J Korean Med Sci.
2013 Jan;28(1):100-105. 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.1.100.
The Role of Urinary Liver-Type Fatty Acid-Binding Protein in Critically Ill Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Anam Hospital, The Institute of Renal Disease, Seoul, Korea. sang-kyung@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2158008
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.1.100
Abstract
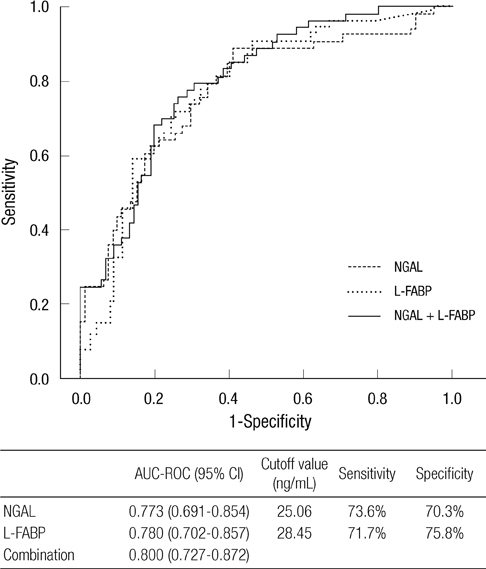
- Although several urinary biomarkers have been validated as early diagnostic markers of acute kidney injury (AKI), their usefulness as outcome predictors is not well established. This study aimed to determine the diagnostic and prognostic abilities of urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein (L-FABP) in heterogeneous critically ill patients. We prospectively collected data on patients admitted to medical and surgical intensive care units (ICUs) from July 2010 to June 2011. Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and L-FABP at the time of ICU admission were quantitated. Of the 145 patients, 54 (37.2%) had AKI defined by the Acute Kidney Injury Network (AKIN) criteria. AKI patients showed significantly higher level of urinary NGAL and L-FABP and also higher mortality than non-AKI patients. The diagnostic performances, assessed by the area under the ROC curve, were 0.773 for NGAL and 0.780 for L-FABP, demonstrating their usefulness in diagnosing AKI. In multivariate Cox analysis, urinary L-FABP was an independent predictor for 90-day mortality. Urinary L-FABP seems to be promising both for the diagnosis of AKI and for the prediction of prognosis in heterogeneous ICU patients. It needs to be further validated for clinical utility.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acute Kidney Injury/*diagnosis/mortality/surgery
Acute-Phase Proteins/urine
Adult
Aged
Area Under Curve
Biological Markers/urine
Critical Illness
Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins/*urine
Female
Humans
Intensive Care Units
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Lipocalins/urine
Male
Middle Aged
Predictive Value of Tests
Prognosis
Proportional Hazards Models
Prospective Studies
Proto-Oncogene Proteins/urine
ROC Curve
Acute-Phase Proteins
Biological Markers
Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins
Lipocalins
Proto-Oncogene Proteins
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bagshaw SM, George C, Bellomo R. Changes in the incidence and outcome for early acute kidney injury in a cohort of Australian intensive care units. Crit Care. 2007. 11:R68.2. Hoste EA, Kellum JA. Acute kidney injury: epidemiology and diagnostic criteria. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2006. 12:531–537.3. Coca SG, Yalavarthy R, Concato J, Parikh CR. Biomarkers for the diagnosis and risk stratification of acute kidney injury: a systematic review. Kidney Int. 2008. 73:1008–1016.4. Kamijo A, Sugaya T, Hikawa A, Yamanouchi M, Hirata Y, Ishimitsu T, Numabe A, Takagi M, Hayakawa H, Tabei F, et al. Urinary liver-type fatty acid binding protein as a useful biomarker in chronic kidney disease. Mol Cell Biochem. 2006. 284:175–182.5. Matsui K, Kamijo-Ikemori A, Hara M, Sugaya T, Kodama T, Fujitani S, Taira Y, Yasuda T, Kimura K. Clinical significance of tubular and podocyte biomarkers in acute kidney injury. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011. 15:220–225.6. Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, Molitoris BA, Ronco C, Warnock DG, Levin A. Acute Kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care. 2007. 11:R31.7. Le Gall JR, Lemeshow S, Saulnier F. A new Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II) based on a European/North American multicenter study. JAMA. 1993. 270:2957–2963.8. Lisowska-Myjak B. Serum and urinary biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Blood Purif. 2010. 29:357–365.9. Kang HK, Kim DK, Lee BH, Om AS, Hong JH, Koh HC, Lee CH, Shin IC, Kang JS. Urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase and malondialdehyde as a markers of renal damage in burned patients. J Korean Med Sci. 2001. 16:598–602.10. Makris K, Markou N, Evodia E, Dimopoulou E, Drakopoulos I, Ntetsika K, Rizos D, Baltopoulos G, Haliassos A. Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as an early marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill multiple trauma patients. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2009. 47:79–82.11. Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R, Mitsnefes MM, Ma Q, Kelly C, Ruff SM, Zahedi K, Shao M, Bean J, et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet. 2005. 365:1231–1238.12. Prabhu A, Sujatha DI, Ninan B, Vijayalakshmi MA. Neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin as a biomarker for acute kidney injury in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting with cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann Vasc Surg. 2010. 24:525–531.13. Haase M, Bellomo R, Devarajan P, Schlattmann P, Haase-Fielitz A. Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injury: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009. 54:1012–1024.14. Yokoyama T, Kamijo-Ikemori A, Sugaya T, Hoshino S, Yasuda T, Kimura K. Urinary excretion of liver type fatty acid binding protein accurately reflects the degree of tubulointerstitial damage. Am J Pathol. 2009. 174:2096–2106.15. Manabe K, Kamihata H, Motohiro M, Senoo T, Yoshida S, Iwasaka T. Urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein level as a predictive biomarker of contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Eur J Clin Invest. 2012. 42:557–563.16. Nakamura T, Sugaya T, Koide H. Urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein in septic shock: effect of polymyxin B-immobilized fiber hemoperfusion. Shock. 2009. 31:454–459.17. Portilla D, Dent C, Sugaya T, Nagothu KK, Kundi I, Moore P, Noiri E, Devarajan P. Liver fatty acid-binding protein as a biomarker of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Kidney Int. 2008. 73:465–472.18. Ferguson MA, Vaidya VS, Waikar SS, Collings FB, Sunderland KE, Gioules CJ, Bonventre JV. Urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein predicts adverse outcomes in acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2010. 77:708–714.19. Doi K, Negishi K, Ishizu T, Katagiri D, Fujita T, Matsubara T, Yahagi N, Sugaya T, Noiri E. Evaluation of new acute kidney injury biomarkers in a mixed intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2011. 39:2464–2469.20. Yang HN, Boo CS, Kim MG, Jo SK, Cho WY, Kim HK. Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: an independent predictor of adverse outcomes in acute kidney injury. Am J Nephrol. 2010. 31:501–509.21. Vaidya VS, Ford GM, Waikar SS, Wang Y, Clement MB, Ramirez V, Glaab WE, Troth SP, Sistare FD, Prozialeck WC, et al. A rapid urine test for early detection of kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2009. 76:108–114.22. Devarajan P. Biomarkers for the early detection of acute kidney injury. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2011. 23:194–200.23. Bagshaw SM, Brophy PD, Cruz D, Ronco C. Fluid balance as a biomarker: impact of fluid overload on outcome in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Crit Care. 2008. 12:169.24. Bouchard J, Mehta RL. Fluid accumulation and acute kidney injury: consequence or cause. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2009. 15:509–513.25. Shum HP, Lee FM, Chan KC, Yan WW. Interaction between fluid balance and disease severity on patient outcome in the critically ill. J Crit Care. 2011. 26:613–619.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intra-abdominal hypertension does not predict renal recovery or in-hospital mortality in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury
- The associations of Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinaseassociated Lipocalin (NGAL) and Liver-type Fatty Acidbinding Protein (L-FABP) Levels with Hematuria in Children and Adolescents
- Predictive Performance of Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin, Liver Type Fatty Acid Binding Protein, and Cystatin C for Acute Kidney Injury and Mortality in Severely Ill Patients
- Association of Serum Adipocyte-Specific Fatty Acid Binding Protein with Fatty Liver Index as a Predictive Indicator of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Polymorphism of the Uncoupling Protein 1 (UCP-1) Gene and Fatty Acid Binding Protein 2 (FABP2) Gene in Korean Type 2 Diabetic Patients