Cancer Res Treat.
2006 Jun;38(3):178-183.
Neoadjuvant Imatinib in Locally Advanced Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors of the Stomach: Report of Three Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ykkang@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
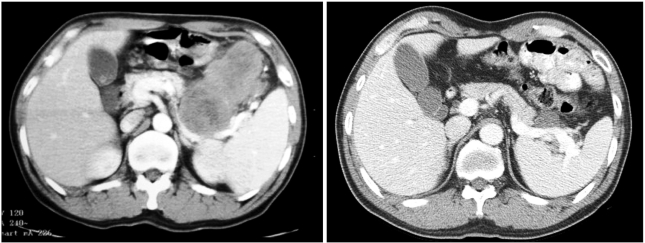
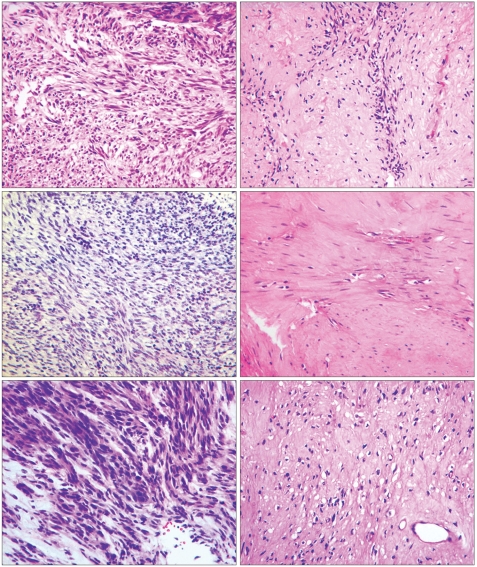
- Neoadjuvant imatinib therapy used to treat locally advanced or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GI ST) remains under active investigation. We studied three cases of locally advanced gastric GISTs treated with imatinib on a neoadjuvant basis, followed by a complete surgical resection. Three patients were diagnosed with locally advanced unresectable GIST of the stomach and were started on imatinib 400 mg/day. After the imatinib treatment, partial responses were achieved in all patients and the tumors were considered resectable. Surgical resection was done after 7, 11, and 8 months of imatinib therapy, respectively. In one case, a metastatic liver lesion was detected during the imatinib treatment using computed tomography scans, so the imatinib therapy was maintained for 11 months postoperatively. In the other two patients without distant metastasis, imatinib treatment was not restarted after surgery. Mutational analysis revealed a mutation in exon 11 of the c-kit gene in two patients, and wild-type c-kit and PDGFRA in one patient. During pathology review of all three cases, we noted several features common to imatinib treatment. There was no evidence of tumor recurrence in all three patients at respective follow-up visits of 22, 15, and 7 months. These results suggest that the neoadjuvant imatinib therapy is a potentially curative approach for selected patients with locally advanced GIST.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Miettinen M, Majidi M, Lasota J. Pathology and diagnostic criteria of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs): a review. Eur J Cancer. 2002; 38(Suppl 5):S39–S51. PMID: 12528772.
Article2. Blay JY, Bonvalot S, Casali P, Choi H, Debiec-Richter M, Dei Tos AP, et al. Consensus meeting for the management of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Report of the GIST Consensus Conference of 20-21 March 2004, under the auspices of ESMO. Ann Oncol. 2005; 16:566–578. PMID: 15781488.
Article3. Dematteo RP, Heinrich MC, El-Rifai WM, Demetri G. Clinical management of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: before and after STI-571. Hum Pathol. 2002; 33:466–477. PMID: 12094371.
Article4. Heinrich MC, Corless CL, Duensing A, McGreevey L, Chen CJ, Joseph N, et al. PDGFRA activating mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science. 2003; 299:708–710. PMID: 12522257.5. Heinrich MC, Corless CL, Demetri GD, Blanke CD, von Mehren M, Joensuu H, et al. Kinase mutations and imatinib response in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:4342–4349. PMID: 14645423.
Article6. Kim TW, Lee HN, Kang YK, Choe MS, Ryu MH, Chang HM, et al. Prognostic significance of c-kit mutation in localized gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2004; 10:3076–3081. PMID: 15131046.
Article7. Verweij J, van Oosterom A, Blay JY, Judson I, Rodenhuis S, van der Graaf W, et al. Imatinib mesylate (STI-571 Glivec, Gleevec) is an active agent for gastrointestinal stromal tumours, but does not yield responses in other soft-tissue sarcomas that are unselected for a molecular target. Results from an EORTC Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group phase II study. Eur J Cancer. 2003; 39:2006–2011. PMID: 12957454.8. Verweij J, Casali PG, Zalcberg J, LeCesne A, Reichardt P, Blay JY, et al. Progression-free survival in gastrointestinal stromal tumours with high-dose imatinib: randomised trial. Lancet. 2004; 364:1127–1134. PMID: 15451219.
Article9. Demetri GD, von Mehren M, Blanke CD, Van den Abbeele AD, Eisenberg B, Roberts PJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of imatinib mesylate in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:472–480. PMID: 12181401.
Article10. De Giorgi U, Verweij J. Imatinib and gastrointestinal stromal tumors: where do we go from here? Mol Cancer Ther. 2005; 4:495–501. PMID: 15767559.
Article11. Ryu MH, Lee HN, Kim TW, Chang HM, Bang YJ, Kang WK, et al. Efficacy of imatinib mesylate and c-kit mutations in metastatic or unresectable GISTs. Ann Oncol. 2004; 15:760. (abstr iii201).12. Loughrey MB, Mitchell C, Mann GB, Michael M, Waring PM. Gastrointestinal stromal tumour treated with neoadjuvant imatinib. J Clin Pathol. 2005; 58:779–781. PMID: 15976351.
Article13. Blanke CD, Joensuu H, Demetri GD, Heinrich MC, Eisenberg B, Fletcher J, et al. Outcome of advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) patients treated with imatinib mesylate: four-year follow-up of a phase II randomized trial. In : ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium Proceeding 2006; (abstr 7).14. Ryu MH, Lee JL, Chang HM, Kim TW, Kang HJ, Sohn HJ, et al. Patterns of progression in gastrointestinal stromal tumor treated with imatinib mesylate. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2006; 36:17–24. PMID: 16418188.
Article15. Rutkowski P, Nowecki Z, Nyckowski P, Dziewirski W, Grzesiakowska U, Nasierowska-Guttmejer A, et al. Surgical treatment of patients with initially inoperable and/or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) during therapy with imatinib mesylate. J Surg Oncol. 2006; 93:304–311. PMID: 16496358.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful Resection of Locally Advanced Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor of the Ampulla of Vater after Treatment with Imatinib
- Efficacy of Imatinib Mesylate Neoadjuvant Treatment for a Locally Advanced Rectal Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
- Surgical Treatment of Gastric Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
- Imatinib-induced DRESS Syndrome in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
- Clinicopathologic change of gastrointestinal stromal tumor after neoadjuvant imatinib followed by surgical resection