Ann Dermatol.
2015 Dec;27(6):765-766. 10.5021/ad.2015.27.6.765.
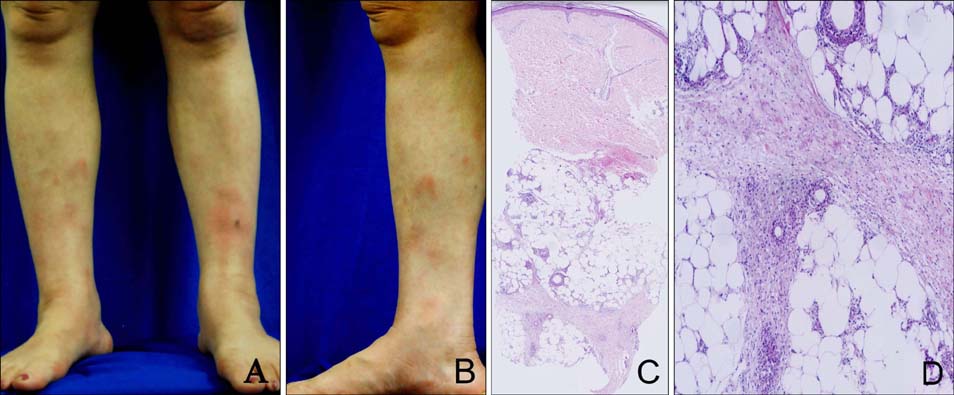
Erythema Nodosum Associated with Valproate
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Eulji University Hospital, Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. sun_lee@ eulji.ac.kr
- KMID: 2157458
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2015.27.6.765
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Requena L, Sánchez Yus E. Erythema nodosum. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2007; 26:114–125.
Article2. Rosenberg G. The mechanisms of action of valproate in neuropsychiatric disorders: can we see the forest for the trees. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007; 64:2090–2103.
Article3. Gerstner T, Büsing D, Bell N, Longin E, Kasper JM, Klostermann W, et al. Valproic acid-induced pancreatitis: 16 new cases and a review of the literature. J Gastroenterol. 2007; 42:39–48.
Article4. Hebert AA, Ralston JP. Cutaneous reactions to anticonvulsant medications. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001; 62:14. 22–26.5. Eyer F, Felgenhauer N, Gempel K, Steimer W, Gerbitz KD, Zilker T. Acute valproate poisoning: pharmacokinetics, alteration in fatty acid metabolism, and changes during therapy. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2005; 25:376–380.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The clinical and histopatholgical study of erythema induratum and erythema nodosum
- A Case of Erythema Nodosum Migrans
- Unusual Hypertrichosis Development on the Skin Involving Erythema Nodosum Migrans
- Erythema Nodosum Associated with Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
- Clinical Observation and Effectiveness of Isoniazid Treatment on erythema nodosum