J Bacteriol Virol.
2010 Dec;40(4):151-157. 10.4167/jbv.2010.40.4.151.
Cleavage of p65 Subunit of NF-kappaB by Orientia tsutsugamushi
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. jaeskang@inha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2168578
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2010.40.4.151
Abstract
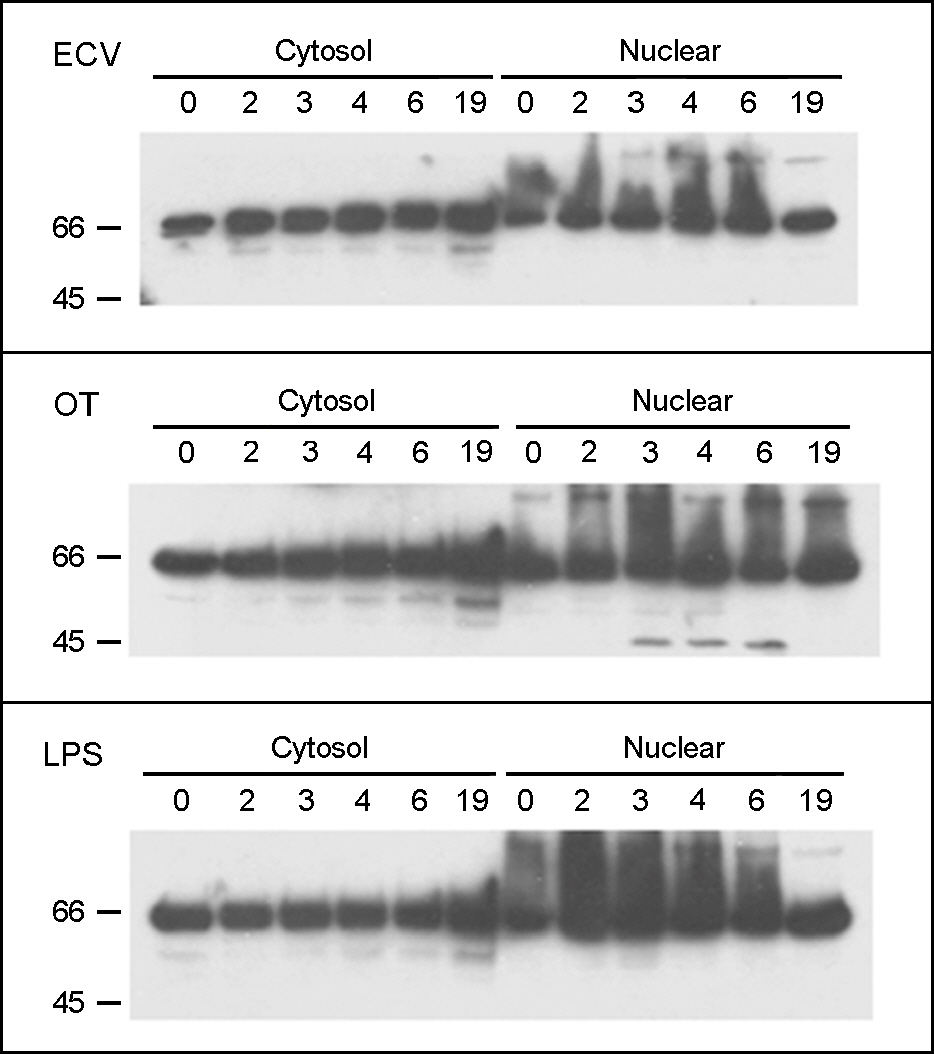
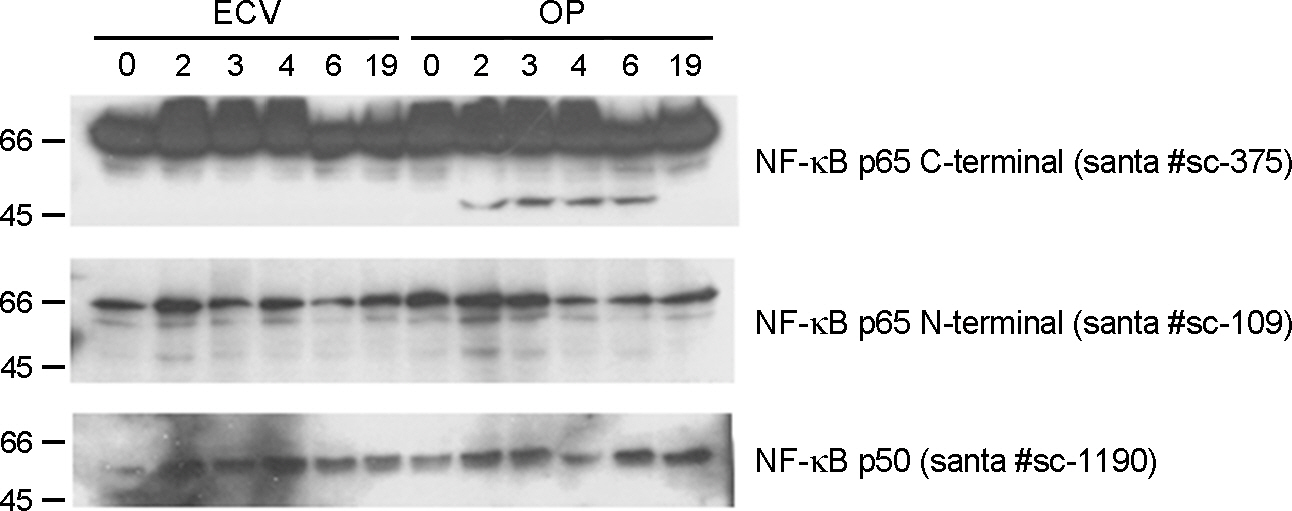
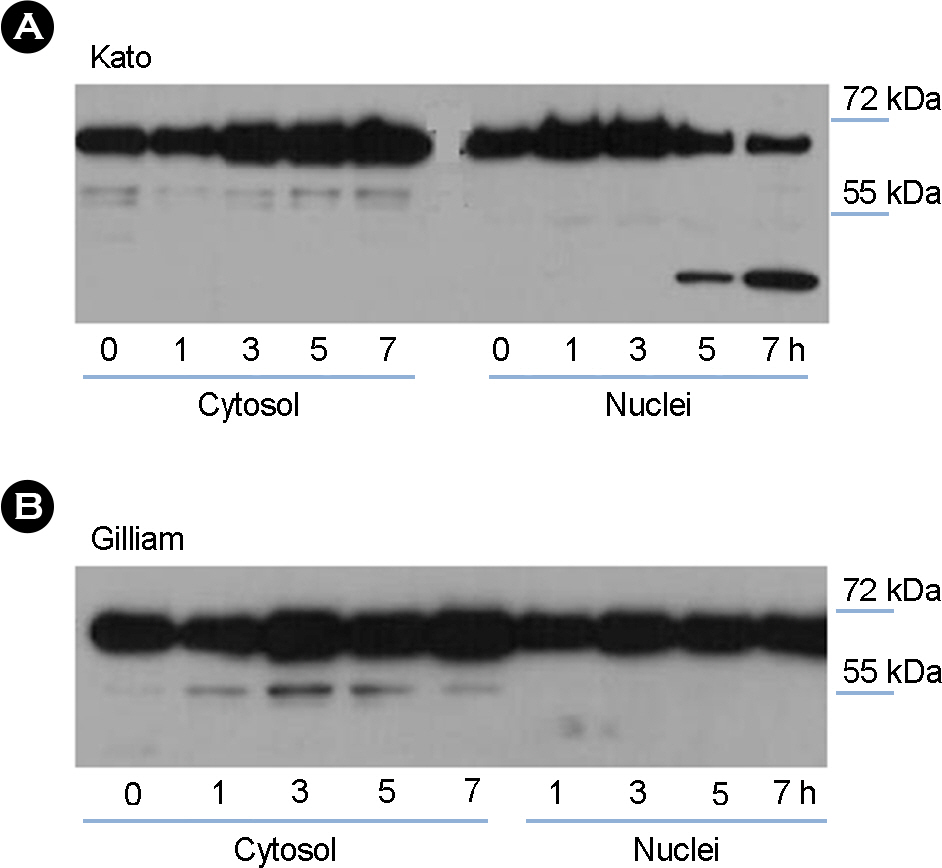
- Orientia tsutsugamushi, a causative agent of scrub typhus, is an obligate intracellular parasite and usually propagates in the cytoplasm of host endothelial cells and macrophages. Macrophages are the first defense line against bacterial infection and NF-kappaB is activated upon contact with bacteria, resulting in the transcription of inflammatory cytokine to control bacterial infection. In this study, we investigated whether O. tsutsugamushi modulates NF-kappaB activation in the macrophages. We examined the changes of NF-kappaB proteins upon infection with O. tsutsugamushi and found that NF-kappaB is activated at a slow rate as judged with EMSA and immunoblot analysis. Interestingly, we found that p65 was cleaved generating a 45 kDa fragment. In addition, fragment of p65 is generated only by the virulent serotype strain of O. tsutsugamushi, suggesting this cleavage may be associated with the mouse virulence. It is still unknown whether this is a direct result of O. tsutsugamushi proteins or enzymes of host cell. Further exploration of the mechanism that modulates NF-kappaB activity by O. tsutsugamushi could contribute to a better understanding of the molecular pathogenesis of O. tsutsugamushi infection.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
In Vitro Activity of Tigecycline Against Orientia tsutsugamushi
Sun-Myoung Lee, Hae-Yoon Kwon, Jae-Hyoung Im, Ji Hyeon Baek, Seung-Sik Hwang, Jae-Seung Kang, Moon-Hyun Chung, Jin-Soo Lee
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(4):1034-1037. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.4.1034.
Reference
-
1). Seong SY., Choi MS., Kim IS. Orientia tsutsugamushi infection: overview and immune responses. Microbes Infect. 2001. 3:11–21.2). Cho KA., Jun YH., Suh JW., Kang JS., Choi HJ., Woo SY. Orientia tsutsugamushi induced endothelial cell activation via the NOD1-IL-32 pathway. Microb Pathog. 2010. 49:95–104.3). Moron CG., Popov VL., Feng HM., Wear D., Walker DH. Identification of the target cells of Orientia tsutsugamushi in human cases of scrub typhus. Mod Pathol. 2001. 14:752–9.4). Kelly DJ., Fuerst PA., Ching WM., Richards AL. Scrub typhus: the geographic distribution of phenotypic and genotypic variants of Orientia tsutsugamushi. Clin Infect Dis. 2009. 48:S203–30.5). Kweon SS., Choi JS., Lim HS., Kim JR., Kim KY., Ryu SY, et al. Rapid increase of scrub typhus, South Korea, 2001-2006. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009. 15:1127–9.
Article6). Hwang TS., Chu YC., Kim YB., Lim BU., Kang JS. Pathologic study of mice infected with Rickettsia tsutsugamushi R19 strain. J Korean Med Sci. 1993. 8:437–45.7). Kumar H., Kawai T., Akira S. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. 388:621–5.
Article8). Naumann M. Nuclear Factor-kappa B activation and innate immune response in microbial pathogen infection. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000. 60:1109–14.9). Li Q., Verma IM. NF-kappa B regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002. 2:725–34.10). al-Ramadi BK., Chen YW., Meissler JJ Jr., Eisenstein TK. Immunosuppression induced by attenuated Salmonella. Reversal by IL-4. J Immunol. 1991. 147:1954–61.11). Kim MJ., Kim MK., Kang JS. Orientia tsutsugamushi inhibits tumor necrosis factor alpha production by inducing interleukin 10 secretion in murine macrophages. Microb Pathog. 2006. 40:1–7.12). Cho NH., Seong SY., Huh MS., Han TH., Koh YS., Choi MS, et al. Expression of chemokine genes in murine macrophages infected with Orientia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 2000. 68:594–602.13). Zhong H., May MJ., Jimi E., Ghosh S. The phosphorylation status of nuclear NF-kappa B determines its association with CBP/p300 or HDAC-1. Mol Cell. 2002. 9:625–36.14). Kim MK., Kang JS. Orientia tsutsugamushi suppresses the production of inflammatory cytokines induced by its own heat-stable component in murine macrophages. Microb Pathog. 2001. 31:145–50.15). Tato CM., Hunter CA. Host-pathogen interactions: subversion and utilization of the NF-kappa B pathway during infection. Infect Immun. 2002. 70:3311–7.16). Silverman N., Maniatis T. NF-kappa B signaling pathways in mammalian and insect innate immunity. Genes Dev. 2001. 15:2321–42.17). Sporn LA., Sahni SK., Lerner NB., Marder VJ., Silverman DJ., Turpin LC, et al. Rickettsia rickettsii infection of cultured human endothelial cells induces NF-kappaB activation. Infect Immun. 1997. 65:2786–91.18). Lin M., Rikihisa Y. Ehrlichia chaffeensis downregulates surface Toll-like receptors 2/4, CD14 and transcription factors PU.1 and inhibits lipopolysaccharide activation of NF-kappa B, ERK 1/2 and p38 MAPK in host monocytes. Cell Microbiol. 2004. 6:175–86.19). Jerrells TR., Geng P. The role of tumor necrosis factor in host defense against scrub typhus rickettsiae. II. Differential induction of tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by Rickettsia tsutsugamushi and Rickettsia conorii. Microbiol Immunol. 1994. 38:713–9.20). Kim HS., Chang I., Kim JY., Choi KH., Lee MS. Caspase-mediated p65 cleavage promotes TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2005. 65:6111–9.
Article21). Neuzil J., Schröder A., von Hundelshausen P., Zernecke A., Weber T., Gellert N, et al. Inhibition of inflammatory endothelial responses by a pathway involving caspase activation and p65 cleavage. Biochemistry. 2001. 40:4686–92.
Article22). Neznanov N., Chumakov KM., Neznanova L., Almasan A., Banerjee AK., Gudkov AV. Proteolytic cleavage of the p65-RelA subunit of NF-kappa B during poliovirus infection. J Biol Chem. 2005. 280:24153–8.23). Lad SP., Li J., da Silva Correia J., Pan Q., Gadwal S., Ulevitch RJ, et al. Cleavage of p65/RelA of the NF-kappaB pathway by Chlamydia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007. 104:2933–8.24). Cho NH., Kim HR., Lee JH., Kim SY., Kim J., Cha S, et al. The Orientia tsutsugamushi genome reveals massive proliferation of conjugative type IV secretion system and host-cell interaction genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007. 104:7981–6.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlation between the Expression of Nuclear Factor-kappaB p65 Protein with the Expression of Nuclear Factor-kappaB p50 Protein and the Clinicopathologic Factors in Colorectal Cancer
- Increased expression of nuclear factor kappa-B p65 subunit in adenomyosis
- Involvement of Nuclear Factor Kappa B in High-Fat Diet-Related Pancreatic Fibrosis in Rats
- Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis Associated with Orientia tsutsugamushi Infection: A Report of Two Cases
- Genetic Heterogeneity in 56 kDa gene of Orientia tsutsugamushi Genotype Karp