J Periodontal Implant Sci.
2015 Aug;45(4):128-135. 10.5051/jpis.2015.45.4.128.
The effect of overlaying titanium mesh with collagen membrane for ridge preservation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Periodontology, Kyung Hee University School of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Periodontology, Research Institute for Periodontal Regeneration, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea. drjew@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2164341
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2015.45.4.128
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to determine the effect of overlaying titanium mesh (TM) with an adjunctive collagen membrane (CM) for preserving the buccal bone when used in association with immediate implant placement in dogs.
METHODS
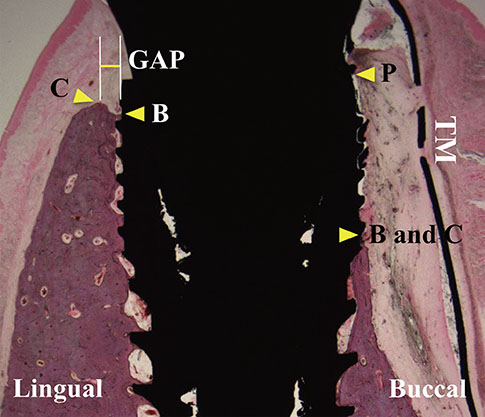
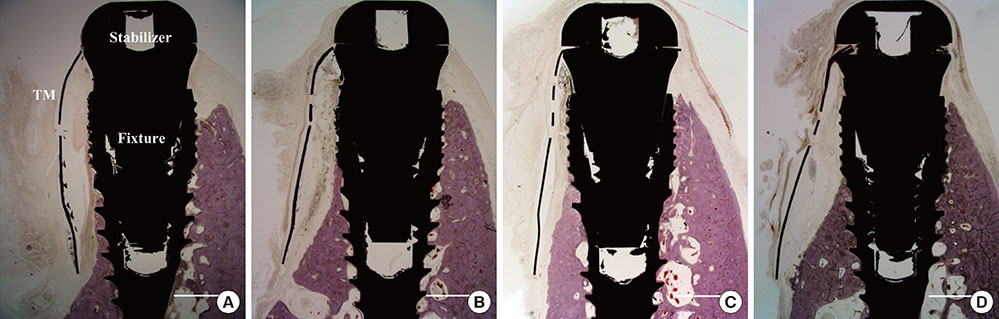
Immediate implant placements were performed in the mesial sockets of the third premolars of five dogs. At one site the TM was attached to the fixture with the aid of its own stabilizers and then covered by a CM (CM group), while the contralateral site received only TM (TM group). Biopsy specimens were retrieved for histologic and histomorphometric analyses after 16 weeks.
RESULTS
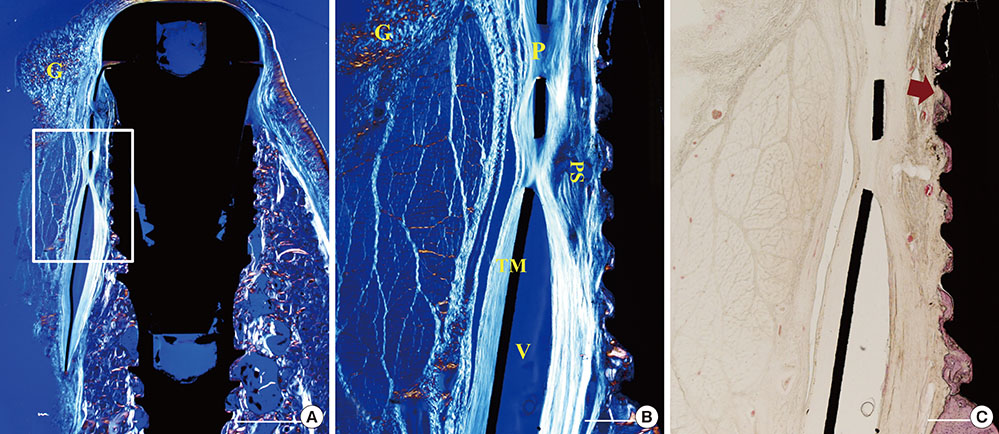
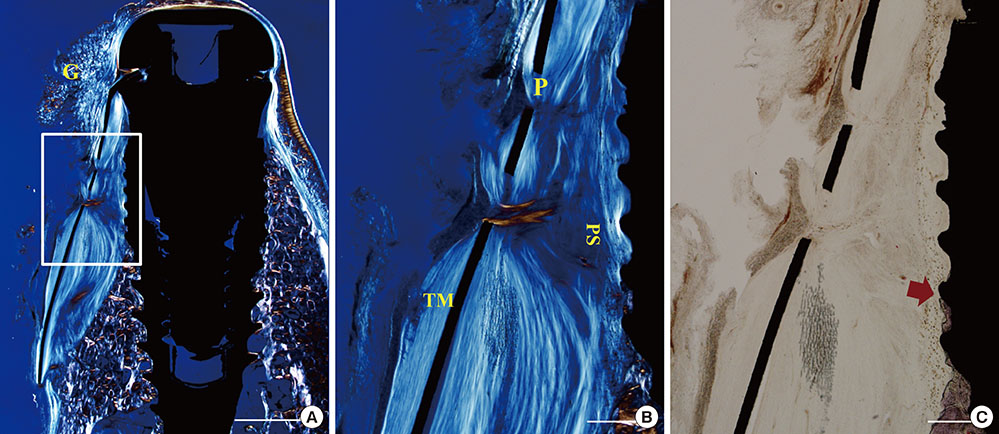
All samples exhibited pronounced buccal bone resorption, and a high rate of TM exposure was noted (in three and four cases of the five samples in each of the TM and CM groups, respectively). A dense fibrous tissue with little vascularity or cellularity had infiltrated through the pores of the TM irrespective of the presence of a CM. The distances between the fixture platform and the first bone-implant contact and the bone crest did not differ significantly between the TM and CM groups.
CONCLUSIONS
Our study suggests that the additional use of a CM over TM does not offer added benefit for mucosal healing and buccal bone preservation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chen ST, Buser D. Clinical and esthetic outcomes of implants placed in postextraction sites. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009; 24:Suppl. 186–217.2. Wang RE, Lang NP. Ridge preservation after tooth extraction. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012; 23:Suppl 6. 147–156.
Article3. Araújo MG, Linder E, Lindhe J. Bio-Oss collagen in the buccal gap at immediate implants: a 6-month study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011; 22:1–8.
Article4. De Buitrago JG, Avila-Ortiz G, Elangovan S. Quality assessment of systematic reviews on alveolar ridge preservation. J Am Dent Assoc. 2013; 144:1349–1357.
Article5. Favero G, Botticelli D, Favero G, García B, Mainetti T, Lang NP. Alveolar bony crest preservation at implants installed immediately after tooth extraction: an experimental study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013; 24:7–12.
Article6. Kostopoulos L, Karring T. Augmentation of the rat mandible using guided tissue regeneration. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1994; 5:75–82.
Article7. Simion M, Dahlin C, Rocchietta I, Stavropoulos A, Sanchez R, Karring T. Vertical ridge augmentation with guided bone regeneration in association with dental implants: an experimental study in dogs. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007; 18:86–94.
Article8. Wang HL, Boyapati L. "PASS" principles for predictable bone regeneration. Implant Dent. 2006; 15:8–17.
Article9. Wikesjö UM, Claffey N, Egelberg J. Periodontal repair in dogs. Effect of heparin treatment of the root surface. J Clin Periodontol. 1991; 18:60–64.
Article10. Lin Z, Fateh A, Salem DM, Intini G. Periosteum: biology and applications in craniofacial bone regeneration. J Dent Res. 2014; 93:109–116.11. Allen MR, Hock JM, Burr DB. Periosteum: biology, regulation, and response to osteoporosis therapies. Bone. 2004; 35:1003–1012.
Article12. Diaz-Flores L, Gutierrez R, Lopez-Alonso A, Gonzalez R, Varela H. Pericytes as a supplementary source of osteoblasts in periosteal osteogenesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992; 280–286.
Article13. Dahlin C, Linde A, Gottlow J, Nyman S. Healing of bone defects by guided tissue regeneration. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1988; 81:672–676.
Article14. Park SH, Lee KW, Oh TJ, Misch CE, Shotwell J, Wang HL. Effect of absorbable membranes on sandwich bone augmentation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008; 19:32–41.
Article15. Weng D, Hürzeler MB, Quiñones CR, Ohlms A, Caffesse RG. Contribution of the periosteum to bone formation in guided bone regeneration. A study in monkeys. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2000; 11:546–554.
Article16. Jung UW, Lee JS, Lee G, Lee IK, Hwang JW, Kim MS, et al. Role of collagen membrane in lateral onlay grafting with bovine hydroxyapatite incorporated with collagen matrix in dogs. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2013; 43:64–71.
Article17. Jung UW, Lee JS, Park WY, Cha JK, Hwang JW, Park JC, et al. Periodontal regenerative effect of a bovine hydroxyapatite/collagen block in one-wall intrabony defects in dogs: a histometric analysis. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2011; 41:285–292.
Article18. Lim HC, Kim MS, Yang C, Lee JS, Hong JY, Choi SH, et al. The effectiveness of a customized titanium mesh for ridge preservation with immediate implantation in dogs. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2015; Forthcoming.
Article19. Her S, Kang T, Fien MJ. Titanium mesh as an alternative to a membrane for ridge augmentation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 70:803–810.
Article20. Louis PJ, Gutta R, Said-Al-Naief N, Bartolucci AA. Reconstruction of the maxilla and mandible with particulate bone graft and titanium mesh for implant placement. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 66:235–245.
Article21. Proussaefs P, Lozada J. Use of titanium mesh for staged localized alveolar ridge augmentation: clinical and histologic-histomorphometric evaluation. J Oral Implantol. 2006; 32:237–247.
Article22. Gutta R, Baker RA, Bartolucci AA, Louis PJ. Barrier membranes used for ridge augmentation: is there an optimal pore size? J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 67:1218–1225.
Article23. Assenza B, Piattelli M, Scarano A, Lezzi G, Petrone G, Piattelli A. Localized ridge augmentation using titanium micromesh. J Oral Implantol. 2001; 27:287–292.
Article24. Degidi M, Scarano A, Piattelli A. Regeneration of the alveolar crest using titanium micromesh with autologous bone and a resorbable membrane. J Oral Implantol. 2003; 29:86–90.
Article25. Lundgren D, Nyman S, Mathisen T, Isaksson S, Klinge B. Guided bone regeneration of cranial defects, using biodegradable barriers: an experimental pilot study in the rabbit. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1992; 20:257–260.
Article26. Engler-Hamm D, Cheung WS, Yen A, Stark PC, Griffin T. Ridge preservation using a composite bone graft and a bioabsorbable membrane with and without primary wound closure: a comparative clinical trial. J Periodontol. 2011; 82:377–387.
Article27. Kim DM, De Angelis N, Camelo M, Nevins ML, Schupbach P, Nevins M. Ridge preservation with and without primary wound closure: a case series. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2013; 33:71–78.
Article28. Zubillaga G, Von Hagen S, Simon BI, Deasy MJ. Changes in alveolar bone height and width following post-extraction ridge augmentation using a fixed bioabsorbable membrane and demineralized freeze-dried bone osteoinductive graft. J Periodontol. 2003; 74:965–975.
Article29. von Arx T, Hardt N, Wallkamm B. The TIME technique: a new method for localized alveolar ridge augmentation prior to placement of dental implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1996; 11:387–394.30. Rakhmatia YD, Ayukawa Y, Furuhashi A, Koyano K. Current barrier membranes: titanium mesh and other membranes for guided bone regeneration in dental applications. J Prosthodont Res. 2013; 57:3–14.
Article31. von Arx T, Kurt B. Implant placement and simultaneous peri-implant bone grafting using a micro titanium mesh for graft stabilization. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1998; 18:117–127.32. Lizio G, Corinaldesi G, Marchetti C. Alveolar ridge reconstruction with titanium mesh: a three-dimensional evaluation of factors affecting bone augmentation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014; 29:1354–1363.
Article33. Boyne PJ, Cole MD, Stringer D, Shafqat JP. A technique for osseous restoration of deficient edentulous maxillary ridges. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1985; 43:87–91.
Article34. Miyamoto I, Funaki K, Yamauchi K, Kodama T, Takahashi T. Alveolar ridge reconstruction with titanium mesh and autogenous particulate bone graft: computed tomography-based evaluations of augmented bone quality and quantity. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2012; 14:304–311.
Article35. Corinaldesi G, Pieri F, Sapigni L, Marchetti C. Evaluation of survival and success rates of dental implants placed at the time of or after alveolar ridge augmentation with an autogenous mandibular bone graft and titanium mesh: a 3- to 8-year retrospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009; 24:1119–1128.36. Pieri F, Corinaldesi G, Fini M, Aldini NN, Giardino R, Marchetti C. Alveolar ridge augmentation with titanium mesh and a combination of autogenous bone and anorganic bovine bone: a 2-year prospective study. J Periodontol. 2008; 79:2093–2103.
Article37. Proussaefs P, Lozada J. The use of resorbable collagen membrane in conjunction with autogenous bone graft and inorganic bovine mineral for buccal/labial alveolar ridge augmentation: a pilot study. J Prosthet Dent. 2003; 90:530–538.
Article38. Roccuzzo M, Ramieri G, Bunino M, Berrone S. Autogenous bone graft alone or associated with titanium mesh for vertical alveolar ridge augmentation: a controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007; 18:286–294.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical effect of porous titanium mesh with cross-linked collagen membrane for guided bone regeneration
- Comparison of Titanium Micro Mesh(R) with Titanium Mesh Screen 1.3(R) in the Reconstruction of Medial Orbital wall Fracture
- Combined Sinus Floor and Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Simultaneously Performed with Extraction of Ankylosed Maxillary Molar: A Case Report
- RECONSTRUCTION OF PREMAXILLA WITH TITANIUM MESH AND ILIAC PMCB
- Effect of pore number of titanium mesh on Bone Formation in the procedure of GBR