Brain Neurorehabil.
2016 Mar;9(1):31-36. 10.12786/bn.2016.9.1.31.
The Intra- and Inter-rater Reliability and the Learning Curve for a Simple Neurological Score for Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Korea. keepwiz@gmail.com
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Kyungpook National University Medical Center, Korea.
- KMID: 2161459
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12786/bn.2016.9.1.31
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To measure the intra- and inter-rater reliability of a simple sensorimotor performance test for rats, and to evaluate the learning efficiency of a novice rater for the test. METHOD: Middle cerebral arteries were occluded by intraluminal sutures in 25 male Sprague-Dawley rats (10~12 weeks old). The sensorimotor performance test was performed by a novice and an experienced rater, with each rater performing the test twice each week for 3 consecutive weeks. A ten-minute standardized video about the rating method was shown to the novice rater after the second test each week.
RESULTS
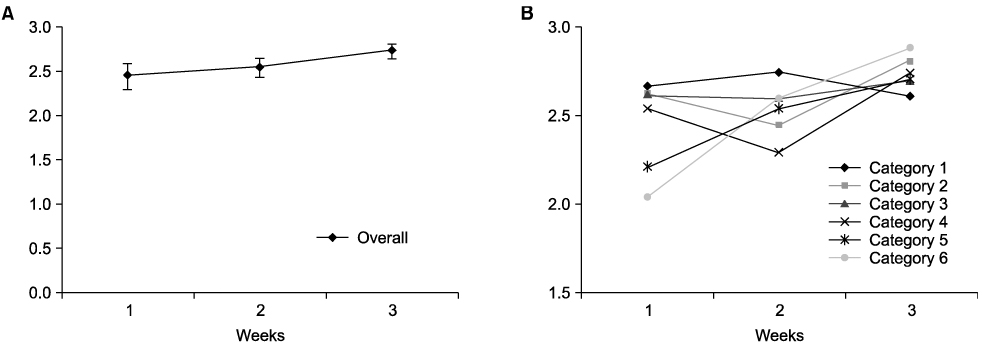
The intra- and inter-rater agreement was determined using Cohen's weighted kappa coefficient. The intra-rater reliability was initially poor for the novice (κ [95% confidence interval], 0.31[-0.02, 0.64]), but it improved significantly after 3-week self education using the standardized video (0.81 [0.69, 0.93], showing almost perfect agreement. The reliability of the experienced researcher was good at all times (κ = 0.64, 0.76, 0.71, for week 1, 2, 3, respectively), indicating substantial agreement. The inter-rater reliability showed clear improvement after self-education (κ = 0.44, 0.69, 0.69, for week 1, 2, 3, respectively). Although the total sum score was highly reliable, some of the individual items showed lower intra-and inter-rater agreement. However, each rater showed greater within-rater variability for different subtests.
CONCLUSION
The simple sensorimotor performance test showed high degree of intra- and inter-rater agreement when performed by experienced or properly educated raters. The inaccuracy of the novice was rectified by 3-week self-education using a video.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Garcia JH, Wagner S, Liu KF, Hu XJ. Neurological deficit and extent of neuronal necrosis attributable to middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Statistical validation. Stroke. 1995; 26:627–663.
Article2. Tomasello F, Mariani F, Fieschi C, Argentino C, Bono G, De Zanche L, Inzitari D, Martini A, Perrone P, Sangiovanni G. Assessment of inter-observer differences in the Italian multicenter study on reversible cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 1982; 13:32–35.
Article3. Pantoni L, Bartolini L, Pracucci G, Inzitari D. Interrater agreement on a simple neurological score in rats. Stroke. 1998; 29:871–872.
Article4. Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977; 33:159–174.
Article5. Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989; 20:84–91.
Article6. Cohen J. Weighted kappa: nominal scale agreement with provision for scaled disagreement or partial credit. Psychol Bull. 1968; 70:213–220.
Article7. Fleiss JL, Levin BA, Paik MC. Wiley J., Hoboken N.J., editors. Statistical methods for rates and proportions. 2003. p. xxvii. p. 760.8. Schallert T, Kozlowski DA, Humm JL, Cocke RR. Use-dependent structural events in recovery of function. Adv Neurol. 1997; 73:229–238.9. Schallert T, Fleming SM, Leasuren JL, Tillerson JL, Bland ST. CNS plasticity and assessment of forelimb sensorimotor outcome in unilateral rat models of stroke, cortical ablation, parkinsonism and spinal cord injury. Neuropharmacology. 2000; 39:777–787.
Article10. Olesen J, Simonsen K, Nørgaard B, Grønbæk M, Johansen OS, Krogsgaard A, Andersen B. Reproducibility and Utility of a Simple Neurological Scoring System for Stroke Patients (Copenhagen Stroke Scale). Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair. 1988; 2:59–63.
Article11. Buchanan GN, Halligan S, Taylor S, Williams A, Cohen R, Bartram C. MRI of fistula in ano: inter- and intraobserver agreement and effects of directed education. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004; 183:135–140.
Article12. Depienne C, Stevanin G, Brice A, Durr A. Hereditary spastic paraplegias: an update. Curr Opin Neurol. 2007; 20:674–680.
Article13. Gagliano ME. A literature review on the efficacy of video in patient education. J Med Educ. 1988; 63:785–792.
Article14. Lyden P, Brott T, Tilley B, Welch KM, Mascha EJ, Levine S, Haley EC, Grotta J, Marler J. NINDS TPA Stroke Study Group. Improved reliability of the NIH Stroke Scale using video training. Stroke. 1994; 25:2220–2226.
Article15. Todd KH, Braslow A, Brennan RT, Lowery DW, Cox RJ, Lipscomb LE, Kellermann AL. Randomized, controlled trial of video self-instruction versus traditional CPR training. Ann Emerg Med. 1998; 31:364–369.
Article16. Katz RJ, Roth KA, Carroll BJ. Acute and chronic stress effects on open field activity in the rat: implications for a model of depression. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1981; 5:247–251.
Article17. Tanaka M, Nakamura F, Mizokawa S, Matsumura A, Nozaki S, Watanabe Y. Establishment and assessment of a rat model of fatigue. Neurosci Lett. 2003; 352:159–162.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intra and Inter-Rater Measurement Reliability of Tibialis Anterior Muscle (TA) Thickness using the Ultrasonography Spring Gauge Technique
- Extraction of the pull force from inertial sensors during the pull test for Parkinson’s disease: A reliability study
- The reliability of an easy measuring method for abutment convergence angle with a computer-aided design (CAD) system
- The Correlation between Modified Ashworth Scale and Biceps T-reflex and Inter-rater and Intra-rater Reliability of Biceps T-reflex
- The Validity and Reliability of the EMC Device; For the Checking ofthe Mobility of the First Ray of the Foot