J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2016 Apr;51(2):109-116. 10.4055/jkoa.2016.51.2.109.
Management of Flexible Flatfoot in Chidren and Adolescent
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea. jrkeem@chonbuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 2162044
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2016.51.2.109
Abstract
- Most children and adolescents with flexible flatfeet are asymptomatic and most do not require treatment. Scant convincing evidence exists to support the use of inserts or shoe modifications for effective relief of symptoms, and there is no evidence that those devices change the shape of the foot. Surgical correction is indicated for failure of prolonged nonsurgical attempts to relieve pain that interferes with normal activities and occurs under the medial midfoot and/or in the sinus tarsi. Osteotomies with supplemental soft-tissue procedures or arthroereisis are the suggested operative procedures for symptomatic flatfoot. An associated contracture of the heel cord is present in nearly all cases. Concurrent rigid forefoot supination deformity should be addressed as well.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
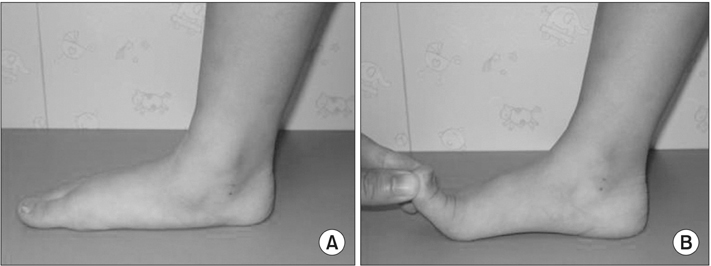
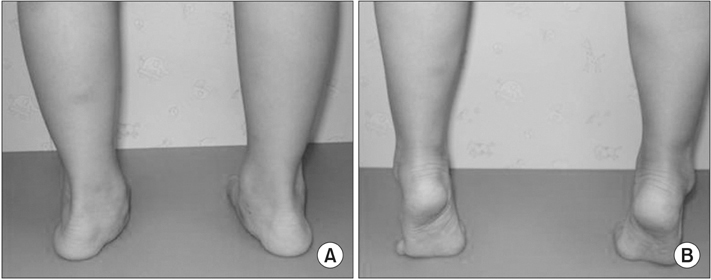
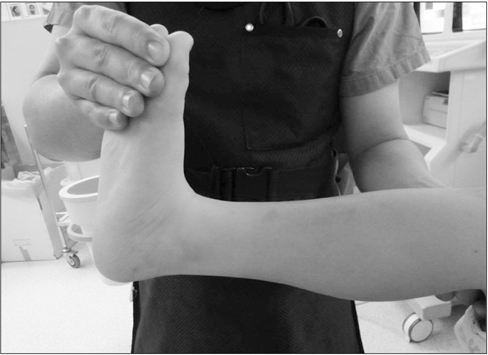
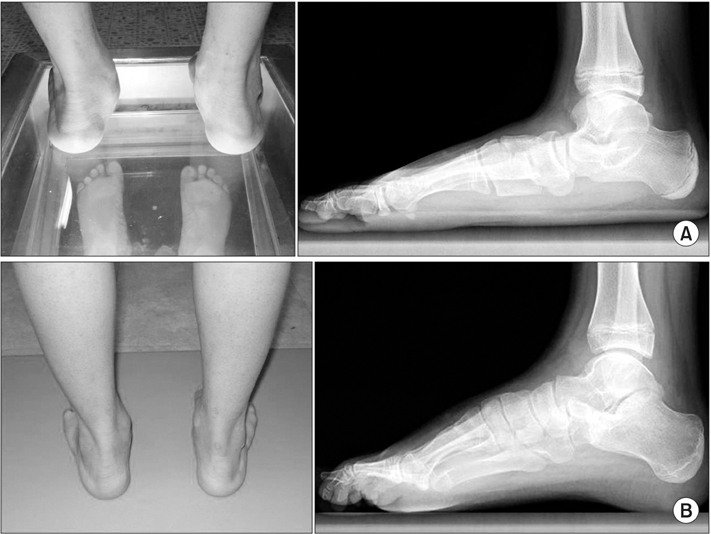
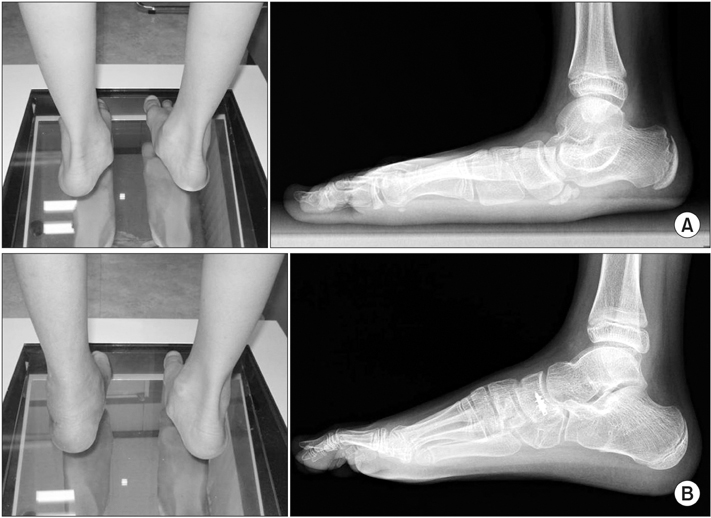
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of Pressure Based Customized 3-Dimensional Printing Insole in Pediatric Flexible Flat Foot Patients
Si-Wook Lee, Jung-Hoon Choi, Hyuk-Jun Kwon, Kwang-Soon Song
J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2020;24(3):113-119. doi: 10.14193/jkfas.2020.24.3.113.
Reference
-
1. Staheli LT, Chew DE, Corbett M. The longitudinal arch. A survey of eight hundred and eighty-two feet in normal children and adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987; 69:426–428.2. Harris RI, Beath T. Hypermobile flat-foot with short tendo achillis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1948; 30:116–140.
Article3. Davids JR, Gibson TW, Pugh LI. Quantitative segmental analysis of weight-bearing radiographs of the foot and ankle for children: normal alignment. J Pediatr Orthop. 2005; 25:769–776.4. Vanderwilde R, Staheli LT, Chew DE, Malagon V. Measurements on radiographs of the foot in normal infants and children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988; 70:407–415.
Article5. Park MS, Kwon SS, Lee SY, Lee KM, Kim TG, Chung CY. Spontaneous improvement of radiographic indices for idiopathic planovalgus with age. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013; 95:e193(1-8).
Article6. Park H, Hwang JH, Seo JO, Kim HW. The relationship between accessory navicular and flat foot: a radiologic study. J Pediatr Orthop. 2015; 35:739–745.7. Bok SK, Kim BO, Lim JH, Ahn SY. Effects of custom-made rigid foot orthosis on pes planus in children over 6 years old. Ann Rehabil Med. 2014; 38:369–375.
Article8. Bordelon RL. Correction of hypermobile flatfoot in children by molded insert. Foot Ankle. 1980; 1:143–150.
Article9. Whitford D, Esterman A. A randomized controlled trial of two types of in-shoe orthoses in children with flexible excess pronation of the feet. Foot Ankle Int. 2007; 28:715–723.
Article10. Wenger DR, Mauldin D, Speck G, Morgan D, Lieber RL. Corrective shoes and inserts as treatment for flexible flatfoot in infants and children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989; 71:800–810.
Article11. Evans AM, Rome K. A Cochrane review of the evidence for non-surgical interventions for flexible pediatric flat feet. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2011; 47:69–89.12. Bettmann E. The treatment of flat-foot by means of exercise. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1937; 19:821–825.13. Mann R, Inman VT. Phasic activity of intrinsic muscles of the foot. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964; 46:469–481.
Article14. Mosca VS. Flexible flatfoot in children and adolescents. J Child Orthop. 2010; 4:107–121.
Article15. Kelikian A, Mosca V, Schoenhaus HD, Winson I, Weil L Jr. When to operate on pediatric flatfoot. Foot Ankle Spec. 2011; 4:112–119.
Article16. Bouchard M, Mosca VS. Flatfoot deformity in children and adolescents: surgical indications and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014; 22:623–632.17. Haraldsson S. Operative treatment of pes planovalgus staticus juvenilis. Preliminary communication. Acta Orthop Scand. 1962; 32:492–498.18. De Pellegrin M, Moharamzadeh D, Strobl WM, Biedermann R, Tschauner C, Wirth T. Subtalar extra-articular screw arthroereisis (SESA) for the treatment of flexible flatfoot in children. J Child Orthop. 2014; 8:479–487.
Article19. Nelson SC, Haycock DM, Little ER. Flexible flatfoot treatment with arthroereisis: radiographic improvement and child health survey analysis. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2004; 43:144–155.
Article20. Jay RM, Din N. Correcting pediatric flatfoot with subtalar arthroereisis and gastrocnemius recession: a retrospective study. Foot Ankle Spec. 2013; 6:101–107.21. Lui TH. Spontaneous subtalar fusion: an irreversible complication of subtalar arthroereisis. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2014; 53:652–656.
Article22. Shah NS, Needleman RL, Bokhari O, Buzas D. 2013 subtalar arthroereisis survey: the current practice patterns of members of the AOFAS. Foot Ankle Spec. 2015; 8:180–185.23. Pavone V, Costarella L, Testa G, Conte G, Riccioli M, Sessa G. Calcaneo-stop procedure in the treatment of the juvenile symptomatic flatfoot. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2013; 52:444–447.
Article24. Usuelli FG, Montrasio UA. The calcaneo-stop procedure. Foot Ankle Clin. 2012; 17:183–194.
Article25. Jerosch J, Schunck J, Abdel-Aziz H. The stop screw technique: a simple and reliable method in treating flexible flatfoot in children. Foot Ankle Surg. 2009; 15:174–178.26. Evans D. Calcaneo-valgus deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1975; 57:270–278.
Article27. Mosca VS. Calcaneal lengthening for valgus deformity of the hindfoot. Results in children who had severe, symptomatic flatfoot and skewfoot. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77:500–512.
Article28. Phillips GE. A review of elongation of os calcis for flat feet. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1983; 65:15–18.
Article29. Rathjen KE, Mubarak SJ. Calcaneal-cuboid-cuneiform osteotomy for the correction of valgus foot deformities in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1998; 18:775–782.
Article30. Moraleda L, Salcedo M, Bastrom TP, Wenger DR, Albiñana J, Mubarak SJ. Comparison of the calcaneo-cuboid-cuneiform osteotomies and the calcaneal lengthening osteotomy in the surgical treatment of symptomatic flexible flatfoot. J Pediatr Orthop. 2012; 32:821–829.
Article31. Kim JR, Shin SJ, Wang SI, Kang SM. Comparison of lateral opening wedge calcaneal osteotomy and medial calcaneal sliding-opening wedge cuboid-closing wedge cuneiform osteotomy for correction of planovalgus foot deformity in children. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2013; 52:162–166.
Article32. Kim JR, Park CI, Moon YJ, Wang SI, Kwon KS. Concomitant calcaneo-cuboid-cuneiform osteotomies and the modified Kidner procedure for severe flatfoot associated with symptomatic accessory navicular in children and adolescents. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014; 9:131.
Article33. Hoke M. An operation for the correction of extremely relaxed flat feet. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1931; 13:773–783.34. Seymour N. The late results of naviculo-cuneiform fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1967; 49:558–559.
Article35. Crego CH Jr, Ford LT. An end-result of various operative procedures for correcting flat feet in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1952; 34:183–195.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Operative Treatment of Adult Flexible Flatfoot with Young's Tenosuspension: Case Report
- The Treatment of Failed Kidner Procedure for Adolescent Prehallux: A Case Report
- Adult Idiopathic Flexible Flat Foot Treated with Medial Sliding Calcaneal Osteotomy and Subtalar Arthroereisis: Report of 1 Case
- Diagnosis of Flatfoot Deformity
- Calcaneo-stop Procedure for Management of Pediatric Symptomatic Flexible Flatfoot