Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2011 Mar;4(1):18-23.
Decreased Immunoreactivities and Functions of the Chloride Transporters, KCC2 and NKCC1, in the Lateral Superior Olive Neurons of Circling Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nanobio Medical Science, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 2Department of Anatomy, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 3Department of Physiology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. ansil67@hanmail.net
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
We tested the possibility of differential expression and function of the potassium-chloride (KCC2) and sodium-potassium-2 chloride (NKCC1) co-transporters in the lateral superior olive (LSO) of heterozygous (+/cir) or homozygous (cir/cir) mice.
METHODS
Mice pups aged from postnatal (P) day 9 to 16 were used. Tails from mice were cut for DNA typing. For Immunohistochemical analysis, rabbit polyclonal anti-KCC2 or rabbit polyclonal anti-NKCC1 was used and the density of immunolabelings was evaluated using the NIH image program. For functional analysis, whole cell voltage clamp technique was used in brain stem slices and the changes of reversal potentials were evaluated at various membrane potentials.
RESULTS
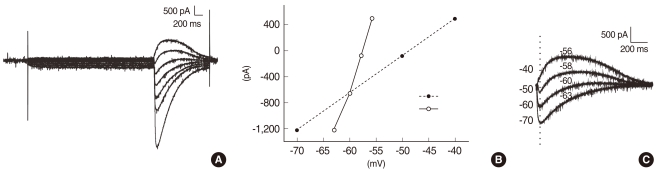
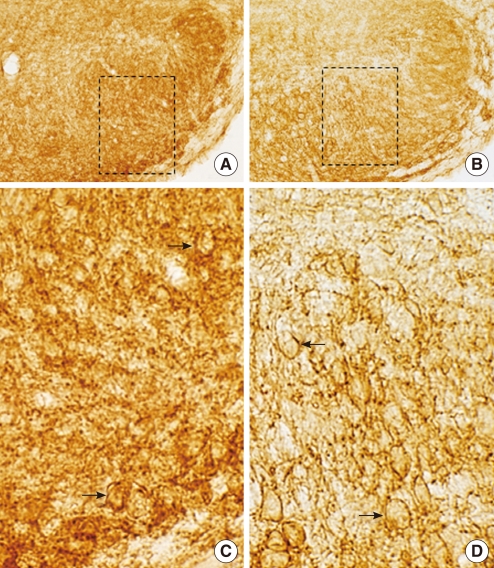
Immunohistochemical analysis revealed both KCC2 and NKCC1 immunoreactivities were more prominent in heterozygous (+/cir) than homozygous (cir/cir) mice on P day 16. In P9-P12 heterozygous (+/cir) mice, the reversal potential (Egly) of glycine-induced currents was shifted to a more negative potential by 50 microM bumetanide, a known NKCC1 blocker, and the negatively shifted Egly was restored by additional application of 1 mM furosemide, a KCC2 blocker (-58.9+/-2.6 mV to -66.0+/-1.5 mV [bumetanide], -66.0+/-1.5 mV to -59.8+/-2.8 mV [furosemide+bumetanide], n=11). However, only bumetanide was weakly, but significantly effective (-60.1+/-2.9 mV to -62.7+/-2.6 mV [bumetanide], -62.7+/-2.6 mV to -62.1+/-2.5 mV [furosemide+bumetanide], n=7) in P9-P12 homozygous (cir/cir) mice.
CONCLUSION
The less prominent immunoreactivities and weak or absent responses to bumetanide or furosemide suggest impaired function or delayed development of both transporters in homozygous (cir/cir) mice.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chung WH, Kim KR, Cho YS, Cho DY, Woo JH, Ryoo ZY, et al. Cochlear pathology of the circling mouse: a new mouse model of DFNB6. Acta Otolaryngol. 2007; 3. 127(3):244–251. PMID: 17364360.
Article2. Lee JW, Lee EJ, Hong SH, Chung WH, Lee HT, Lee TW, et al. Circling mouse: possible animal model for deafness. Comp Med. 2001; 12. 51(6):550–554. PMID: 11924819.3. Lee JW, Ryoo ZY, Lee EJ, Hong SH, Chung WH, Lee HT, et al. Circling mouse, a spontaneous mutant in the inner ear. Exp Anim. 2002; 4. 51(2):167–171. PMID: 12012726.
Article4. Gillespie DC, Kim G, Kandler K. Inhibitory synapses in the developing auditory system are glutamatergic. Nat Neurosci. 2005; 3. 8(3):332–338. PMID: 15746915.
Article5. Hong SH, Kim MJ, Ahn SC. Glutamatergic transmission is sustained at a later period of development of medial nucleus of the trapezoid body-lateral superior olive synapses in circling mice. J Neurosci. 2008; 11. 26. 28(48):13003–13007. PMID: 19036993.
Article6. Chen G, Trombley PQ, van den Pol AN. Excitatory actions of GABA in developing rat hypothalamic neurones. J Physiol. 1996; 7. 15. 494(Pt 2):451–464. PMID: 8842004.
Article7. Cherubini E, Rovira C, Gaiarsa JL, Corradetti R, Ben Ari Y. GABA mediated excitation in immature rat CA3 hippocampal neurons. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1990; 8(4):481–490. PMID: 2174638.
Article8. Luhmann HJ, Prince DA. Postnatal maturation of the GABAergic system in rat neocortex. J Neurophysiol. 1991; 2. 65(2):247–263. PMID: 1673153.
Article9. Singer JH, Talley EM, Bayliss DA, Berger AJ. Development of glycinergic synaptic transmission to rat brain stem motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1998; 11. 80(5):2608–2620. PMID: 9819267.
Article10. Wu WL, Ziskind-Conhaim L, Sweet MA. Early development of glycine- and GABA-mediated synapses in rat spinal cord. J Neurosci. 1992; 10. 12(10):3935–3945. PMID: 1403091.
Article11. Kandler K, Friauf E. Development of glycinergic and glutamatergic synaptic transmission in the auditory brainstem of perinatal rats. J Neurosci. 1995; 10. 15(10):6890–6904. PMID: 7472446.
Article12. Lohrke S, Srinivasan G, Oberhofer M, Doncheva E, Friauf E. Shift from depolarizing to hyperpolarizing glycine action occurs at different perinatal ages in superior olivary complex nuclei. Eur J Neurosci. 2005; 12. 22(11):2708–2722. PMID: 16324105.13. Plotkin MD, Snyder EY, Hebert SC, Delpire E. Expression of the Na-K-2Cl cotransporter is developmentally regulated in postnatal rat brains: a possible mechanism underlying GABA's excitatory role in immature brain. J Neurobiol. 1997; 11. 20. 33(6):781–795. PMID: 9369151.
Article14. Rivera C, Voipio J, Payne JA, Ruusuvuori E, Lahtinen H, Lamsa K, et al. The K+/Cl- co-transporter KCC2 renders GABA hyperpolarizing during neuronal maturation. Nature. 1999; 1. 21. 397(6716):251–255. PMID: 9930699.
Article15. Kitamura A, Ishibashi H, Watanabe M, Takatsuru Y, Brodwick M, Nabekura J. Sustained depolarizing shift of the GABA reversal potential by glutamate receptor activation in hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Res. 2008; 12. 62(4):270–277. PMID: 18840481.
Article16. Shibata S, Kakazu Y, Okabe A, Fukuda A, Nabekura J. Experience-dependent changes in intracellular Cl- regulation in developing auditory neurons. Neurosci Res. 2004; 2. 48(2):211–220. PMID: 14741396.
Article17. Fiumelli H, Woodin MA. Role of activity-dependent regulation of neuronal chloride homeostasis in development. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007; 2. 17(1):81–86. PMID: 17234400.
Article18. Vale C, Schoorlemmer J, Sanes DH. Deafness disrupts chloride transporter function and inhibitory synaptic transmission. J Neurosci. 2003; 8. 20. 23(20):7516–7524. PMID: 12930790.
Article19. DeFazio RA, Keros S, Quick MW, Hablitz JJ. Potassium-coupled chloride cotransport controls intracellular chloride in rat neocortical pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci. 2000; 11. 01. 20(21):8069–8076. PMID: 11050128.
Article20. Balakrishnan V, Becker M, Lohrke S, Nothwang HG, Guresir E, Friauf E. Expression and function of chloride transporters during development of inhibitory neurotransmission in the auditory brainstem. J Neurosci. 2003; 5. 15. 23(10):4134–4145. PMID: 12764101.
Article21. Russell JM. Sodium-potassium-chloride cotransport. Physiol Rev. 2000; 1. 80(1):211–276. PMID: 10617769.
Article22. Payne JA. Functional characterization of the neuronal-specific K-Cl cotransporter: implications for [K+]o regulation. Am J Physiol. 1997; 11. 273(5 Pt 1):C1516–C1525. PMID: 9374636.23. Bormann J, Hamill OP, Sakmann B. Mechanism of anion permeation through channels gated by glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid in mouse cultured spinal neurones. J Physiol. 1987; 4. 385:243–286. PMID: 2443667.
Article24. Backus KH, Deitmer JW, Friauf E. Glycine-activated currents are changed by coincident membrane depolarization in developing rat auditory brainstem neurones. J Physiol. 1998; 3. 15. 507(Pt 3):783–794. PMID: 9508839.
Article25. Friauf E, Wenz M, Oberhofer M, Nothwang HG, Balakrishnan V, Knipper M, et al. Hypothyroidism impairs chloride homeostasis and onset of inhibitory neurotransmission in developing auditory brainstem and hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 2008; 12. 28(12):2371–2380. PMID: 19087168.
Article26. Kakazu Y, Akaike N, Komiyama S, Nabekura J. Regulation of intracellular chloride by cotransporters in developing lateral superior olive neurons. J Neurosci. 1999; 4. 15. 19(8):2843–2851. PMID: 10191302.
Article27. de Jong JC, Willems PH, Mooren FJ, van den Heuvel LP, Knoers NV, Bindels RJ. The structural unit of the thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransporter is a homodimer. J Biol Chem. 2003; 7. 04. 278(27):24302–24307. PMID: 12704198.
Article28. Moore-Hoon ML, Turner RJ. The structural unit of the secretory Na+-K+-2Cl-cotransporter (NKCC1) is a homodimer. Biochemistry. 2000; 4. 04. 39(13):3718–3724. PMID: 10736171.29. Blaesse P, Guillemin I, Schindler J, Schweizer M, Delpire E, Khiroug L, et al. Oligomerization of KCC2 correlates with development of inhibitory neurotransmission. J Neurosci. 2006; 10. 11. 26(41):10407–10419. PMID: 17035525.
Article30. Maric D, Liu QY, Maric I, Chaudry S, Chang YH, Smith SV, et al. GABA expression dominates neuronal lineage progression in the embryonic rat neocortex and facilitates neurite outgrowth via GABA(A) autoreceptor/Cl- channels. J Neurosci. 2001; 4. 01. 21(7):2343–2360. PMID: 11264309.31. Ben-Ari Y, Khazipov R, Leinekugel X, Caillard O, Gaiarsa JL. GABAA, NMDA and AMPA receptors: a developmentally regulated 'ménage à trois'. Trends Neurosci. 1997; 11. 20(11):523–529. PMID: 9364667.
Article32. Kirsch J, Betz H. Glycine-receptor activation is required for receptor clustering in spinal neurons. Nature. 1998; 4. 16. 392(6677):717–720. PMID: 9565032.
Article33. Ben-Ari Y, Tseeb V, Raggozzino D, Khazipov R, Gaiarsa JL. Gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA): a fast excitatory transmitter which may regulate the development of hippocampal neurones in early postnatal life. Prog Brain Res. 1994; 102:261–273. PMID: 7800817.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Decreased Immunoreactivities of the Chloride Transporters, KCC2 and NKCC1, in the Lateral Superior Olive Neurons of Kanamycin-treated Rats
- Investigation of Developmental Changes of Convergence Ratios of MNTB-LSO Synapses in Circling Mice
- Melatonin modulates nitric oxide-regulated WNK-SPAK/OSR1-NKCC1 signaling in dorsal raphe nucleus of rats
- Loss of MicroRNA-137 Impairs the Homeostasis of Potassium in Neurons via KCC2
- Morphologic Change of the Vestibular Organ in the Na+-K+-2Cl- Cotransporter Deficiency Mouse