Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2012 Nov;4(6):332-340. 10.4168/aair.2012.4.6.332.
Most Highly Cytokinergic IgEs Have Polyreactivity to Autoantigens
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cell Biology, La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology, La Jolla, CA, USA. toshi@liai.org
- 2Division of Molecular Cell Immunology and Allergology, Advanced Medical Research Center, Nihon University Graduate School of Medical Science, Itabashi-ku, Tokyo, Japan.
- 3Department of Dermatology, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan.
- 4Department of Dermatology, University of Occupational and Environmental Health, Kitakyushu, Japan.
- 5Department of Dermatology, University of Yamanashi, Yamanashi, Japan.
- 6Receptors and Signal Transduction Section, OIIB, National Institute for Dental and Craniofacial Research, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA.
- KMID: 2167018
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2012.4.6.332
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Monomeric IgE molecules, when bound to the high-affinity receptor, exhibit a vast heterogeneity in their ability to induce survival promotion and cytokine production in mast cells. At one end of this spectrum, highly cytokinergic (HC) IgEs can induce potent survival promotion, degranulation, cytokine production, migration, etc., whereas at the other end, poorly cytokinergic (PC) IgEs can do so inefficiently. In this study, we investigated whether IgEs recognize autoantigens and whether IgEs' binding of autoantigens correlates with difference s in HC versus PC properties.
METHODS
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays were performed to test whether IgEs bind antigens. Histamine-releasing factor in human sera was quantified by western blotting. Cultured mast cells derived from human cord blood were used to test the effects of human sera on cytokine production.
RESULTS
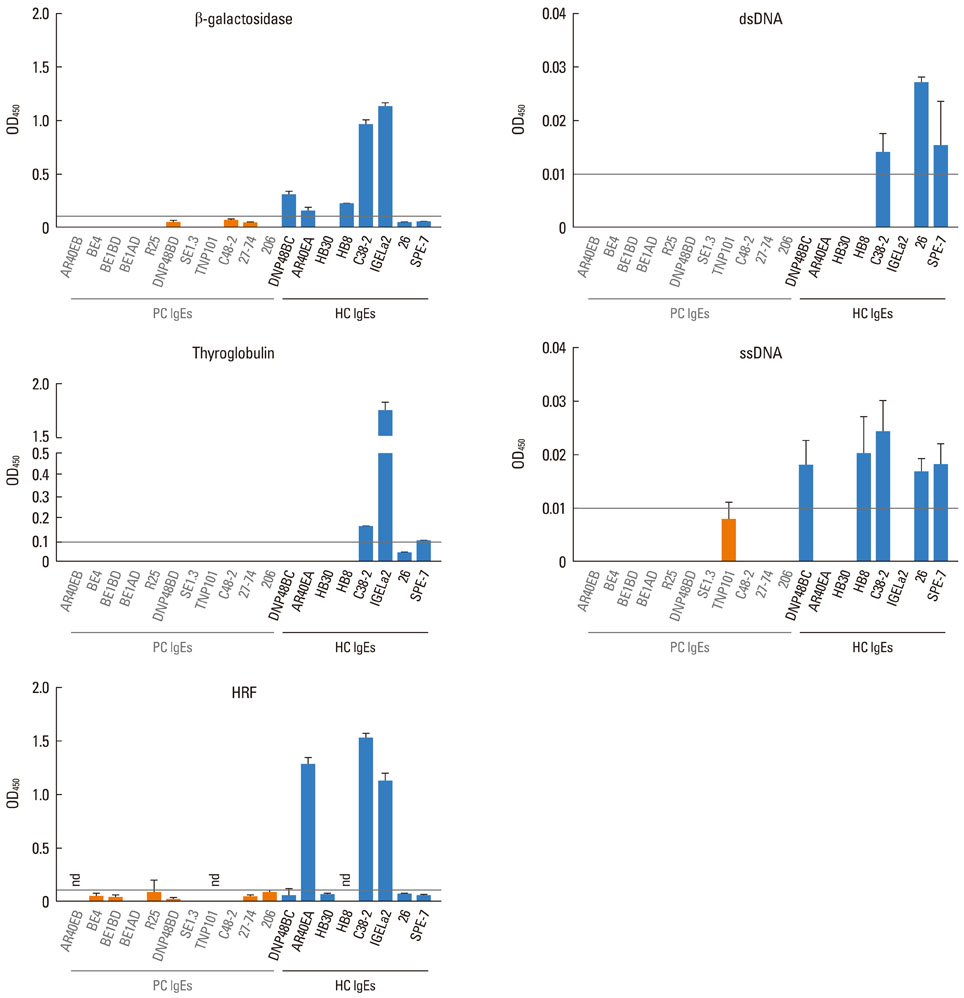
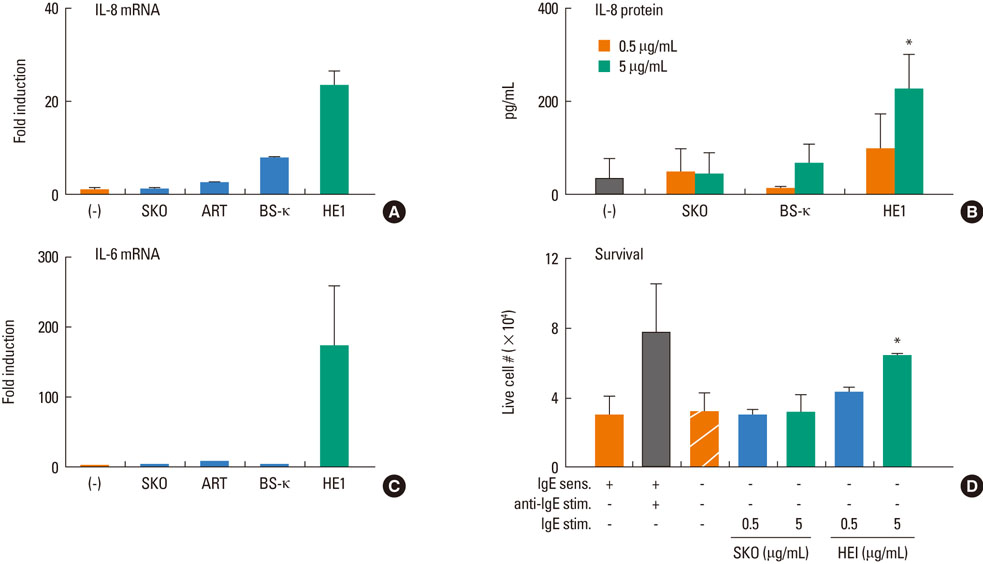
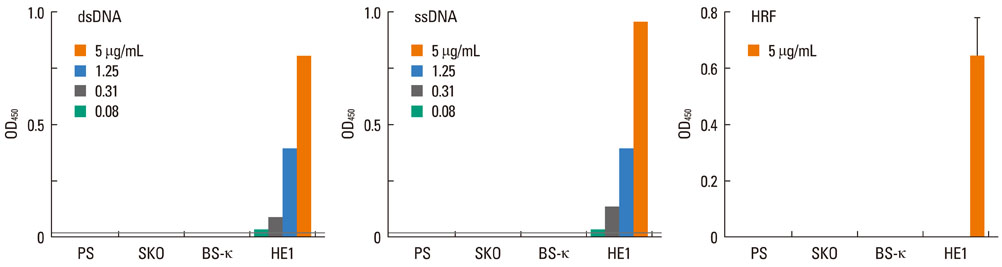
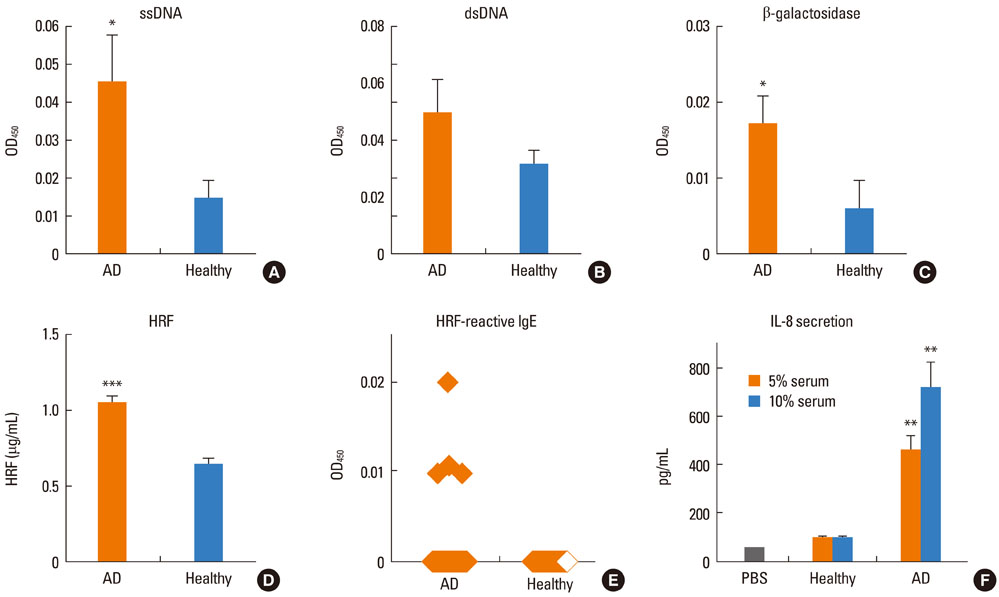
Most (7/8) of mouse monoclonal HC IgEs exhibited polyreactivity to double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), beta-galactosidase, thyroglobulin and/or histamine-releasing factor. By contrast, mouse PC IgEs failed to react with these antigens. A human monoclonal HC IgE also showed polyreactivity to histamine-releasing factor, dsDNA and ssDNA. Interestingly, sera from atopic dermatitis patients showed increased reactivity to ssDNA and beta-galactosidase and increased levels of histamine-releasing factor. Some atopic dermatitis patients, but not healthy individuals, had substantial serum levels of HRF-reactive IgE. Sera from atopic dermatitis patients with high titers of DNA-reactive IgE could induce several fold more IL-8 secretion in human mast cells than sera from healthy individuals.
CONCLUSIONS
The results show that most HC, but not PC, IgEs exhibit polyreactivity to autoantigens, supporting the autoimmune mechanism in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Autoantigens
beta-Galactosidase
Blotting, Western
Dermatitis, Atopic
DNA
DNA, Single-Stranded
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Fetal Blood
Humans
Immunoglobulin E
Interleukin-8
Mast Cells
Mice
Population Characteristics
Thyroglobulin
Autoantigens
DNA
DNA, Single-Stranded
Immunoglobulin E
Interleukin-8
Thyroglobulin
beta-Galactosidase
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Anti-TPO IgE Autoantibody in Chronic Urticaria: Is It Clinically Relevant?
Bastsetseg Ulambayar, Hae-Sim Park
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019;11(1):1-3. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Galli SJ. Mast cells and basophils. Curr Opin Hematol. 2000. 7:32–39.2. Galli SJ, Maurer M, Lantz CS. Mast cells as sentinels of innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 1999. 11:53–59.3. Metzger H. The receptor with high affinity for IgE. Immunol Rev. 1992. 125:37–48.4. Furuichi K, Rivera J, Isersky C. The receptor for immunoglobulin E on rat basophilic leukemia cells: effect of ligand binding on receptor expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985. 82:1522–1525.5. Hsu C, MacGlashan D Jr. IgE antibody up-regulates high affinity IgE binding on murine bone marrow-derived mast cells. Immunol Lett. 1996. 52:129–134.6. Yamaguchi M, Lantz CS, Oettgen HC, Katona IM, Fleming T, Miyajima I, Kinet JP, Galli SJ. IgE enhances mouse mast cell FcεRI expression in vitro and in vivo: evidence for a novel amplification mechanism in IgE-dependent reactions. J Exp Med. 1997. 185:663–672.7. Asai K, Kitaura J, Kawakami Y, Yamagata N, Tsai M, Carbone DP, Liu FT, Galli SJ, Kawakami T. Regulation of mast cell survival by IgE. Immunity. 2001. 14:791–800.8. Kalesnikoff J, Huber M, Lam V, Damen JE, Zhang J, Siraganian RP, Krystal G. Monomeric IgE stimulates signaling pathways in mast cells that lead to cytokine production and cell survival. Immunity. 2001. 14:801–811.9. Tanaka S, Takasu Y, Mikura S, Satoh N, Ichikawa A. Antigen-independent induction of histamine synthesis by immunoglobulin E in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells. J Exp Med. 2002. 196:229–235.10. Kitaura J, Song J, Tsai M, Asai K, Maeda-Yamamoto M, Mocsai A, Kawakami Y, Liu FT, Lowell CA, Barisas BG, Galli SJ, Kawakami T. Evidence that IgE molecules mediate a spectrum of effects on mast cell survival and activation via aggregation of the FcεRI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. 100:12911–12916.11. Yamada N, Matsushima H, Tagaya Y, Shimada S, Katz SI. Generation of a large number of connective tissue type mast cells by culture of murine fetal skin cells. J Invest Dermatol. 2003. 121:1425–1432.12. Oka T, Hori M, Tanaka A, Matsuda H, Karaki H, Ozaki H. IgE alone-induced actin assembly modifies calcium signaling and degranulation in RBL-2H3 mast cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004. 286:C256–C263.13. Pandey V, Mihara S, Fensome-Green A, Bolsover S, Cockcroft S. Monomeric IgE stimulates NFAT translocation into the nucleus, a rise in cytosol Ca2+, degranulation, and membrane ruffling in the cultured rat basophilic leukemia-2H3 mast cell line. J Immunol. 2004. 172:4048–4058.14. Lam V, Kalesnikoff J, Lee CW, Hernandez-Hansen V, Wilson BS, Oliver JM, Krystal G. IgE alone stimulates mast cell adhesion to fibronectin via pathways similar to those used by IgE + antigen but distinct from those used by Steel factor. Blood. 2003. 102:1405–1413.15. Kitaura J, Eto K, Kinoshita T, Kawakami Y, Leitges M, Lowell CA, Kawakami T. Regulation of highly cytokinergic IgE-induced mast cell adhesion by Src, Syk, Tec, and protein kinase C family kinases. J Immunol. 2005. 174:4495–4504.16. Matsuda K, Piliponsky AM, Iikura M, Nakae S, Wang EW, Dutta SM, Kawakami T, Tsai M, Galli SJ. Monomeric IgE enhances human mast cell chemokine production: IL-4 augments and dexamethasone suppresses the response. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005. 116:1357–1363.17. Beaven MA, Metzger H. Signal transduction by Fc receptors: the FcεRI case. Immunol Today. 1993. 14:222–226.18. Macglashan D Jr. IgE and Fc{epsilon}RI regulation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. 1050:73–88.19. Kawakami T, Kitaura J. Mast cell survival and activation by IgE in the absence of antigen: a consideration of the biologic mechanisms and relevance. J Immunol. 2005. 175:4167–4173.20. Kashiwakura J, Kawakami Y, Yuki K, Zajonc DM, Hasegawa S, Tomimori Y, Caplan B, Saito H, Furue M, Oettgen HC, Okayama Y, Kawakami T. Polyclonal IgE induces mast cell survival and cytokine production. Allergol Int. 2009. 58:411–419.21. Gilchrest H, Cheewatrakoolpong B, Billah M, Egan RW, Anthes JC, Greenfeder S. Human cord blood-derived mast cells synthesize and release I-309 in response to IgE. Life Sci. 2003. 73:2571–2581.22. Cruse G, Kaur D, Yang W, Duffy SM, Brightling CE, Bradding P. Activation of human lung mast cells by monomeric immunoglobulin E. Eur Respir J. 2005. 25:858–863.23. MacDonald SM, Lichtenstein LM, Proud D, Plaut M, Naclerio RM, MacGlashan DW, Kagey-Sobotka A. Studies of IgE-dependent histamine releasing factors: heterogeneity of IgE. J Immunol. 1987. 139:506–512.24. Kashiwakura JC, Ando T, Matsumoto K, Kimura M, Kitaura J, Matho MH, Zajonc DM, Ozeki T, Ra C, MacDonald SM, Siraganian RP, Broide DH, Kawakami Y, Kawakami T. Histamine-releasing factor has a proinflammatory role in mouse models of asthma and allergy. J Clin Invest. 2012. 122:218–228.25. Ishizaka K. Immunoglobulin E (IgE). Methods Enzymol. 1985. 116:76–94.26. Hanifin JM, Rajka G. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh). 1980. 59:44–47.27. Iida M, Matsumoto K, Tomita H, Nakajima T, Akasawa A, Ohtani NY, Yoshida NL, Matsui K, Nakada A, Sugita Y, Shimizu Y, Wakahara S, Nakao T, Fujii Y, Ra C, Saito H. Selective down-regulation of high-affinity IgE receptor (FcεRI) alpha-chain messenger RNA among transcriptome in cord blood-derived versus adult peripheral blood-derived cultured human mast cells. Blood. 2001. 97:1016–1022.28. James LC, Roversi P, Tawfik DS. Antibody multispecificity mediated by conformational diversity. Science. 2003. 299:1362–1367.29. Toru H, Ra C, Nonoyama S, Suzuki K, Yata J, Nakahata T. Induction of the high-affinity IgE receptor (FcεRI) on human mast cells by IL-4. Int Immunol. 1996. 8:1367–1373.30. Lane JE, Cheyney JM, Lane TN, Kent DE, Cohen DJ. Treatment of recalcitrant atopic dermatitis with omalizumab. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006. 54:68–72.31. Park SY, Choi MR, Na JI, Youn SW, Park KC, Huh CH. Recalcitrant atopic dermatitis treated with omalizumab. Ann Dermatol. 2010. 22:349–352.32. Sheinkopf LE, Rafi AW, Do LT, Katz RM, Klaustermeyer WB. Efficacy of omalizumab in the treatment of atopic dermatitis: a pilot study. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2008. 29:530–537.33. Strunk RC, Bloomberg GR. Omalizumab for asthma. N Engl J Med. 2006. 354:2689–2695.34. Valenta R, Mittermann I, Werfel T, Garn H, Renz H. Linking allergy to autoimmune disease. Trends Immunol. 2009. 30:109–116.35. Talmage DW. Immunological specificity, unique combinations of selected natural globulins provide an alternative to the classical concept. Science. 1959. 129:1643–1648.36. Varga JM, Konigsberg WH, Richards FF. Antibodies with multiple binding functions. Induction of single immunoglobin species by structurally dissimilar haptens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973. 70:3269–3274.37. Black P. Why is the prevalence of allergy and autoimmunity increasing? Trends Immunol. 2001. 22:354–355.38. Rabin RL, Levinson AI. The nexus between atopic disease and autoimmunity: a review of the epidemiological and mechanistic literature. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008. 153:19–30.39. Valenta R, Seiberler S, Natter S, Mahler V, Mossabeb R, Ring J, Stingl G. Autoallergy: a pathogenetic factor in atopic dermatitis? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000. 105:432–437.40. Aichberger KJ, Mittermann I, Reininger R, Seiberler S, Swoboda I, Spitzauer S, Kopp T, Stingl G, Sperr WR, Valent P, Repa A, Bohle B, Kraft D, Valenta R. Hom s 4, an IgE-reactive autoantigen belonging to a new subfamily of calcium-binding proteins, can induce Th cell type 1-mediated autoreactivity. J Immunol. 2005. 175:1286–1294.41. Mittermann I, Reininger R, Zimmermann M, Gangl K, Reisinger J, Aichberger KJ, Greisenegger EK, Niederberger V, Seipelt J, Bohle B, Kopp T, Akdis CA, Spitzauer S, Valent P, Valenta R. The IgE-reactive autoantigen Hom s 2 induces damage of respiratory epithelial cells and keratinocytes via induction of IFN-γ. J Invest Dermatol. 2008. 128:1451–1459.42. Crameri R, Faith A, Hemmann S, Jaussi R, Ismail C, Menz G, Blaser K. Humoral and cell-mediated autoimmunity in allergy to Aspergillus fumigatus. J Exp Med. 1996. 184:265–270.43. Mayer C, Appenzeller U, Seelbach H, Achatz G, Oberkofler H, Breitenbach M, Blaser K, Crameri R. Humoral and cell-mediated autoimmune reactions to human acidic ribosomal P2 protein in individuals sensitized to Aspergillus fumigatus P2 protein. J Exp Med. 1999. 189:1507–1512.44. Schmid-Grendelmeier P, Flückiger S, Disch R, Trautmann A, Wüthrich B, Blaser K, Scheynius A, Crameri R. IgE-mediated and T cell-mediated autoimmunity against manganese superoxide dismutase in atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005. 115:1068–1075.45. Spitzauer S, Schweiger C, Sperr WR, Pandjaitan B, Valent P, Mühl S, Ebner C, Scheiner O, Kraft D, Rumpold H, Valenta R. Molecular characterization of dog albumin as a cross-reactive allergen. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1994. 93:614–627.46. Valenta R, Duchêne M, Pettenburger K, Sillaber C, Valent P, Bettelheim P, Breitenbach M, Rumpold H, Kraft D, Scheiner O. Identification of profilin as a novel pollen allergen; IgE autoreactivity in sensitized individuals. Science. 1991. 253:557–560.47. Zeller S, Rhyner C, Meyer N, Schmid-Grendelmeier P, Akdis CA, Crameri R. Exploring the repertoire of IgE-binding self-antigens associated with atopic eczema. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009. 124:278–285. 285.e1-748. Matsuda H, Watanabe N, Geba GP, Sperl J, Tsudzuki M, Hiroi J, Matsumoto M, Ushio H, Saito S, Askenase PW, Ra C. Development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesion with IgE hyperproduction in NC/Nga mice. Int Immunol. 1997. 9:461–466.49. Matsubara T, Aoki N, Hino S, Okajima T, Nadano D, Matsuda T. Serum and monoclonal immunoglobulin E antibodies from NC/Nga mice with severe atopic-like dermatitis recognize an auto-antigen, histone H3. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009. 39:579–590.50. Kashiwakura J, Otani IM, Kawakami T. Monomeric IgE and mast cell development, survival and function. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011. 716:29–46.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Highly Cytokinergic IgE Antibodies and Autoimmune Mechanisms
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of GABRG2 in Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsies(IGEs)
- Proteomic Analysis of Airway Epithelial Cell Autoantigens Associated with Bronchial Asthma: Target Protein Identification Using Cultured Cell Fractionation Method
- The Role of B Cells in Transplantation and Immunopathic Diseases
- Potential Role of Bacterial Infection in Autoimmune Diseases: A New Aspect of Molecular Mimicry