasegawa Y, Fisher M, Latour LL, Dardzinski BJ, Sotak CH. MRI diffusion mapping of reversible and irreversible ischemic injury in focal brain ischemia. Neurology. 1994. 44:1484–1490.16. Ishii T, Moriyoshi K, Sugihara H, et al. Molecular characterization of the family of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits. J Biol Chem. 1993. 268:2836–2843.17. Kasischke KA, Vishwasrao HD, Fisher PJ, Zipfel WR, Webb WW. Neural activity triggers neuronal oxidative metabolism followed by astrocytic glycolysis. Science. 2004. 305:99–103.18. Kiedrowski L. N-methyl-D-aspartate excitotoxicity: relationships among plasma membrane potential, Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchange, mitochondrial Ca(2+) overload, and cytoplasmic concentrations of Ca(2+), H(+), and K(+). Mol Pharmacol. 1999. 56:619–632.19. Kiedrowski L. Repolarization of the plasma membrane shapes NMDA-induced cytosolic [Ca2+] transients. Neuroreport. 2001. 12:3579–3582.20. Kölker S, Okun JG, Ahlemeyer B, et al. Chronic treatment with glutaric acid induces partial tolerance to excitotoxicity in neuronal cultures from chick embryo telencephalons. J Neurosci Res. 2002. 68:424–431.21. Lees GJ, Leong W. Interactions between excitotoxins and the Na+/K+-ATPase inhibitor ouabain in causing neuronal lesions in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 1996. 714:145–155.22. Lipton SA, Rosenberg PA. Excitatory amino acids as a final common pathway for neurologic disorders. N Engl J Med. 1994. 330:613–622.23. MacDonald JF, Xiong ZG, Jackson MF. Paradox of Ca2+ signaling, cell death and stroke. Trends Neurosci. 2006. 29:75–81.24. Madl JE, Burgesser K. Adenosine triphosphate depletion reverses sodium-dependent, neuronal uptake of glutamate in rat hippocampal slices. J Neurosci. 1993. 13:4429–4444.25. Martin RL, Lloyd HG, Cowan AI. The early events of oxygen and glucose deprivation: setting the scene for neuronal death? Trends Neurosci. 1994. 17:251–257.26. Matsuda T, Arakawa N, Takuma K, et al. SEA0400, a novel and selective inhibitor of the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger, attenuates reperfusion injury in the in vitro and in vivo cerebral ischemic models. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001. 298:249–256.27. Meguro H, Mori H, Araki K, et al. Functional characterization of a heteromeric NMDA receptor channel expressed from cloned cDNAs. Nature. 1992. 357:70–74.28. Monyer H, Sprengel R, Schoepfer R, et al. Heteromeric NMDA receptors: molecular and functional distinction of subtypes. Science. 1992. 256:1217–1221.29. Mori H, Mishina M. Structure and function of the NMDA receptor channel. Neuropharmacology. 1995. 34:1219–1237.30. Perkel DJ, Petrozzino JJ, Nicoll RA, Connor JA. The role of Ca2+ entry via synaptically activated NMDA receptors in the induction of long-term potentiation. Neuron. 1993. 11:817–823.31. Pignataro G, Tortiglione A, Scorziello A, et al. Evidence for a protective role played by the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in cerebral ischemia induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion in male rats. Neuropharmacology. 2004. 46:439–448.32. Quednau BD, Nicoll DA, Philipson KD. Tissue specificity and alternative splicing of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger isoforms NCX1, NCX2, and NCX3 in rat. Am J Physiol. 1997. 272:C1250–C1261.33. Resink A, Villa M, Benke D, Hidaka H, Möhler H, Balázs R. Characterization of agonist-induced down-regulation of NMDA receptors in cerebellar granule cell cultures. J Neurochem. 1996. 66:369–377.34. Rumbaugh G, Vicini S. Distinct synaptic and extrasynaptic NMDA receptors in developing cerebellar granule neurons. J Neurosci. 1999. 19:10603–10610.35. Schröder UH, Breder J, Sabelhaus CF, Reymann KG. The novel Na+/Ca2+ exchange inhibitor KB-R7943 protects CA1 neurons in rat hippocampal slices against hypoxic/hypoglycemic injury. Neuropharmacology. 1999. 38:319–321.36. Silver IA, Deas J, Erecińska M. Ion homeostasis in brain cells: differences in intracellular ion responses to energy limitation between cultured neurons and glial cells. Neuroscience. 1997. 78:589–601.37. Storck T, Schulte S, Hofmann K, Stoffel W. Structure, expression, and functional analysis of a Na(+)-dependent glutamate/aspartate transporter from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992. 89:10955–10959.38. Stys PK, Waxman SG, Ransom BR. Ionic mechanisms of anoxic injury in mammalian CNS white matter: role of Na+ channels and Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. J Neurosci. 1992. 12:430–439.39. Tasker RC, Coyle JT, Vornov JJ. The regional vulnerability to hypoglycemia-induced neurotoxicity in organotypic hippocampal culture: protection by early tetrodotoxin or delayed MK-801. J Neurosci. 1992. 12:4298–4308.40. Veldhuis WB, van der Stelt M, Delmas F, et al. In vivo excitotoxicity induced by ouabain, a Na+/K+-ATPase inhibitor. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003. 23:62–74.41. Witte OW, Bidmon HJ, Schiene K, Redecker C, Hagemann G. Functional differentiation of multiple perilesional zones after focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000. 20:1149–1165.42. Yu AC, Gregory GA, Chan PH. Hypoxia-induced dysfunctions and injury of astrocytes in primary cell cultures. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1989. 9:20–28.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Increased Expressions of eNBC and NHE1 in Ischemic Penumbra after Permanent Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
- The Effect of Indomethacin on Na-K-ATPase and K-pNPPase Activity of Rat Brain
- Effect of Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor on Excitatory Synaptic Transmission in Hippocampal Neurons
- Ca2+-dependent Long-term Inactivation of Cardiac Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger
- Anethesia and Glutamate Receptors