Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2012 May;4(3):161-164. 10.4168/aair.2012.4.3.161.
A Case of Hypereosinophilic Syndrome Presenting With Multiorgan Infarctions Associated With Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Allergy, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. leebj@skku.edu
- KMID: 2167069
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2012.4.3.161
Abstract
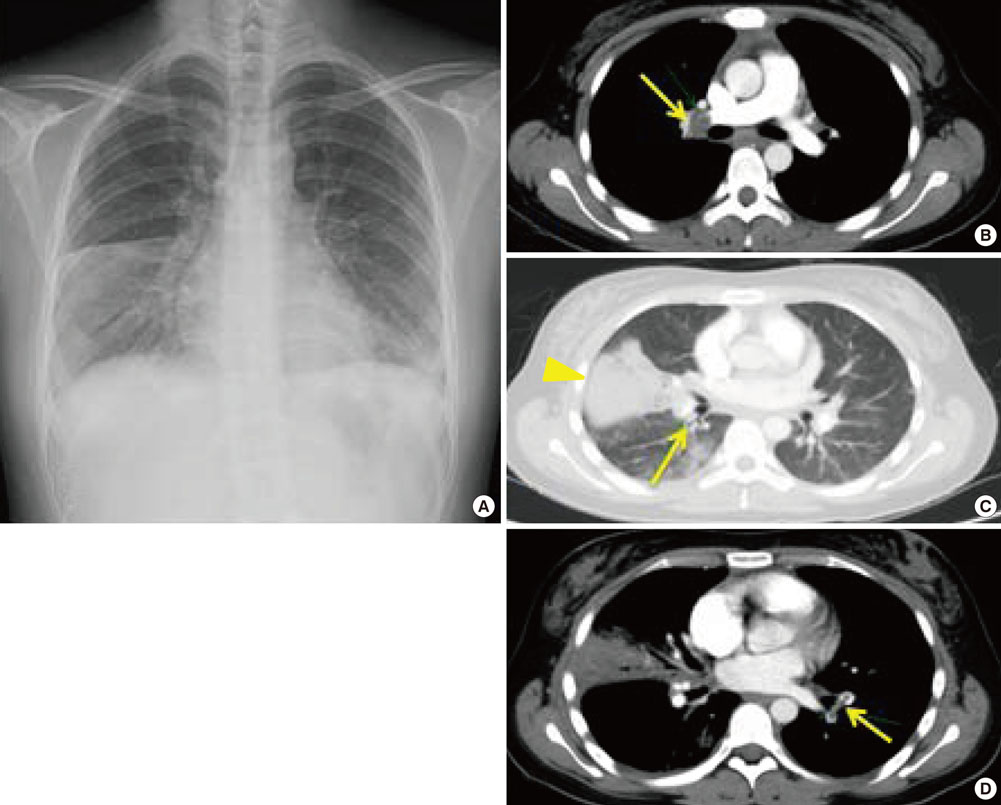
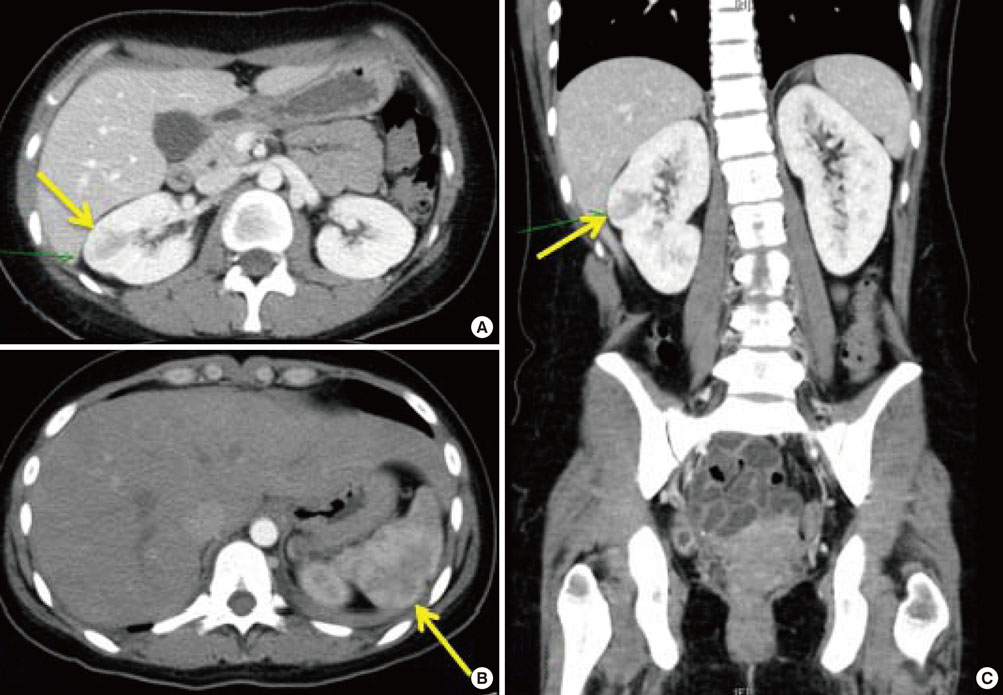
- Thromboembolism is one of the most critical complications of hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES). We report here a case of multi-organ infarctions related to HES. A 23-year-old woman was referred to our hospital with hemoptysis. Not only pulmonary, but also renal and splenic infarctions were detected on computed tomography images. Blood tests showed profound peripheral eosinophilia. She was diagnosed with HES with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). We initiated infusion of corticosteroids, which effectively suppressed peripheral eosinophilia. However, consumptive coagulopathy did not improve and intracerebral hemorrhage related to thrombosis then developed. Addition of interferon-alpha resulted in the correction of the DIC associated with HES.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Klion A. Hypereosinophilic syndrome: current approach to diagnosis and treatment. Annu Rev Med. 2009. 60:293–306.2. Ogbogu PU, Rosing DR, Horne MK 3rd. Cardiovascular manifestations of hypereosinophilic syndromes. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2007. 27:457–475.3. Yeung TF, Lau SW, Wong K. An unusual case of hypereosinophilic syndrome and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Chin Med J (Engl). 2005. 118:1582–1584.4. Miyagi J, Ichimiya M, Ozaki K, Goto T, Fujino O, Nagata J, Hiasa Y. Hypereosinophilic syndrome complicated by disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi. 2004. 93:364–366.5. Nagashima M, Nishizawa M, Yamauchi T, Mori S, Honma Y. A case of the idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome presenting with mononeuritis multiplex, multiple thrombosis, and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1986. 26:698–703.6. Fukuta A, Hara T, Tsurumi H, Moriwaki H. Hypereosinophilic syndrome with DIC treated successfully with a combination of high-dose methylprednisolone and cyclosporin A. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2001. 42:1145–1147.7. Chusid MJ, Dale DC, West BC, Wolff SM. The hypereosinophilic syndrome: analysis of fourteen cases with review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1975. 54:1–27.8. Simon HU, Rothenberg ME, Bochner BS, Weller PF, Wardlaw AJ, Wechsler ME, Rosenwasser LJ, Roufosse F, Gleich GJ, Klion AD. Refining the definition of hypereosinophilic syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 126:45–49.9. Venge P, Dahl R, Hallgren R. Enhancement of factor XII dependent reactions by eosinophil cationic protein. Thromb Res. 1979. 14:641–649.10. Rohrbach MS, Wheatley CL, Slifman NR, Gleich GJ. Activation of platelets by eosinophil granule proteins. J Exp Med. 1990. 172:1271–1274.11. Slungaard A, Vercellotti GM, Tran T, Gleich GJ, Key NS. Eosinophil cationic granule proteins impair thrombomodulin function. A potential mechanism for thromboembolism in hypereosinophilic heart disease. J Clin Invest. 1993. 91:1721–1730.12. Mukai HY, Ninomiya H, Ohtani K, Nagasawa T, Abe T. Major basic protein binding to thrombomodulin potentially contributes to the thrombosis in patients with eosinophilia. Br J Haematol. 1995. 90:892–899.13. Wang JG, Mahmud SA, Thompson JA, Geng JG, Key NS, Slungaard A. The principal eosinophil peroxidase product, HOSCN, is a uniquely potent phagocyte oxidant inducer of endothelial cell tissue factor activity: a potential mechanism for thrombosis in eosinophilic inflammatory states. Blood. 2006. 107:558–565.14. Park YM, Bochner BS. Eosinophil survival and apoptosis in health and disease. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2010. 2:87–101.15. Kobayashi M, Komatsu N, Kuwayama Y, Bandobashi K, Kubota T, Uemura Y, Taguchi H. Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome presenting acute abdomen. Intern Med. 2007. 46:675–678.16. Ferguson GT, Starkebaum G. Thromboangiitis obliterans associated with idiopathic hypereosinophilia. Arch Intern Med. 1985. 145:1726–1728.17. Ceretelli S, Capochiani E, Petrini M. Interferon-alpha in the idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome: consideration of five cases. Ann Hematol. 1998. 77:161–164.18. Yamada O, Kitahara K, Imamura K, Ozasa H, Okada M, Mizoguchi H. Clinical and cytogenetic remission induced by interferon-alpha in a patient with chronic eosinophilic leukemia associated with a unique t(3;9;5) translocation. Am J Hematol. 1998. 58:137–141.19. Fruehauf S, Fiehn C, Haas R, Doehner H, Hunstein W. Sustained remission of idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome following alpha-interferon therapy. Acta Haematol. 1993. 89:91–93.20. Terrier B, Piette AM, Kerob D, Cordoliani F, Tancréde E, Hamidou L, Lebbé C, Blétry O, Kahn JE. Superficial venous thrombophlebitis as the initial manifestation of hypereosinophilic syndrome: study of the first 3 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2006. 142:1606–1610.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic Syndrome Complicated with Pulmonary Thromboembolism and Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
- A Case of Stewart-Treves Syndrome Associated with Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
- Occlusion o Left Middle Cerebral Artery Manifested as Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
- A case of disseminated intravascular coagulation and acute renal insufficiency induced by falciparum malaria
- A Case of Kasabach-Merritt Syndrome with Disseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy Treated with Interferon alfa-2a