Cancer Res Treat.
2012 Jun;44(2):74-84.
Personalized Combined Modality Therapy for Locally Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA. hak.choy@utsouthwestern.edu
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
Abstract
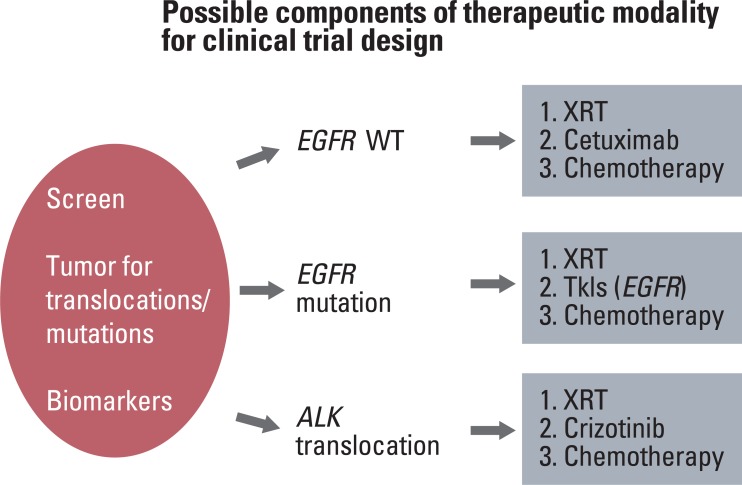
- Locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a heterogeneous disease, and we have embarked on an era where patients will benefit from individualized therapeutic strategies based on identifiable molecular characteristics of the tumor. The landmark studies demonstrating the importance of molecular characterization of tumors for NSCLC patients, the promising molecular pathways, and the potential molecular targets/agents for treatment of this disease will be reviewed. Understanding these issues will aid in the development of rationally designed clinical trials, so as to determine best means of appropriately incorporating these molecular strategies, to the current standard of radiation and chemotherapy regimens, for the treatment of locally advanced NSCLC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim DW, Choy H. Combined modality therapy for non-small cell lung cancer, past, present, and future. Lung Cancer. 2003; 42(Suppl 2):S35–S40. PMID: 14644534.
Article2. Subramanian J, Madadi AR, Dandona M, Williams K, Morgensztern D, Govindan R. Review of ongoing clinical trials in non-small cell lung cancer: a status report for 2009 from the ClinicalTrials. gov website. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5:1116–1119. PMID: 20592626.3. Mason KA, Komaki R, Cox JD, Milas L. Biology-based combined-modality radiotherapy: workshop report. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001; 50:1079–1089. PMID: 11429236.
Article4. Belani CP, Choy H, Bonomi P, Scott C, Travis P, Haluschak J, et al. Combined chemoradiotherapy regimens of paclitaxel and carboplatin for locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomized phase II locally advanced multi-modality protocol. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:5883–5891. PMID: 16087941.
Article5. Mendelsohn J, Fan Z. Epidermal growth factor receptor family and chemosensitization. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1997; 89:341–343. PMID: 9060954.
Article6. Schmidt-Ullrich RK, Dent P, Grant S, Mikkelsen RB, Valerie K. Signal transduction and cellular radiation responses. Radiat Res. 2000; 153:245–257. PMID: 10669545.
Article7. Liang K, Ang KK, Milas L, Hunter N, Fan Z. The epidermal growth factor receptor mediates radioresistance. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003; 57:246–254. PMID: 12909240.
Article8. Huguenin P, Beer KT, Allal A, Rufibach K, Friedli C, Davis JB, et al. Concomitant cisplatin significantly improves locoregional control in advanced head and neck cancers treated with hyperfractionated radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:4665–4673. PMID: 15534360.
Article9. Dickstein BM, Wosikowski K, Bates SE. Increased resistance to cytotoxic agents in ZR75B human breast cancer cells transfected with epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1995; 110:205–211. PMID: 7672450.
Article10. Harari PM, Allen GW, Bonner JA. Biology of interactions: antiepidermal growth factor receptor agents. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:4057–4065. PMID: 17827454.
Article11. Huang SM, Bock JM, Harari PM. Epidermal growth factor receptor blockade with C225 modulates proliferation, apoptosis, and radiosensitivity in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Cancer Res. 1999; 59:1935–1940. PMID: 10213503.12. Huang SM, Harari PM. Modulation of radiation response after epidermal growth factor receptor blockade in squamous cell carcinomas: inhibition of damage repair, cell cycle kinetics, and tumor angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 2000; 6:2166–2174. PMID: 10873065.13. Milas L, Mason K, Hunter N, Petersen S, Yamakawa M, Ang K, et al. In vivo enhancement of tumor radioresponse by C225 antiepidermal growth factor receptor antibody. Clin Cancer Res. 2000; 6:701–708. PMID: 10690556.14. Lammering G, Hewit TH, Valerie K, Contessa JN, Amorino GP, Dent P, et al. EGFRvIII-mediated radioresistance through a strong cytoprotective response. Oncogene. 2003; 22:5545–5553. PMID: 12944901.
Article15. Baselga J, Pfister D, Cooper MR, Cohen R, Burtness B, Bos M, et al. Phase I studies of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor chimeric antibody C225 alone and in combination with cisplatin. J Clin Oncol. 2000; 18:904–914. PMID: 10673534.
Article16. Robert F, Ezekiel MP, Spencer SA, Meredith RF, Bonner JA, Khazaeli MB, et al. Phase I study of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody cetuximab in combination with radiation therapy in patients with advanced head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2001; 19:3234–3243. PMID: 11432891.
Article17. Tuccillo C, Romano M, Troiani T, Martinelli E, Morgillo F, De Vita F, et al. Antitumor activity of ZD6474, a vascular endothelial growth factor-2 and epidermal growth factor receptor small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in combination with SC-236, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res. 2005; 11:1268–1276. PMID: 15709198.18. Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N, Shin DM, Cohen RB, et al. Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354:567–578. PMID: 16467544.
Article19. Harari PM, Huang S. Radiation combined with EGFR signal inhibitors: head and neck cancer focus. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2006; 16:38–44. PMID: 16378905.
Article20. Kelly K, Chansky K, Gaspar LE, Albain KS, Jett J, Ung YC, et al. Phase III trial of maintenance gefitinib or placebo after concurrent chemoradiotherapy and docetaxel consolidation in inoperable stage III non-small-cell lung cancer: SWOG S0023. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:2450–2456. PMID: 18378568.
Article21. Blumenschein GR Jr, Paulus R, Curran WJ, Robert F, Fossella F, Werner-Wasik M, et al. Phase II study of cetuximab in combination with chemoradiation in patients with stage IIIA/B non-small-cell lung cancer: RTOG 0324. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:2312–2318. PMID: 21555682.
Article22. Govindan R, Bogart J, Stinchcombe T, Wang X, Hodgson L, Kratzke R, et al. Randomized phase II study of pemetrexed, carboplatin, and thoracic radiation with or without cetuximab in patients with locally advanced unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer: Cancer and Leukemia Group B trial 30407. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:3120–3125. PMID: 21747084.
Article23. Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, Tamura T, Nakagawa K, Douillard JY, et al. Multi-institutional randomized phase II trial of gefitinib for previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (The IDEAL 1 Trial) [corrected]. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:2237–2246. PMID: 12748244.24. Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS, Lynch TJ Jr, Prager D, Belani CP, et al. Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2003; 290:2149–2158. PMID: 14570950.25. Giaccone G, Herbst RS, Manegold C, Scagliotti G, Rosell R, Miller V, et al. Gefitinib in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial--INTACT 1. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:777–784. PMID: 14990632.
Article26. Herbst RS, Giaccone G, Schiller JH, Natale RB, Miller V, Manegold C, et al. Gefitinib in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial--INTACT 2. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:785–794. PMID: 14990633.27. Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2129–2139. PMID: 15118073.
Article28. Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004; 304:1497–1500. PMID: 15118125.29. Ready N, Jänne PA, Bogart J, Dipetrillo T, Garst J, Graziano S, et al. Chemoradiotherapy and gefitinib in stage III non-small cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor and KRAS mutation analysis: cancer and leukemia group B (CALEB) 30106, a CALGB-stratified phase II trial. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5:1382–1390. PMID: 20686428.
Article30. Choong NW, Mauer AM, Haraf DJ, Lester E, Hoffman PC, Kozloff M, et al. Phase I trial of erlotinib-based multimodality therapy for inoperable stage III non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2008; 3:1003–1011. PMID: 18758303.
Article31. Gatzemeier U, Pluzanska A, Szczesna A, Kaukel E, Roubec J, De Rosa F, et al. Phase III study of erlotinib in combination with cisplatin and gemcitabine in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: the Tarceva Lung Cancer Investigation Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:1545–1552. PMID: 17442998.
Article32. Herbst RS, Prager D, Hermann R, Fehrenbacher L, Johnson BE, Sandler A, et al. TRIBUTE: a phase III trial of erlotinib hydrochloride (OSI-774) combined with carboplatin and paclitaxel chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:5892–5899. PMID: 16043829.
Article33. Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, Tan EH, Hirsh V, Thongprasert S, et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:123–132. PMID: 16014882.
Article34. Janne PA, Wang XF, Socinski MA, Crawford J, Capelletti M, Edelman MJ, et al. Randomized phase II trial of erlotinib (E) alone or in combination with carboplatin/paclitaxel (CP) in never or light former smokers with advanced lung adenocarcinoma: CALGB 30406. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28(15s):7503.
Article35. Coudert B, Ciuleanu T, Park K, Wu YL, Giaccone G, Brugger W, et al. Survival benefit with erlotinib maintenance therapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) according to response to first-line chemotherapy. Ann Oncol. 2012; 23:388–394. PMID: 21610154.
Article36. Mauceri HJ, Hanna NN, Beckett MA, Gorski DH, Staba MJ, Stellato KA, et al. Combined effects of angiostatin and ionizing radiation in antitumour therapy. Nature. 1998; 394:287–291. PMID: 9685160.
Article37. Jain RK. Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science. 2005; 307:58–62. PMID: 15637262.
Article38. Willett CG, Boucher Y, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Munn LL, Tong RT, et al. Direct evidence that the VEGF-specific antibody bevacizumab has antivascular effects in human rectal cancer. Nat Med. 2004; 10:145–147. PMID: 14745444.
Article39. Garcia-Barros M, Paris F, Cordon-Cardo C, Lyden D, Rafii S, Haimovitz-Friedman A, et al. Tumor response to radiotherapy regulated by endothelial cell apoptosis. Science. 2003; 300:1155–1159. PMID: 12750523.
Article40. Mazeron R, Anderson B, Supiot S, Paris F, Deutsch E. Current state of knowledge regarding the use of antiangiogenic agents with radiation therapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 2011; 37:476–486. PMID: 21546163.
Article41. Kim DW, Huamani J, Fu A, Hallahan DE. Molecular strategies targeting the host component of cancer to enhance tumor response to radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006; 64:38–46. PMID: 16377414.
Article42. Bao S, Wu Q, Sathornsumetee S, Hao Y, Li Z, Hjelmeland AB, et al. Stem cell-like glioma cells promote tumor angiogenesis through vascular endothelial growth factor. Cancer Res. 2006; 66:7843–7848. PMID: 16912155.
Article43. Zips D, Le K, Yaromina A, Dörfler A, Eicheler W, Zhou X, et al. Triple angiokinase inhibition, tumour hypoxia and radiation response of FaDu human squamous cell carcinomas. Radiother Oncol. 2009; 92:405–410. PMID: 19409639.
Article44. Spigel DR, Hainsworth JD, Yardley DA, Raefsky E, Patton J, Peacock N, et al. Tracheoesophageal fistula formation in patients with lung cancer treated with chemoradiation and bevacizumab. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:43–48. PMID: 19901100.
Article45. Raje N, Anderson K. Thalidomide: a revival story. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341:1606–1609. PMID: 10564693.46. Lebrin F, Srun S, Raymond K, Martin S, van den Brink S, Freitas C, et al. Thalidomide stimulates vessel maturation and reduces epistaxis in individuals with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Nat Med. 2010; 16:420–428. PMID: 20364125.
Article47. Fanelli M, Sarmiento R, Gattuso D, Carillio G, Capaccetti B, Vacca A, et al. Thalidomide: a new anticancer drug? Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2003; 12:1211–1225.
Article48. Schiller JH, Dahlberg SE, Mehta M, Johnson DH. A phase III trial of carboplatin, paclitaxel, and thoracic radiation therapy with or without thalidomide in patients with stage III non-small cell carcinoma of the lung (NSCLC): E3598. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27(15s):7503.
Article49. Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007; 448:561–566. PMID: 17625570.
Article50. Sasaki T, Jänne PA. New strategies for treatment of ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 17:7213–7218. PMID: 22010214.
Article51. Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, Shaw AT, Solomon B, Maki RG, et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:1693–1703. PMID: 20979469.52. Romond EH, Perez EA, Bryant J, Suman VJ, Geyer CE Jr, Davidson NE, et al. Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for operable HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:1673–1684. PMID: 16236738.
Article53. Dematteo RP, Ballman KV, Antonescu CR, Maki RG, Pisters PW, Demetri GD, et al. Adjuvant imatinib mesylate after resection of localised, primary gastrointestinal stromal tumour: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2009; 373:1097–1104. PMID: 19303137.
Article54. Tol J, Punt CJ. Monoclonal antibodies in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: a review. Clin Ther. 2010; 32:437–453. PMID: 20399983.
Article55. Paik S, Shak S, Tang G, Kim C, Baker J, Cronin M, et al. A multigene assay to predict recurrence of tamoxifen-treated, node-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004; 351:2817–2826. PMID: 15591335.
Article56. Kumar R, Amado RG. Predictive genomic biomarkers. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2011; 8. 30. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/82_2011_164 .
Article57. Amann JM, Lee JW, Roder H, Brahmer J, Gonzalez A, Schiller JH, et al. Genetic and proteomic features associated with survival after treatment with erlotinib in first-line therapy of non-small cell lung cancer in Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group 3503. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5:169–178. PMID: 20035238.
Article58. Rosell R, Moran T, Queralt C, Porta R, Cardenal F, Camps C, et al. Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:958–967. PMID: 19692684.
Article59. Bunn PA Jr, Hirsch FR, Doebele RC, Camidge DR, Varella-Garcia M, Franklin W. Biomarkers are here to stay for clinical research and standard care. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5:1113–1115. PMID: 20661083.
Article60. Nguyen KS, Kobayashi S, Costa DB. Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancers dependent on the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009; 10:281–289. PMID: 19632948.
Article61. Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Gale CM, Lifshits E, Gonzales AJ, Shimamura T, et al. PF00299804, an irreversible pan-ERBB inhibitor, is effective in lung cancer models with EGFR and ERBB2 mutations that are resistant to gefitinib. Cancer Res. 2007; 67:11924–11932. PMID: 18089823.
Article62. Jänne PA, Boss DS, Camidge DR, Britten CD, Engelman JA, Garon EB, et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of the pan-HER inhibitor, PF299804, in patients with advanced malignant solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 17:1131–1139. PMID: 21220471.
Article63. Janne PA, Reckamp K, Koczywas M, Engelman JA, Camidge DR, Rajan A, et al. Efficacy and safety of PF-00299804 (PF299) in patients (pt) with advanced NSCLC after failure of at least one prior chemotherapy regimen and prior treatment with erlotinib (E): a two-arm, phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27(15s):8063.
Article64. Schütze C, Dörfler A, Eicheler W, Zips D, Hering S, Solca F, et al. Combination of EGFR/HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibition by BIBW 2992 and BIBW 2669 with irradiation in FaDu human squamous cell carcinoma. Strahlenther Onkol. 2007; 183:256–264. PMID: 17497097.
Article65. Yap TA, Vidal L, Adam J, Stephens P, Spicer J, Shaw H, et al. Phase I trial of the irreversible EGFR and HER2 kinase inhibitor BIBW 2992 in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:3965–3972. PMID: 20679611.
Article66. Wong KK. HKI-272 in non small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13(15 Pt 2):s4593–s4596. PMID: 17671147.67. Wong KK, Fracasso PM, Bukowski RM, Lynch TJ, Munster PN, Shapiro GI, et al. A phase I study with neratinib (HKI-272), an irreversible pan ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2009; 15:2552–2558. PMID: 19318484.
Article68. Sequist LV, Besse B, Lynch TJ, Miller VA, Wong KK, Gitlitz B, et al. Neratinib, an irreversible pan-ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor: results of a phase II trial in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:3076–3083. PMID: 20479403.
Article69. Chung EJ, Brown AP, Asano H, Mandler M, Burgan WE, Carter D, et al. In vitro and in vivo radiosensitization with AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), an inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 kinase. Clin Cancer Res. 2009; 15:3050–3057. PMID: 19366835.
Article70. Shannon AM, Telfer BA, Smith PD, Babur M, Logie A, Wilkinson RW, et al. The mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) enhances the radiation responsiveness of lung and colorectal tumor xenografts. Clin Cancer Res. 2009; 15:6619–6629. PMID: 19843666.
Article71. Hainsworth JD, Cebotaru CL, Kanarev V, Ciuleanu TE, Damyanov D, Stella P, et al. A phase II, open-label, randomized study to assess the efficacy and safety of AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) versus pemetrexed in patients with non-small cell lung cancer who have failed one or two prior chemotherapeutic regimens. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5:1630–1636. PMID: 20802351.
Article72. Mross K, Stefanic M, Gmehling D, Frost A, Baas F, Unger C, et al. Phase I study of the angiogenesis inhibitor BIBF 1120 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2010; 16:311–319. PMID: 20028771.
Article73. Reck M. BIBF 1120 for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010; 19:789–794.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Combined Modality Therapy for Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Management of Locally Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- Surgery for Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Chemo-radiation Therapy for Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Early response of cardiopulmonary exercise test(CPET) in patients with locally advanced Non-Small Cell Lung cancer treated with radiation