J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Aug;21(4):596-601. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.4.596.
Association of TNFA Promoter Region Haplotype in Behcet's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biology, Sungshin Women's University, Seoul, Korea. kspark@sungshin.ac.kr
- 2Department of Dermatology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Dermatology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2157807
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.4.596
Abstract
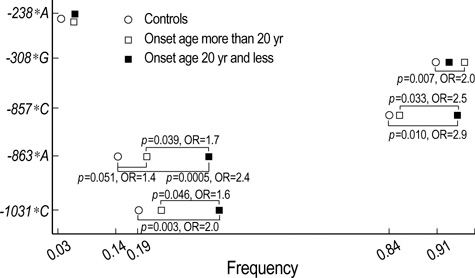
- Although the etiology of Behcet's Disease (BD; MIM 109650) remains to be clearly elucidated, levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) have been reported to be significantly elevated in BD patients, and TNF-alpha blockers have been demonstrated to exhibit some degree of therapeutic efficacy for a certain subset of BD sufferers. In this study, we have conducted an analysis of the TNFA haplotypes in the promoter response element that affect the binding affinity of specific transcription factors, in order to characterize their association with the clinical features of BD. Six polymorphisms in the promoter region of TNFA were genotyped in 254 BD patients and 344 control subjects, via the PCR-RFLP technique. TNFA -1031*C, -863*A and -308*G alleles were associated with an increased risk of BD (p=0.030, OR=1.4; p=0.008, OR=1.5; p=0.010, OR=1.8, respectively). The sole TNFA haplotype -1031C-863A-857C-376G-308G-238G, was associated with a 1.6 fold increase in the risk of BD, whereas the TNFA haplotype -1031T-863C-857C-376G-308A-238G was associated with a 0.6 decreased risk of BD. The TNFA -1031*C, -863*A, -857*C and -308*G alleles were significantly associated with BD. The findings of this study, collectively, indicate that TNFA haplotypes in the promoter response elements may exert significant influence on susceptibility to BD.
MeSH Terms
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha/*genetics
Promoter Regions (Genetics)/*genetics
Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide/genetics
Odds Ratio
Middle Aged
Male
Linkage Disequilibrium
Humans
Haplotypes/*genetics
Genotype
Genetic Predisposition to Disease/genetics
Gene Frequency
Female
Behcet Syndrome/*genetics/pathology
Aged
Adult
Adolescent
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bang DS, Oh SH, Lee KH, Lee ES, Lee SN. Influence of sex on patients with Behcet's disease in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2003. 18:231–235.
Article2. Zierhut M, Mizuki N, Ohno S, Inoko H, Gul A, Onoe K, Isogai E. Immunology and functional genomics of Behcet's disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003. 60:1903–1922.3. Karasneh J, Gul A, Ollier WE, Silman AJ, Worthington J. Whole-genome screening for susceptibility genes in multicase families with Behcet's disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2005. 52:1836–1842.4. Oztas MO, Onder M, Gurer MA, Bukan N, Sancak B. Serum interleukin 18 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels are increased in Behcet's disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2005. 30:61–63.5. Sayinalp N, Ozcebe OI, Ozdemir O, Haznedaroglu IC, Dundar S, Kirazli S. Cytokines in Behcet's disease. J Rheumatol. 1996. 23:321–322.6. Higuchi T, Seki N, Kamizono S, Yamada A, Kimura A, Kato H, Itoh K. Polymorphism of the 5'-flanking region of the human tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha gene in Japanese. Tissue Antigens. 1998. 51:605–612.7. Wilson AG, Symons JA, McDowell TL, McDevitt HO, Duff GW. Effects of a polymorphism in the human tumor necrosis factor alpha promoter on transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997. 94:3195–3199.8. Kroeger KM, Carville KS, Abraham LJ. The -308 tumor necrosis factor-alpha promoter polymorphism effects transcription. Mol Immunol. 1997. 34:391–399.9. Negoro K, Kinouchi Y, Hiwatashi N, Takahashi S, Takagi S, Satoh J, Shimosegawa T, Toyota T. Crohn's disease is associated with novel polymorphisms in the 5'-flanking region of the tumor necrosis factor gene. Gastroenterology. 1999. 117:1062–1068.
Article10. Mege JL, Dilsen N, Sanguedolce V, Gul A, Bongrand P, Roux H, Ocal L, Inanc M, Capo C. Overproduction of monocyte derived tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin (IL) 6, IL-8 and increased neutrophil superoxide generation in Behcet's disease. A comparative study with familial Mediterranean fever and healthy subjects. J Rheumatol. 1993. 20:1544–1549.11. Yamashita N, Kaneoka H, Kaneko S, Takeno M, Oneda K, Koizumi H, Kogure M, Inaba G, Sakane T. Role of γ/δ T lymphocytes in the development of Behcet's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1997. 107:241–247.
Article12. Sfikakis PP, Theodossiadis PG, Katsiari CG, Kaklamanis P, Markomichelakis NN. Effect of infliximab on sight-threatening panuveitis in Behcet's disease. Lancet. 2001. 358:295–296.
Article13. Melikoglu M, Fresko I, Mat C, Ozyazgan Y, Gogus F, Yurdakul S, Hamuryudan V, Yazici H. Short-term trial of etanercept in Behcet's disease: a double blind, placebo controlled study. J Rheumatol. 2005. 32:98–105.14. Allen RD. Polymorphism of the human TNF-alpha promoter; random variation or functional diversity? Mol Immunol. 1999. 36:1017–1027.15. Ates AK, Kinikli G, Duzgun N, Duman M. Lack of association of tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene polymorphisms with disease susceptibility and severity in Behcet's disease. Rheumatol Int. 2006. 26:348–353.16. Wang XT, Ohtsuka Y, Kimura K, Muroi M, Ishida T, Saito J, Munakata M. Antithetical effect of tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene polymorphism on coal workers' pneumoconiosis (CWP). Am J Ind Med. 2005. 48:24–29.17. Lee EB, Kim JY, Lee YJ, Park MH, Song YW. TNF and TNF receptor polymorphisms in Korean Behcet's disease patients. Hum Immunol. 2003. 64:614–620.18. International Study Group for Behcet's Disease. Criteria for diagnosis of Behcet's disease. Lancet. 1990. 335:1078–1080.19. Soga Y, Nishimura F, Ohyama H, Maeda H, Takashiba S, Murayama Y. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene (TNF-alpha) -1031/-863, -857 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are associated with severe adult periodontitis in Japanese. J Clin Periodontol. 2002. 30:524–531.20. Skoog T, van't Hooft FM, Kallin B, Jovinge S, Boquist S, Nilsson J, Eriksson P, Hamsten A. A common functional polymorphism (C->A substitution at position -863) in the promoter region of the tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) gene associated with reduced circulating levels of TNF-alpha. Hum Mol Genet. 1999. 8:1443–1449.21. Moukoko CE, El Wali N, Saeed OK, Mohamed-Ali Q, Gaudart J, Dessein AJ, Chevillard C. No evidence for a major effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha gene polymorphisms in periportal fibrosis caused by Schistosoma mansoni infection. Infect Immun. 2003. 71:5456–5460.22. Stephens M, Smith NJ, Donnelly P. A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. 68:978–989.
Article23. Ahmad T, Wallace GR, James T, Neville M, Bunce M, Mulcahy-Hawes K, Armuzzi A, Crawshaw J, Fortune F, Walton R, Stanford MR, Welsh KI, Marshall SE, Jewell DP. Mapping the HLA association in Behcet's disease: a role for tumor necrosis factor polymorphisms? Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:807–813.24. Duymaz-Tozkir J, Gul A, Uyar FA, Ozbek U, Saruhan-Direskeneli G. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha gene promoter region -308 and -376 G-->A polymorphisms in Behcet's disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003. 21:Suppl 30. 15–18.25. Oz D, Karsli F, Atalay A, Sahin S. Bang D, Lee ES, Lee S, editors. TNF-alpha gene polymorphisms in Behcet's disease. Proceedings of the 9th international conference on Behcet's disease. 2000. Seoul: Design Mecca Publishing;161–165.26. Gul A. Behcet's disease: an update on the pathogenesis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2001. 19:Suppl 24. 6–12.27. Bouwmeester T, Bauch A, Ruffner H, Angrand PO, Bergamini G, Croughton K, Cruciat C, Eberhard D, Gagneur J, Ghidelli S, Hopf C, Huhse B, Mangano R, Michon AM, Schirle M, Schlegl J, Schwab M, Stein MA, Bauer A, Casari G, Drewes G, Gavin AC, Jackson DB, Joberty G, Neubauer G, Rick J, Kuster B, Superti-Furga G. A physical and functional map of the human TNF-alpha/NF-kappa B signal transduction pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2004. 6:97–105.28. Udalova IA, Richardson A, Denys A, Smith C, Ackerman H, Foxwell B, Kwiatkowski D. Functional consequences of a polymorphism affecting NF-kappaB p50-p50 binding to the TNF promoter region. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. 20:9113–9119.29. van Heel DA, Udalova IA, De Silva AP, McGovern DP, Kinouchi Y, Hull J, Lench NJ, Cardon LR, Carey AH, Jewell DP, Kwiatkowski D. Inflammatory bowel disease is associated with a TNF polymorphism that affects an interaction between the OCT1 and NF (-kappa) B transcription factors. Hum Mol Genet. 2002. 11:1281–1289.30. Verity DH, Wallace GR, Vaughan RW, Kondeatis E, Madanat W, Zureikat H, Fayyad F, Marr JE, Kanawati CA, Stanford MR. HLA and tumour necrosis factor (TNF) polymorphisms in ocular Behcet's disease. Tissue Antigens. 1999. 54:264–272.
Article31. Park KS, Min K, Nam JH, Bang D, Lee ES, Lee S. Association of HYPA haplotype in the mannose-binding lectin gene-2 with Behcet's disease. Tissue Antigens. 2005. 65:260–265.
Article32. Madsen HO, Garred P, Thiel S, Kurtzhals JA, Lamm LU, Ryder LP, Svejgaard A. Interplay between promoter and structural gene variants control basal serum level of mannan-binding protein. J Immunol. 1995. 155:3013–3020.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Promoter Polymorphism of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Korean
- Functional Haplotype Frequencies of the Interleukin-1B Promoter in the Korean Population
- Association of the Promoter Haplotype of IFN-γ-Inducible Protein 16 Gene with Schizophrenia in a Korean Population
- Investigation of -308G>A and -1031T>C Polymorphisms in the TNFA Promoter Region in Polish Peptic Ulcer Patients
- Difference in the Transcriptional Activity of the Interleukin-4 Promoter Haplotypes